Lay health supporters aided by a mobile phone messaging system to improve care of villagers with schizophrenia in Liuyang, China: protocol for a randomised control trial
- PMID: 26792221
- PMCID: PMC4735204
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2015-010120
Lay health supporters aided by a mobile phone messaging system to improve care of villagers with schizophrenia in Liuyang, China: protocol for a randomised control trial
Abstract
Introduction: Schizophrenia is a severe, chronic and disabling mental illness. Non-adherence to medication and relapse may lead to poorer patient function. This randomised controlled study, under the acronym LEAN (Lay health supporter, e-platform, award, and iNtegration), is designed to improve medication adherence and high relapse among people with schizophrenia in resource poor settings.
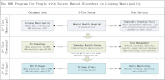
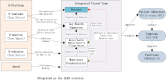
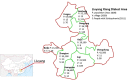
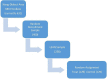
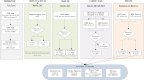
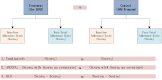
Methods/analysis: The community-based LEAN has four parts: (1) Lay health supporters (LHSs), mostly family members who will help supervise patient medication, monitor relapse and side effects, and facilitate access to care, (2) an E-platform to support two-way mobile text and voice messaging to remind patients to take medication; and alert LHSs when patients are non-adherent, (3) an Award system to motivate patients and strengthen LHS support, and (4) iNtegration of the efforts of patients and LHSs with those of village doctors, township mental health administrators and psychiatrists via the e-platform. A random sample of 258 villagers with schizophrenia will be drawn from the schizophrenic '686' Program registry for the 9 Xiang dialect towns of the Liuyang municipality in China. The sample will be further randomised into a control group and a treatment group of equal sizes, and each group will be followed for 6 months after launch of the intervention. The primary outcome will be medication adherence as measured by pill counts and supplemented by pharmacy records. Other outcomes include symptoms and level of function. Outcomes will be assessed primarily when patients present for medication refill visits scheduled every 2 months over the 6-month follow-up period. Data from the study will be analysed using analysis of covariance for the programme effect and an intent-to-treat approach.
Ethics and dissemination: University of Washington: 49464 G; Central South University: CTXY-150002-6. Results will be published in peer-reviewed journals with deidentified data made available on FigShare.
Trial registration number: ChiCTR-ICR-15006053; Pre-results.
Keywords: implementation science; lay health worker; mHealth; medication adherence; schizophrenia; “686” program.
Published by the BMJ Publishing Group Limited. For permission to use (where not already granted under a licence) please go to http://www.bmj.com/company/products-services/rights-and-licensing/
Figures

Similar articles
-
Mobile Texting and Lay Health Supporters to Improve Schizophrenia Care in a Resource-Poor Community in Rural China (LEAN Trial): Randomized Controlled Trial Extended Implementation.J Med Internet Res. 2020 Dec 1;22(12):e22631. doi: 10.2196/22631. J Med Internet Res. 2020. PMID: 33258788 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Lay health supporters aided by mobile text messaging to improve adherence, symptoms, and functioning among people with schizophrenia in a resource-poor community in rural China (LEAN): A randomized controlled trial.PLoS Med. 2019 Apr 23;16(4):e1002785. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1002785. eCollection 2019 Apr. PLoS Med. 2019. PMID: 31013275 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Residual Effect of Texting to Promote Medication Adherence for Villagers with Schizophrenia in China: 18-Month Follow-up Survey After the Randomized Controlled Trial Discontinuation.JMIR Mhealth Uhealth. 2022 Apr 19;10(4):e33628. doi: 10.2196/33628. JMIR Mhealth Uhealth. 2022. PMID: 35438649 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
[Cost-effectiveness analysis of schizophrenic patient care settings: impact of an atypical antipsychotic under long-acting injection formulation].Encephale. 2005 Mar-Apr;31(2):235-46. doi: 10.1016/s0013-7006(05)82390-5. Encephale. 2005. PMID: 15959450 Review. French.
-
Interventions to Improve Medication Adherence in People with Schizophrenia: A Systematic Review.Patient Prefer Adherence. 2022 Sep 1;16:2431-2449. doi: 10.2147/PPA.S378951. eCollection 2022. Patient Prefer Adherence. 2022. PMID: 36072918 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Innovative Models in Mental Health Delivery Systems: Task Sharing Care with Non-specialist Providers to Close the Mental Health Treatment Gap.Curr Psychiatry Rep. 2019 Apr 30;21(6):44. doi: 10.1007/s11920-019-1028-x. Curr Psychiatry Rep. 2019. PMID: 31041554 Review.
-
Mobile Texting and Lay Health Supporters to Improve Schizophrenia Care in a Resource-Poor Community in Rural China (LEAN Trial): Randomized Controlled Trial Extended Implementation.J Med Internet Res. 2020 Dec 1;22(12):e22631. doi: 10.2196/22631. J Med Internet Res. 2020. PMID: 33258788 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Leveraging Personal Technologies in the Treatment of Schizophrenia Spectrum Disorders: Scoping Review.JMIR Ment Health. 2024 Sep 30;11:e57150. doi: 10.2196/57150. JMIR Ment Health. 2024. PMID: 39348196 Free PMC article.
-
The association between a free medicine program and functioning in people with schizophrenia: a cross-sectional study in Liuyang, China.PeerJ. 2020 Apr 24;8:e8929. doi: 10.7717/peerj.8929. eCollection 2020. PeerJ. 2020. PMID: 32355575 Free PMC article.
-
Elements and Performance Indicators of Integrated Healthcare Programmes on Chronic Diseases in Six Countries in the Asia-Pacific Region: A Scoping Review.Int J Integr Care. 2021 Feb 8;21(1):3. doi: 10.5334/ijic.5439. Int J Integr Care. 2021. PMID: 33613135 Free PMC article.
References
-
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders fifth edition (DSM-5). Arlington, VA: American Psychiatric Association, 2013.
-
- Babiker IE. Noncompliance in schizophrenia. Psychiatr Dev 1985;4:329–37. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
