Recombinant human erythropoietin versus placebo or no treatment for the anaemia of chronic kidney disease in people not requiring dialysis
- PMID: 26790135
- PMCID: PMC7144724
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD003266.pub3
Recombinant human erythropoietin versus placebo or no treatment for the anaemia of chronic kidney disease in people not requiring dialysis
Abstract
Background: Treatment with recombinant human erythropoietin (rHuEPO) in dialysis patients has been shown to be highly effective in terms of correcting anaemia and improving quality of life. There is debate concerning the benefits of rHuEPO use in predialysis patients which may accelerate the deterioration of kidney function. However the opposing view is that if rHuEPO is as effective in predialysis patients, improving the patient's sense of well-being may result in the onset of dialysis being delayed. This is an update of a review first published in 2001 and last updated in 2005.
Objectives: The objective of this review was to ascertain the effects of rHuEPO treatment in predialysis patients primarily in terms of the timing of the onset of dialysis; but also that predialysis rHuEPO: 1) corrects haemoglobin/haematocrit (markers of anaemia); 2) improves quality of life; and 3) is not associated with an increased incidence of adverse events such as hastening of the onset of dialysis, increased hypertension, clotting of arterio-venous fistulae or seizures.
Search methods: We searched the Cochrane Kidney and Transplant's Specialised Register (up to 29 June 2015) through contact with the Trials' Search Co-ordinator using search terms relevant to this review.
Selection criteria: Randomised controlled trials (RCTs) or quasi-RCTs comparing the use of rHuEPO with no treatment or placebo in predialysis patients.
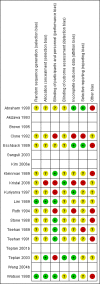
Data collection and analysis: Only published data were used. Quality assessment was performed by two assessors independently. Data were abstracted by a single author onto a standard form, a sample of which was checked by another author. Results were expressed as risk ratio (RR) or mean difference (MD) with 95% confidence intervals (CI).
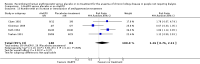
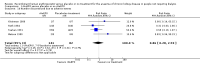
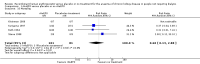
Main results: Nineteen studies (enrolling 993 participants) were included. Due to the age of the included studies (most performed prior to 2000) the risk of bias was judged to be unclear in the majority of the studies for most of the domains. There was an improvement in haemoglobin (MD 1.90 gm/L, 95% CI -2.34 to -1.47) and haematocrit (MD 9.85%, 95% CI 8.35 to 11.34) with treatment and a decrease in the number of patients requiring blood transfusions (RR 0.32, 95% CI 0.12 to 0.83). The data from studies reporting quality of life or exercise capacity demonstrated an improvement in the treatment group. Most of the measures of progression of kidney disease showed no statistically significant difference. No significant increase in adverse events was identified.
Authors' conclusions: Treatment with rHuEPO in predialysis patients corrects anaemia, avoids the requirement for blood transfusions and also improves quality of life and exercise capacity. We were unable to assess the effects of rHuEPO on progression of kidney disease, delay in the onset of dialysis or adverse events. Based on the current evidence, decisions on the putative benefits in terms of quality of life are worth the extra costs of predialysis rHuEPO need careful evaluation.
Conflict of interest statement
None known.
Figures













Update of
-
Recombinant human erythropoietin for chronic renal failure anaemia in pre-dialysis patients.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005 Jul 20;(3):CD003266. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003266.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Jan 20;(1):CD003266. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003266.pub3. PMID: 16034896 Updated.
Comment in
- Dtsch Med Wochenschr. 2016 Apr;141(8):534
-
Erythropoietin corrects anaemia and reduces the risk of blood transfusion in people with chronic kidney disease, but has uncertain effects on other patient-level outcomes.Evid Based Med. 2016 Oct;21(5):178. doi: 10.1136/ebmed-2016-110418. Epub 2016 Aug 12. Evid Based Med. 2016. PMID: 27519812 No abstract available.
