Mutations in TUBB8 and Human Oocyte Meiotic Arrest
- PMID: 26789871
- PMCID: PMC4767273
- DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa1510791
Mutations in TUBB8 and Human Oocyte Meiotic Arrest
Abstract
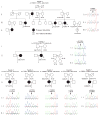
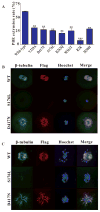
Background Human reproduction depends on the fusion of a mature oocyte with a sperm cell to form a fertilized egg. The genetic events that lead to the arrest of human oocyte maturation are unknown. Methods We sequenced the exomes of five members of a four-generation family, three of whom had infertility due to oocyte meiosis I arrest. We performed Sanger sequencing of a candidate gene, TUBB8, in DNA samples from these members, additional family members, and members of 23 other affected families. The expression of TUBB8 and all other β-tubulin isotypes was assessed in human oocytes, early embryos, sperm cells, and several somatic tissues by means of a quantitative reverse-transcriptase-polymerase-chain-reaction assay. We evaluated the effect of the TUBB8 mutations on the assembly of the heterodimer consisting of one α-tubulin polypeptide and one β-tubulin polypeptide (α/β-tubulin heterodimer) in vitro, on microtubule architecture in HeLa cells, on microtubule dynamics in yeast cells, and on spindle assembly in mouse and human oocytes. Results We identified seven mutations in the primate-specific gene TUBB8 that were responsible for oocyte meiosis I arrest in 7 of the 24 families. TUBB8 expression is unique to oocytes and the early embryo, in which this gene accounts for almost all the expressed β-tubulin. The mutations affect chaperone-dependent folding and assembly of the α/β-tubulin heterodimer, disrupt microtubule behavior on expression in cultured cells, alter microtubule dynamics in vivo, and cause catastrophic spindle-assembly defects and maturation arrest on expression in mouse and human oocytes. Conclusions TUBB8 mutations have dominant-negative effects that disrupt microtubule behavior and oocyte meiotic spindle assembly and maturation, causing female infertility. (Funded by the National Basic Research Program of China and others.).
Figures


Comment in
-
Exacting Requirements for Development of the Egg.N Engl J Med. 2016 Jan 21;374(3):279-80. doi: 10.1056/NEJMe1515512. N Engl J Med. 2016. PMID: 26789878
References
-
- Eppig JJ. Regulation of mammalian oocyte maturation. In: Adash PCKL, editor. The Ovary. San Diego: Elsevier/Academic Press; 1993. pp. 113–29.
-
- Mehlmann LM. Stops and starts in mammalian oocytes: recent advances in understanding the regulation of meiotic arrest and oocyte maturation. REPRODUCTION. 2005;130:791–9. - PubMed
-
- Park JY, Su YQ, Ariga M, Law E, Jin SL, Conti M. EGF-like growth factors as mediators of LH action in the ovulatory follicle. SCIENCE. 2004;303:682–4. - PubMed
-
- Eppig JJ. Coordination of nuclear and cytoplasmic oocyte maturation in eutherian mammals. Reprod Fertil Dev. 1996;8:485–9. - PubMed
-
- Santos MA, Kuijk EW, Macklon NS. The impact of ovarian stimulation for IVF on the developing embryo. REPRODUCTION. 2010;139:23–34. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
