Modulation of Ca2+ oscillation and melatonin secretion by BKCa channel activity in rat pinealocytes
- PMID: 26791489
- PMCID: PMC4867307
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpcell.00342.2015
Modulation of Ca2+ oscillation and melatonin secretion by BKCa channel activity in rat pinealocytes
Abstract
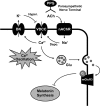
The pineal glands regulate circadian rhythm through the synthesis and secretion of melatonin. The stimulation of nicotinic acetylcholine receptor due to parasympathetic nerve activity causes an increase in intracellular Ca(2+) concentration and eventually downregulates melatonin production. Our previous report shows that rat pinealocytes have spontaneous and nicotine-induced Ca(2+) oscillations that are evoked by membrane depolarization followed by Ca(2+) influx through voltage-dependent Ca(2+) channels (VDCCs). These Ca(2+) oscillations are supposed to contribute to the inhibitory mechanism of melatonin secretion. Here we examined the involvement of large-conductance Ca(2+)-activated K(+) (BKCa) channel conductance on the regulation of Ca(2+) oscillation and melatonin production in rat pinealocytes. Spontaneous Ca(2+) oscillations were markedly enhanced by BKCa channel blockers (1 μM paxilline or 100 nM iberiotoxin). Nicotine (100 μM)-induced Ca(2+) oscillations were also augmented by paxilline. In contrast, spontaneous Ca(2+) oscillations were abolished by BKCa channel opener [3 μM 12,14-dichlorodehydroabietic acid (diCl-DHAA)]. Under whole cell voltage-clamp configurations, depolarization-elicited outward currents were significantly activated by diCl-DHAA and blocked by paxilline. Expression analyses revealed that the α and β3 subunits of BKCa channel were highly expressed in rat pinealocytes. Importantly, the activity of BKCa channels modulated melatonin secretion from whole pineal gland of the rat. Taken together, BKCa channel activation attenuates these Ca(2+) oscillations due to depolarization-synchronized Ca(2+) influx through VDCCs and results in a recovery of reduced melatonin secretion during parasympathetic nerve activity. BKCa channels may play a physiological role for melatonin production via a negative-feedback mechanism.
Keywords: calcium oscillation; calcium-activated potassium channel; parasympathetic nerve; pineal gland.
Copyright © 2016 the American Physiological Society.
Figures

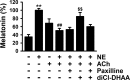
Similar articles
-
TMEM16A and TMEM16B channel proteins generate Ca2+-activated Cl- current and regulate melatonin secretion in rat pineal glands.J Biol Chem. 2018 Jan 19;293(3):995-1006. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA117.000326. Epub 2017 Nov 29. J Biol Chem. 2018. PMID: 29187602 Free PMC article.
-
Spontaneous and nicotine-induced Ca2+ oscillations mediated by Ca2+ influx in rat pinealocytes.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2014 Jun 1;306(11):C1008-16. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00014.2014. Epub 2014 Apr 2. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2014. PMID: 24696145
-
Involvement of small-conductance Ca2+-activated K+ (SKCa2) channels in spontaneous Ca2+ oscillations in rat pinealocytes.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2022 Jul 30;615:157-162. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2022.05.052. Epub 2022 May 21. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2022. PMID: 35643055
-
Control of CREB phosphorylation and its role for induction of melatonin synthesis in rat pinealocytes.Biol Cell. 1997 Nov;89(8):505-11. doi: 10.1016/s0248-4900(98)80006-3. Biol Cell. 1997. PMID: 9618900 Review.
-
Cholinergic signal transduction cascades in rat pinealocytes: functional and ontogenetic aspects.Reprod Nutr Dev. 1999 May-Jun;39(3):305-14. doi: 10.1051/rnd:19990303. Reprod Nutr Dev. 1999. PMID: 10420433 Review.
Cited by
-
The Hyperglycemic Effect of Melatonin in the Chinese Mitten Crab, Eriocheir sinensis.Front Physiol. 2018 Mar 21;9:270. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2018.00270. eCollection 2018. Front Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29618988 Free PMC article.
-
Circadian rhythm in melatonin release as a mechanism to reinforce the temporal organization of the circadian system in crayfish.Invert Neurosci. 2017 Jun;17(2):6. doi: 10.1007/s10158-017-0199-6. Epub 2017 May 24. Invert Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 28540583
-
Melatonin promotes sleep by activating the BK channel in C. elegans.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020 Oct 6;117(40):25128-25137. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2010928117. Epub 2020 Sep 21. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020. PMID: 32958651 Free PMC article.
-
TMEM16A and TMEM16B channel proteins generate Ca2+-activated Cl- current and regulate melatonin secretion in rat pineal glands.J Biol Chem. 2018 Jan 19;293(3):995-1006. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA117.000326. Epub 2017 Nov 29. J Biol Chem. 2018. PMID: 29187602 Free PMC article.
-
Serotonin modulates melatonin synthesis as an autocrine neurotransmitter in the pineal gland.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021 Oct 26;118(43):e2113852118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2113852118. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021. PMID: 34675083 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Behrens R, Nolting A, Reimann F, Schwarz M, Waldschutz R, Pongs O. hKCNMB3 and hKCNMB4, cloning and characterization of two members of the large-conductance calcium-activated potassium channel β subunit family. FEBS Lett 474: 99–106, 2000. - PubMed
-
- Berkefeld H, Fakler B, Schulte U. Ca2+-activated K+ channels: from protein complexes to function. Physiol Rev 90: 1437–1459, 2010. - PubMed
-
- Castellano A, López-Barneo J, Armstrong CM. Potassium currents in dissociated cells of the rat pineal gland. Pflügers Arch 413: 644–650, 1989. - PubMed
-
- Castellano A, Pintado E, Lopez-Barneo J. Ca2+- and voltage-dependent K+ conductance in dispersed parathyroid cells. Cell Calcium 8: 377–383, 1987. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