References
References to studies included in this review
Abraham 1990 {published data only}
-
- Abraham PA, Opsahl JA, Rachael KM, Asinger R, Halstenson CE. Renal function during erythropoietin therapy for anemia in predialysis chronic renal failure patients. American Journal of Nephrology 1990;10(2):128‐36. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Opsahl JA, Halstenson CE, Rachael KM, Abraham PA. Recombinant‐human erythropoietin (EPO) in chronic renal failure (CRF): no adverse effect on renal hemodynamics or progression of disease [abstract]. Kidney International 1989;35(1):198. [CENTRAL: CN‐00766225]
Akizawa 1993 {published data only}
-
- Akizawa T, Koshikawa S. Effect of rHuEPO on progression of renal disease [abstract]. 12th International Congress of Nephrology; 1993 June 13‐18; Jerusalem, Israel. 1993:300. [CENTRAL: CN‐00764752]
Brown 1995 {published data only}
-
- Brown CD, Zhao ZH, Thomas LL, Friedman EA. Erythropoietin delays the onset of uremia in anemic azotemic diabetic predialysis patients [abstract]. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 1995;6(3):447A. [MEDLINE: ]
Clyne 1992 {published data only}
-
- Clyne N, Jogestrand T. Effect of erythropoietin treatment on physical exercise capacity and on renal function in predialytic uremic patients. Nephron 1992;60(4):390‐6. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Eschbach 1989 {published data only}
-
- Eschbach JW, Kelly MR, Haley NR, Abels RI, Adamson JW. Treatment of the anemia of progressive renal failure with recombinant human erythropoietin. New England Journal of Medicine 1989;321(3):158‐63. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Ganguli 2003 {published data only}
-
- Ganguli A, Singh NP, Ahuja N. A comparative study of nandrolone decanoate and erythropoietin on albumin levels, quality of life, and progression of renal disease in Indian predialysis CKD patients [abstract no: W455]. Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation 2003;18(Suppl 4):692. [CENTRAL: CN‐00653811]
-
- Ganguli A, Singh NP, Singh T, Agarwal SK, Neeraj A. Nandrolone decanoate is equiefacious to erythropoietin in correcting anemia and quality of life in predialysis chronic kidney disease patients [abstract no: 137]. Journal of the Association of Physicians of India 2003;51(Dec):1188. [CENTRAL: CN‐00765715]
-
- Singh NP, Anirban G, Singh T, Agarwal SK, Neera A. Long term effects of anemia correction on progression of renal disease and cognitive function using erythropoietin and androgenic steroids [abstract no: 136]. Journal of the Association of Physicians of India 2003;51(Dec):1188. [CENTRAL: CN‐00783567]
-
- Singh NP, Ganguli A, Singh T. A comparative study of nandrolone decanoate versus recombinant human erythropoietin on anemia in Indian predialysis chronic kidney disease patients [abstract no: W456]. Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation 2003;18(Suppl 4):692‐3. [CENTRAL: CN‐00447760]
Kim 2006e {published data only}
-
- Kim BS, Do JY, Kim DJ, Kim Y, Kim C, Park S, et al. Renal outcome of CKD patients with predialysis erythropoietin therapy: a prospective, randomized, multicenter clinical study [abstract no: TH‐FC057]. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 2006;17(Abstracts):13A. [CENTRAL: CN‐00766279]
Kleinman 1989 {published data only}
-
- Kleinman KS, Schweitzer SU. Human recombinant erythropoietin (rHuEPO) treatment of severe anemia associated with progressive renal failure may delay the need to initiate regular dialytic therapy [abstract]. Kidney International 1990;37:240. [CENTRAL: CN‐00626057]
-
- Kleinman KS, Schweitzer SU, Perdue ST, Abels RI. The use of recombinant human erythropoietin in the correction of anemia in pre‐dialysis patients and its effects on renal function: a double blind placebo controlled trial [abstract]. Kidney International 1989;35(1):229. [CENTRAL: CN‐00636148] - PubMed
-
- Kleinman KS, Schweitzer SU, Perdue ST, Bleifer KH, Abels RI. The use of recombinant human erythropoietin in the correction of anemia in predialysis patients and its effect on renal function: a double‐blind, placebo‐controlled trial. American Journal of Kidney Diseases 1989;14(6):486‐95. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Kristal 2008 {published data only}
