BET Bromodomain Inhibitors Enhance Efficacy and Disrupt Resistance to AR Antagonists in the Treatment of Prostate Cancer
- PMID: 26792867
- PMCID: PMC4834259
- DOI: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-15-0472
BET Bromodomain Inhibitors Enhance Efficacy and Disrupt Resistance to AR Antagonists in the Treatment of Prostate Cancer
Abstract
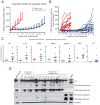
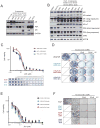
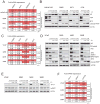
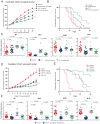
Next-generation antiandrogen therapies, such as enzalutamide and abiraterone, have had a profound impact on the management of metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (mCRPC). However, mCRPC patients invariably develop resistance to these agents. Here, a series of clonal cell lines were developed from enzalutamide-resistant prostate tumor xenografts to study the molecular mechanism of resistance and test their oncogenic potential under various treatment conditions. Androgen receptor (AR) signaling was maintained in these cell lines, which acquired potential resistance mechanisms, including expression of AR-variant 7 (AR-v7) and glucocorticoid receptor. BET bromodomain inhibitors were shown previously to attenuate AR signaling in mCRPC; here, we demonstrate the efficacy of bromodomain and extraterminal (BET) inhibitors in enzalutamide-resistant prostate cancer models. AR antagonists, enzalutamide, and ARN509 exhibit enhanced prostate tumor growth inhibition when combined with BET inhibitors, JQ1 and OTX015, respectively. Taken together, these data provide a compelling preclinical rationale to combine BET inhibitors with AR antagonists to subvert resistance mechanisms.
Implications: Therapeutic combinations of BET inhibitors and AR antagonists may enhance the clinical efficacy in the treatment of mCRPC.
Visual overview: http://mcr.aacrjournals.org/content/molcanres/14/4/324/F1.large.jpg
©2016 American Association for Cancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
A.M.C. and S.W. are co-founders of Oncofusion Therapeutics, which is developing novel BET bromodomain inhibitors. I.A.A. has served as consultant to Oncofusion Therapeutics.
Figures
References
-
- American Cancer Society. Cancer Facts and Figures 2015. 2015 http://wwwcancerorg/acs/groups/content/@editorial/documents/document/acs....
-
- Chen CD, Welsbie DS, Tran C, Baek SH, Chen R, Vessella R, et al. Molecular determinants of resistance to antiandrogen therapy. Nat Med. 2004;10(1):33–9. - PubMed
-
- Visakorpi T, Hyytinen E, Koivisto P, Tanner M, Keinanen R, Palmberg C, et al. In vivo amplification of the androgen receptor gene and progression of human prostate cancer. Nat Genet. 1995;9(4):401–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

