Effects of Extreme Dilutions of Apis mellifica Preparations on Gene Expression Profiles of Human Cells
- PMID: 26788033
- PMCID: PMC4710123
- DOI: 10.1177/1559325815626685
Effects of Extreme Dilutions of Apis mellifica Preparations on Gene Expression Profiles of Human Cells
Abstract
Gene expression analysis has been employed in the past to test the effects of high dilutions on cell systems. However, most of the previous studies were restricted to the investigation of few dilutions, making it difficult to explore underlying mechanisms of action. Using whole-genome transcriptomic analysis, we investigated the effects of a wide range of Apis mellifica dilutions on gene expression profiles of human cells. RWPE-1 cells, a nonneoplastic adult human epithelial prostate cell line, were exposed to Apis mellifica preparations (3C, 5C, 7C, 9C, 12C, 15C, and 30C) or to the reference solvent solutions for 24 hours; nonexposed cells were also checked for gene expression variations. Our results showed that even the most diluted solutions retained the ability to trigger significant variations in gene expression. Gene pathway analysis revealed consistent variations in gene expression induced by Apis mellifica when compared to nonexposed reference cells but not to reference solvent solutions. Since the effects of Apis Mellifica at extreme dilutions did not show dose-effect relationships, the biological or functional interpretation of these results remains uncertain.
Keywords: Apis mellifica; extreme dilutions; gene expression; homeopathy; microarrays.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
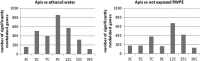
Comment in
-
Dose response of high dilutions in gene expression and the concept of hormesis.Hum Exp Toxicol. 2017 Aug;36(8):876-877. doi: 10.1177/0960327116665677. Epub 2016 Sep 5. Hum Exp Toxicol. 2017. PMID: 27596069 No abstract available.
References
-
- Bigagli E, Luceri C, Bernardini S, Dei A, Dolara P. Extremely low copper concentrations affect gene expression profiles of human prostate epithelial cell lines. Chem Biol Interact. 2010;188(1):214–219. - PubMed
-
- Bigagli E, Luceri C, Bernardini S, Dei A, Filippini A, Dolara P. Exploring the effects of homeopathic Apis mellifica preparations on human gene expression profiles. Homeopathy. 2014;103(2):127–132. - PubMed
-
- Kwon YB, Kim JH, Yoon JH, et al. The analgesic efficacy of bee venom acupuncture for knee osteoarthritis: a comparative study with needle acupuncture. Am J Chin Med. 2001;29(2):187–199. - PubMed
-
- Liu XD, Zhang JL, Zheng HG, Liu FY, Chen Y. Clinical randomized study of bee-sting therapy for rheumatoid arthritis. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2008;33(3):197–200. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