-
- Kristal B, Shurtz‐Swirski R, Tanhilevski O, Shapiro G, Shkolnik G, Chezar J, et al. Epoetin‐alpha: preserving kidney function via attenuation of polymorphonuclear leukocyte priming. Israel Medical Association Journal ‐ Imaj 2008;10(4):266‐72. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Kuriyama 1997 {published data only}
-
- Kuriyama S, Tomonari H, Hashimoto T, Kawaguchi Y, Sakai O. Reversal of anemia by EPO therapy retards the progression of chronic renal failure in non‐diabetic pre‐dialysis patients [abstract]. Nephrology 1997;3(Suppl 1):S506. [CENTRAL: CN‐00461123] - PubMed
-
- Kuriyama S, Tomonari H, Yoshida H, Hashimoto T, Kawaguchi Y, Sakai O. Reversal of anemia by erythropoietin therapy retards the progression of chronic renal failure, especially in nondiabetic patients. Nephron 1997;77(2):176‐85. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Lim 1989 {published data only}
-
- Lim VS, DeGowin RL, Zavala D, Kirchner PT, Abels R, Perry P, et al. Recombinant human erythropoietin treatment in pre‐dialysis patients. A double‐blind placebo‐controlled trial. Annals of Internal Medicine 1989;110(2):108‐14. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Roth 1994 {published data only}
-
- Benz R, Teehan B, Roth D, Buckalew V, Freedman B, Hatch F, et al. Renal function and quality of life (QOL) studies in anemic, pre‐dialysis chronic renal failure (CRF) patients receiving recombinant human erythropoietin (r‐HuEPO): results of a multi‐center trial [abstract]. 12th International Congress of Nephrology; 1993 June 13‐18; Jerusalem, Israel. 1993:316. [CENTRAL: CN‐00602029]
-
- Revicki DA, Brown RE, Feeny DH, Henry D, Teehan BP, Rudnick MR, et al. Health‐related quality of life associated with recombinant human erythropoietin therapy for predialysis chronic renal disease patients. American Journal of Kidney Diseases 1995;25(4):548‐54. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Roth D, Smith RD, Schulman G, Steinman TI, Hatch FE, Rudnick MR, et al. Effects of recombinant human erythropoietin on renal function in chronic renal failure predialysis patients. American Journal of Kidney Diseases 1994;24(5):777‐84. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Stone 1988 {published data only}
-
- Stone WJ, Graber SE, Krantz SB, Dessypris EN, O'Neil VL, Olsen NJ, et al. Treatment of the anemia of predialysis patients with recombinant human erythropoietin: a randomized, placebo‐controlled trial. American Journal of Medical Sciences 1988;296(3):171‐9. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Teehan 1989 {published data only}
-
- Teehan BP, Sigler MH, Brown JM, Benz RL, Gilgore GS, Schleifer CR, et al. Hematologic and physiologic studies during correction of anaemia with recombinant human erythropoietin in predialysis patients. Transplantation Proceedings 1989;21 Suppl(2):63‐6. [EMBASE: 1990284570]
Teehan 1991 {published data only}
-
- Double‐blind, placebo‐controlled study of the therapeutic use of recombinant human erythropoietin for anemia associated with chronic renal failure in predialysis patients. The US Recombinant Human Erythropoietin Predialysis Study Group.[Erratum appears in Am J Kidney Dis 1991 Sep;18(3):420]. American Journal of Kidney Diseases 1991;18(1):50‐9. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Teplan 2001b {published data only}
-
- Teplan V, Schuck O, Knotek A, Hojny J, Horackova M. Ketoacids and recombinant human erythro‐poietin may influence progression of chronic renal insufficiency: Czech multicentre study [abstract]. Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation 2001;16(6):A96. [CENTRAL: CN‐00447973]
Teplan 2003 {published data only}
-
