Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus Intra-Host Populations Are Characterized by Numerous High Frequency Variants
- PMID: 26790002
- PMCID: PMC4720378
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0146251
Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus Intra-Host Populations Are Characterized by Numerous High Frequency Variants
Erratum in
-
Correction: Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus Intra-Host Populations Are Characterized by Numerous High Frequency Variants.PLoS One. 2016 Apr 25;11(4):e0154424. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0154424. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27111439 Free PMC article.
Abstract
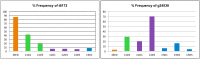
Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV) is an emerging human pathogen related to SARS virus. In vitro studies indicate this virus may have a broad host range suggesting an increased pandemic potential. Genetic and epidemiological evidence indicate camels serve as a reservoir for MERS virus but the mechanism of cross species transmission is unclear and many questions remain regarding the susceptibility of humans to infection. Deep sequencing data was obtained from the nasal samples of three camels that had been experimentally infected with a human MERS-CoV isolate. A majority of the genome was covered and average coverage was greater than 12,000x depth. Although only 5 mutations were detected in the consensus sequences, 473 intrahost single nucleotide variants were identified. Many of these variants were present at high frequencies and could potentially influence viral phenotype and the sensitivity of detection assays that target these regions for primer or probe binding.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Reusken CBEM, Haagmans BL, Müller MA, Gutierrez C, Godeke G-J, Meyer B, et al. (2013) Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus neutralising serum antibodies in dromedary camels: a comparative serological study. The Lancet Infectious Diseases 13: 859–866. 10.1016/S1473-3099(13)70164-6 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

