Increase in cholinergic modulation with pyridostigmine induces anti-inflammatory cell recruitment soon after acute myocardial infarction in rats
- PMID: 26791829
- PMCID: PMC4867407
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpregu.00328.2015
Increase in cholinergic modulation with pyridostigmine induces anti-inflammatory cell recruitment soon after acute myocardial infarction in rats
Abstract
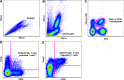
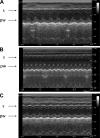
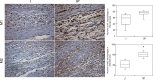
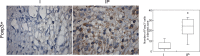
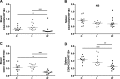
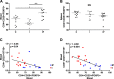
We tested the hypothesis that an increase in the anti-inflammatory cholinergic pathway, when induced by pyridostigmine (PY), may modulate subtypes of lymphocytes (CD4+, CD8+, FOXP3+) and macrophages (M1/M2) soon after myocardial infarction (MI) in rats. Wistar rats, randomly allocated to receive PY (40 mg·kg(-1)·day(-1)) in drinking water or to stay without treatment, were followed for 4 days and then were subjected to ligation of the left coronary artery. The groups-denominated as the pyridostigmine-treated infarcted (IP) and infarcted control (I) groups-were submitted to euthanasia 3 days after MI; the heart was removed for immunohistochemistry, and the peripheral blood and spleen were collected for flow cytometry analysis. Noninfarcted and untreated rats were used as controls (C Group). Echocardiographic measurements were registered on the second day after MI, and heart rate variability was measured on the third day after MI. The infarcted groups had similar MI areas, degrees of systolic dysfunction, blood pressures, and heart rates. Compared with the I Group, the IP Group showed a significant higher parasympathetic modulation and a lower sympathetic modulation, which were associated with a small, but significant, increase in diastolic function. The IP Group showed a significant increase in M2 macrophages and FOXP3(+)cells in the infarcted and peri-infarcted areas, a significantly higher frequency of circulating Treg cells (CD4(+)CD25(+)FOXP3(+)), and a less extreme decrease in conventional T cells (CD25(+)FOXP3(-)) compared with the I Group. Therefore, increasing cholinergic modulation with PY induces greater anti-inflammatory cell recruitment soon after MY in rats.
Keywords: T lymphocytes; anticholinesterase drugs; cholinergic anti-inflammatory reflex; macrophage activation; myocardial infarction.
Copyright © 2016 the American Physiological Society.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cholinergic Stimulation Improves Oxidative Stress and Inflammation in Experimental Myocardial Infarction.Sci Rep. 2017 Oct 20;7(1):13687. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-14021-8. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 29057895 Free PMC article.
-
Cholinergic stimulation with pyridostigmine modulates a heart-spleen axis after acute myocardial infarction in spontaneous hypertensive rats.Sci Rep. 2021 May 5;11(1):9563. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-89104-8. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33953291 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor by ITE Improves Cardiac Function in Mice After Myocardial Infarction.J Am Heart Assoc. 2021 Jul 6;10(13):e020502. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.120.020502. Epub 2021 Jun 23. J Am Heart Assoc. 2021. PMID: 34157850 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of immune cell-derived exosomes in the cardiac tissue repair after myocardial infarction: Molecular mechanisms and pre-clinical evidence.J Cell Mol Med. 2021 Jul;25(14):6500-6510. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.16686. Epub 2021 Jun 5. J Cell Mol Med. 2021. PMID: 34092017 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Macrophage Polarization in Cardiac Tissue Repair Following Myocardial Infarction.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Mar 8;22(5):2715. doi: 10.3390/ijms22052715. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33800220 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Pyridostigmine improves cardiac function and rhythmicity through RyR2 stabilization and inhibition of STIM1-mediated calcium entry in heart failure.J Cell Mol Med. 2021 May;25(10):4637-4648. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.16356. Epub 2021 Mar 23. J Cell Mol Med. 2021. PMID: 33755308 Free PMC article.
-
Pyridostigmine Treatment Significantly Alleviates Isoprenaline-Induced Chronic Heart Failure in Rats.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jul 17;26(14):6892. doi: 10.3390/ijms26146892. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40725139 Free PMC article.
-
Regulatory T cells in multiple sclerosis and myasthenia gravis.J Neuroinflammation. 2017 Jun 9;14(1):117. doi: 10.1186/s12974-017-0892-8. J Neuroinflammation. 2017. PMID: 28599652 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cholinergic Stimulation Improves Oxidative Stress and Inflammation in Experimental Myocardial Infarction.Sci Rep. 2017 Oct 20;7(1):13687. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-14021-8. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 29057895 Free PMC article.
-
Cholinergic Stimulation Exerts Cardioprotective Effects and Alleviates Renal Inflammatory Responses after Acute Myocardial Infarction in Spontaneous Hypertensive Rats (SHRs).Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 Apr 24;17(5):547. doi: 10.3390/ph17050547. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38794117 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abbate A, Bonanno E, Mauriello A, Bussani R, Biondi-Zoccai GG, Liuzzo G, Leone AM, Silvestri F, Dobrina A, Baldi F, Pandolfi F, Biasucci LM, Baldi A, Spagnoli LG, Crea F. Widespread myocardial inflammation and infarct-related artery patency. Circulation 110: 46–50, 2004. - PubMed
-
- Akinci SB, Ulu N, Yondem OZ, Firat P, Guc MO, Kanbak M, Aypar U. Effect of neostigmine on organ injury in murine endotoxemia: missing facts about the cholinergic antiinflammatory pathway. World J Surg 2005: 29: 1483–1489. - PubMed
-
- Antonica A, Magni E, Mearini L, Paolocci N. Vagal control of lymphocyte release from thymus. J Auton Nerv Syst 48: 187–197, 1994. - PubMed
-
- Anzai T. Post-infarction inflammation and left ventricular remodeling. Circ J 77: 580–587, 2013. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