- Teplan V, Schuck O, Knotek A, Hajny J, Horackova M, Kvapil M, Czech multicenter study. Enhanced metabolic effect of erythropoietin and keto acids in CRF patients on low‐protein diet: Czech multicenter study. American Journal of Kidney Diseases 2003;41(3 Suppl 1):S26‐30. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Teplan V, Schuck O, Knotek A, Hajny J, Surel S. Metabolic effect of erythropoietin and keto acids in CRF: Czech multicentre study [abstract]. Nutrition 2003;19(4):399. - PubMed
-
- Teplan V, Schuck O, Poledne R, Mengerova O. The influence of erythropoietin (r‐Hu EPO) and keto amino acids (KA) on lipid metabolism and renal function tests in chronic renal failure (CRF) [abstract no: A3094]. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 1996;7(9):1865. [CENTRAL: CN‐00766750]
-
- Teplan V, Schuck O, et al. Erythropoietin (r‐Hu EPO) and keto amino acids (KA): an effect on lipid metabolism in predialysis [abstract]. Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation 1996;11(6):A263. [CENTRAL: CN‐00261317]
Wang 2004b {published data only}
-
- Wang AY, Chook P, Chow K, Sanderson J, Li PK, Lui S, et al. A prospective randomized study to evaluate erythropoietin treatment as a novel strategy for improving vascular dysfunction and atherosclerosis prevention in chronic renal failure. [abstract no: SA‐FC104]. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 2004;15(Oct):43A. [CENTRAL: CN‐00763755]
Watson 1990 {published data only}
-
- Watson A, Gimenez L, Walser M, Cotton S, Spivak J. A prospective double‐blind study of subcutaneous recombinant‐human erythropoietin in predialysis renal failure. Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 1989;29:856.
-
- Watson AJ, Gimenez LF, Cotton S, Walser M, Spivak JL. Treatment of the anemia of chronic renal failure with subcutaneous recombinant human erythropoietin. American Journal of Medicine 1990;89(4):432‐5. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Brown 1988 {published data only}
-
- Brown CD, Kieran M, Dosunmu BV, Zhao Z, Larson RH, Friedman EA. Raised hematocrit (HCT) persists six‐weeks after stopping treatment with human recombinant erythropoietin (r‐HuEPO) in azotemic anemic patients [abstract]. Kidney International 1988;33(1):184. [CENTRAL: CN‐00602117]
CREATE Study 2001 {published data only}
-
- Clyne N, Drueke T, Eckardt K, Locatelli F, Macdougall I, Tsakiris D. Quality of life assessment in the 'cardiovascular risk reduction by early anaemia treatment with epoetin beta' (CREATE) study [abstract]. Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation 2003;18(Suppl 4):155‐6. [CENTRAL: CN‐00444859]
-
- Clyne N, Drueke TB, Eckardt K, Locatelli F, Macdougall IC, Tsakiris D, et al. Diagnostic value of NT‐proBNP in CKD patients: baseline and 6‐month data from the CREATE Study [abstract no: F‐PO320]. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 2004;15(Oct):136A. [CENTRAL: CN‐00550685]
-
- Clyne N, Macdougall I, Bilous R, Ritz E, CREATE Study Group, ACORD Study Group. Haemoglobin control with epoetin beta: results from the Cardiovascular risk Reduction by Early Anaemia Treatment with Epoetin beta (CREATE) and Anaemia Correction in Diabetes (ACORD) studies [abstract no: SP457]. Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation 2006;21(Suppl 4):iv169. [CENTRAL: CN‐00583337]
-
- Drueke T, Clyne N, Eckardt K, Locatelli F, Macdougall I, Tsakiris D, et al. Diagnostic value of NT‐proBNP and cardiac troponin T in chronic kidney disease patients: correlation with baseline characteristics in the CREATE study [abstract no: P210]. 41st Congress. European Renal Association. European Dialysis and Transplantation Association; 2004 May 15‐18; Lisbon, Portugal. 2004:85. [CENTRAL: CN‐00509163]
-
- Drueke T, Clyne N, Eckardt K, Locatelli F, Macdougall I, Tsakiris D, et al. Homocysteine as a cardiovascular risk marker in patients with chronic kidney disease: baseline data and risk profiles from the CREATE study [abstract no: SP207]. 41st Congress. European Renal Association. European Dialysis and Transplantation Association; 2004 May 15‐18; Lisbon, Portugal. 2004:84. [CENTRAL: CN‐00509164]
EPOCARES Study 2010 {published data only}
-
- Emans ME, Braam B, Diepenbroek A, Putten K, Cramer MJ, Wielders JP, et al. Neutrophil gelatinase‐associated lipocalin (NGAL) in chronic cardiorenal failure is correlated with endogenous erythropoietin levels and decreases in response to low‐dose erythropoietin treatment. Kidney & Blood Pressure Research 2013;36(1):344‐54. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Emans ME, PK, Velthuis BK, Vries JJ, Cramer MJ, America YG, et al. Atherosclerotic renal artery stenosis is prevalent in cardiorenal patients but not associated with left ventricular function and myocardial fibrosis as assessed by cardiac magnetic resonance imaging. BMC Cardiovascular Disorders 2012;12:76. [MEDLINE: ] - PMC - PubMed
-
- Emans ME, PK, Rooijen KL, Kraaijenhagen RJ, Swinkels D, Solinge WW, et al. Determinants of red cell distribution width (RDW) in cardiorenal patients: RDW is not related to erythropoietin resistance. Journal of Cardiac Failure 2011;17(8):626‐33. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Frenken 1989 {published data only}
-
- Frenken LA, Verberckmoes R, Michielsen P, Koene RA. Efficacy and tolerance of treatment with recombinant‐human erythropoietin in chronic renal failure (pre‐dialysis) patients. Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation 1989;4(9):782‐6. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Frenken LA, Verberckmoes R, Sluiter HE, Schrijver G, Michielsen P, Koene RA. An open study of the safety and efficacy of multiple doses of recombinant human erythropoietin in end‐stage renal disease (predialysis) patients [abstract]. Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation 1988;3(4):495. [CENTRAL: CN‐00260377]
-
- Frenken LA, Verberckmoes R, Sluiter HE, Schrijver G, Michielsen P, Koene RA. An open study of the safety and efficacy of multiple doses of recombinant‐human erythropoietin in end‐state renal disease (pre‐dialysis) patients [abstract]. Kidney International 1988;34(4):558. [CENTRAL: CN‐00644276]
Frenken 1992 {published data only}
-
- Frenken LA, Wetzels JF, Sluiter HE, Koene RA. Evidence for renal vasodilation in pre‐dialysis patients during correction of anemia by erythropoietin. Kidney International 1992;41(2):384‐7. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Furukawa 1992 {published data only}
-
- Furukawa A, Numata A, Imagawa A, Kaifu Y, Sumikura T, Miyake H, et al. Study of recombinant human erythropoietin treatment on the anemia of predialysis patients. Nippon Jinzo Gakkai Shi [Japanese Journal of Nephrology] 1992;34(6):693‐700. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Jabs 1994 {published data only}
-
- Beeghly M, Jabs K, Johnson B, Tronick E, McCabe D, Alexander S, et al. Cognitive and adaptive function of children with end‐stage renal disease (ESRD): a report of the National Pediatric Recombinant Erythropoietin Study [abstract]. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 1992;3(3):280. [CENTRAL: CN‐00460367]
-
- Jabs K, Alexander S, McCabe D, Lerner G, Harmon W. Primary results from the U.S. multicenter pediatric recombinant erythropoietin (EPO) study [abstract]. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 1994;5(3):456. [CENTRAL: CN‐00583204]
-
- Dop C, Jabs KL, Alexander SA, Salusky IB, McCabe D. Correction of anemia does not improve growth or endocrine function in children with ESRD: a report from the U.S. multicenter pediatric recombinant erythropoietin (EPO) study [abstract]. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 1995;6(3):407. [CENTRAL: CN‐00486268]
Koene 1990 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- Koene R, Frenken L. Does treatment of predialysis patients with recombinant human erythropoietin compromise renal function?. Nefrologia 1990;10 Suppl(2):131‐6. - PubMed
-
- Koene RA, Frenken LA. Does treatment of predialysis patients with recombinant human erythropoietin compromise renal function?. Contributions to Nephrology 1990;87:105‐12. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Macdougall 2007 {published data only}
-
- Bennett‐Jones D. Use of epoetin alpha in the treatment in anaemia in predialysis patients. www.nihr.ac.uk/Profile/Pages/NRRResults.aspx?publication_id=N0055116759 (last accessed July 2014).
-
- Kwan JT, Temple M, Macdougall I. Is early treatment of anemia with epoetin‐alfa beneficial to predialysis renal patients? An UK multi‐centre study [abstract: SU‐PO057]. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 2004;15(Oct):545A. [CENTRAL: CN‐00765503]
-
- Macdougall IC, Kwan J, Temple RM, EPO‐GBR‐2 Investigator Study Group. UK multicentre randomised controlled study of epoetin alfa in early renal insufficiency (ERI) ‐ a 12‐month interim analysis [abstract]. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 2001;12(Program & Abstracts):395A. [CENTRAL: CN‐00766947]
-
- Macdougall IC, Temple RM, Kwan JT. Is early treatment of anaemia with epoetin‐alpha beneficial to pre‐dialysis chronic kidney disease patients? Results of a multicentre, open‐label, prospective, randomized, comparative group trial. Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation 2007;22(3):784‐93. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Marcas 2003 {published data only}
-
- Marcas L, Martinez‐Vea A, Bardaji A, Gutierrez C, Garcia C, Compte T, et al. Cardiovascular effects of the partial or complete correction of anemia with erythropoietin therapy in predialysis patients [abstract]. Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation 2003;18(Suppl 4):156‐7. [CENTRAL: CN‐00446594]
Meloni 2003 {published data only}
-
- Meloni C, Tozzo C, Rossi V, Borzi M, Flamini M, Grotta BD, et al. Early anaemia correction with EPO: one year effects on LVH and progression of chronic renal failure (CRF) in predialysis patients (PTS) [abstract]. Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation 2003;18(Suppl 4):157. [CENTRAL: CN‐00446732]
Mignon 2001 {published data only}
-
- Mignon F, Andrassy K, Esnault VL, Kuhlmann MK, Sinnassamy P. Epoetin delta corrects and maintains haemoglobin in pre‐end stage renal disease [abstract]. 38th Congress. European Renal Association. European Dialysis and Transplantation Association; 2001 Jun 24‐27; Vienna, Austria. 2001:140. [CENTRAL: CN‐00461317]
-
- Mignon F, Andrassy K, Esnault VL, Kuhlmann MK, Sinnassamy P, European HMR4396 Study Group. Novel human erythropoietin corrects and maintains hemoglobin in pre‐end stage renal disease (ESRD) when administered twice weekly subcutaneously [abstract no: A0384]. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 2000;11(Sept):71A. [CENTRAL: CN‐00794723]
Muirhead 1992 {published data only}
-
- Muirhead N. Changes in quality of life in chronic renal failure patients treated with recombinant human erythropoiein [abstract]. 9th Asian Colloquium in Nephrology; 1992 May 17‐21; Seoul, Korea. 1992:45‐6. [CENTRAL: CN‐00461371]
N0287023177 {published data only}
-
- Bradley JR. An open label prospective randomised comparative group study to assess the effects of epoeitin alfa therapy in predialysis chronic renal failure patients at an early stage in the development of their anaemia. www.nihr.ac.uk/Profile/Pages/NRRResults.aspx?publication_id=N0287023177 (last accessed 3 July 2014).
Palazzuoli 2007 {published data only}
-
- Palazzuoli A, Silverberg DS, Iovine F, Calabro A, Campagna MS, Gallotta M, et al. Effects of beta‐erythropoietin treatment on left ventricular remodeling, systolic function, and B‐type natriuretic peptide levels in patients with the cardiorenal anemia syndrome. American Heart Journal 2007;154(4):645.e9‐15. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Pratt 2006 {published data only}
-
- Pratt RD. Epoetin delta for the treatment of anemia in patients with CKD not requiring hemodialysis [abstract no: TH‐PO377]. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 2006;17(Abstracts):187A. [CENTRAL: CN‐00765050]
Schwartz 1989 {published data only}
-
- Prior JE, Terzian A, Schwartz AB, Kim KE, Mintz GS, Kahn SB. Prolonged RBC survival and hematopoietic response to recombinant human erythropoietin (rHuEPO) in chronic renal failure (CRF) [abstract]. Kidney International 1989;35(1):318. [CENTRAL: CN‐00766056]
-
- Schwartz AB, Mintz GS, Kim KE, Prior JE, Kahn SB. Recombinant human erythropoietin (rHuEPO) increases MAP, TPRI and systolic and diastolic dysfunction with increased impedance to LV ejection due to increased HCT and RBC mass in PTS with CRF [abstract]. Kidney International 1989;35(1):334. [CENTRAL: CN‐00766227]
Singh 1999 {published data only}
-
- Singh NP, Aggarwal L, Singh T, Anuradha S, Kohli R. Anaemia, iron studies and erythropoietin in patients of chronic renal failure. Journal of the Association of Physicians of India 1999;47(3):284‐90. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Teehan 1990 {published data only}
-
- Teehan P, Benz R, Sigler M, Brown J. Early intervention with recombinant human erythropoietin therapy. Seminars in Nephrology 1990;10(2 Suppl 1):28‐34. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Yamazaki 1993 {published data only}
-
- Yamazaki C, Watanabe Y, Sakamoto N. Pharmacokinetic study of recombinant human erythropoietin treatment in pre‐dialysis end stage renal disease patients. Nippon Jinzon Gakkai Shi [Japanese Journal of Nephrology] 1993;35(11):1233‐42. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Zheng 1992 {published data only}
-
- Zheng FL, Bi ZQ, Yang ZP, Li XW, Pu YF, Duan L. Effect of administration of low doses of rHuEPO in predialysis patients [abstract]. 9th Asian Colloquium in Nephrology; 1992 May 17‐21; Seoul, Korea. 1992:175. [CENTRAL: CN‐00462065]
Additional references
Canadian EPO Study Group 1990
Garcia 1985
-
- Garcia DL, Anderson S, Rennke HG, Bremner BM. Anemia lessens and its prevention with recombinant human erythropoietin worsens glomerular injury and hypertension in rats with reduced renal mass. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 1988;85(16):6142‐6. [MEDLINE: ] - PMC - PubMed
Harnett 1995
-
- Harnett JD, Foley RN, Kent GM, Barre PE, Murray D, Parfrey PS. Congestive heart failure in dialysis patients: prevalence, incidence, prognosis and risk factors. Kidney International 1995;47(3):884‐90. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Higgins 2003
Higgins 2011
-
- Higgins JP, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Jensen 1994
-
- Jensen JD, Madsen JK, Jensen LW, Pedersen EB. Reduced production, absorption, and elimination of erythropoietin in uremia compared with healthy volunteers. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 1994;5(2):177‐85. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Koch 1991
-
- Koch KM, Frei U. Treatment of renal anemia, 1960‐1990. Advances in Nephrology From the Necker Hospital 1991;20:19‐30. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Levin 1996
-
- Levin A, Singer J, Thompson CR, Ross H, Lewis M. Prevalent left ventricular hypertrophy in the predialysis population: identifying opportunities for intervention. American Journal of Kidney Diseases 1996;27(3):347‐54. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Lin 1985
Lundin 1989
-
- Lundin AP. Quality of life: subjective and objective improvements with recombinant human erythropoietin therapy. Seminars in Nephrology 1989;9(1 Suppl 1):22‐9. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Muirhead 1994
-
- Muirhead N, Cattran DC, Zaltman J, Jindal K, First MR, Boucher A, et al. Safety and efficacy of recombinant human erythropoietin in correcting the anemia of patients with chronic renal allograft dysfunction. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 1994;5(5):1216‐22. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Palmer 2012
Palmer 2014
Sheingold 1990
-
- Sheingold SH. Cost‐benefit analysis of using recombinant human erythropoietin for the anemia of chronic renal failure. Kidney International ‐ Supplement 1990;3(7):20.
Thompson 1994
Ward 1990
-
- Ward HJ. Implications of recombinant erythropoietin therapy for renal transplantation. American Journal of Nephrology 1990;10 Suppl 2:44‐52. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Winearls 1986
-
- Winearls CG, Oliver DO, Pippard MJ, Reid C, Downing MR, Cotes PM. Effect of human erythropoietin derived from recombinant DNA on the anaemia of patients maintained by chronic haemodialysis. Lancet 1986;2(8517):1175‐8. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
References to other published versions of this review
Cody 2001
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

