Histone H3K36 trimethylation is essential for multiple silencing mechanisms in fission yeast
- PMID: 26792892
- PMCID: PMC4872076
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkw008
Histone H3K36 trimethylation is essential for multiple silencing mechanisms in fission yeast
Abstract
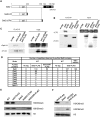
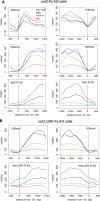
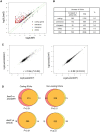
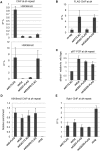
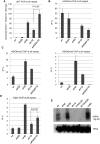
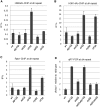
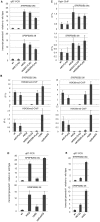
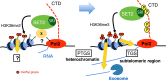
In budding yeast, Set2 catalyzes di- and trimethylation of H3K36 (H3K36me2 and H3K36me3) via an interaction between its Set2-Rpb1 interaction (SRI) domain and C-terminal repeats of RNA polymerase II (Pol2) phosphorylated at Ser2 and Ser5 (CTD-S2,5-P). H3K36me2 is sufficient for recruitment of the Rpd3S histone deacetylase complex to repress cryptic transcription from transcribed regions. In fission yeast, Set2 is also responsible for H3K36 methylation, which represses a subset of RNAs including heterochromatic and subtelomeric RNAs, at least in part via recruitment of Clr6 complex II, a homolog of Rpd3S. Here, we show that CTD-S2P-dependent interaction of fission yeast Set2 with Pol2 via the SRI domain is required for formation of H3K36me3, but not H3K36me2. H3K36me3 silenced heterochromatic and subtelomeric transcripts mainly through post-transcriptional and transcriptional mechanisms, respectively, whereas H3K36me2 was not enough for silencing. Clr6 complex II appeared not to be responsible for heterochromatic silencing by H3K36me3. Our results demonstrate that H3K36 methylation has multiple outputs in fission yeast; these findings provide insights into the distinct roles of H3K36 methylation in metazoans, which have different enzymes for synthesis of H3K36me1/2 and H3K36me3.
© The Author(s) 2016. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Context-Dependent and Locus-Specific Role of H3K36 Methylation in Transcriptional Regulation.J Mol Biol. 2025 Jan 1;437(1):168796. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2024.168796. Epub 2024 Sep 19. J Mol Biol. 2025. PMID: 39299382 Review.
-
Roles for Ctk1 and Spt6 in regulating the different methylation states of histone H3 lysine 36.Mol Cell Biol. 2008 Aug;28(16):4915-26. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00001-08. Epub 2008 Jun 9. Mol Cell Biol. 2008. PMID: 18541663 Free PMC article.
-
Unique and Shared Roles for Histone H3K36 Methylation States in Transcription Regulation Functions.Cell Rep. 2020 Jun 9;31(10):107751. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2020.107751. Cell Rep. 2020. PMID: 32521276 Free PMC article.
-
Elucidation of the Two H3K36me3 Histone Methyltransferases Set2 and Ash1 in Fusarium fujikuroi Unravels Their Different Chromosomal Targets and a Major Impact of Ash1 on Genome Stability.Genetics. 2018 Jan;208(1):153-171. doi: 10.1534/genetics.117.1119. Epub 2017 Nov 16. Genetics. 2018. PMID: 29146582 Free PMC article.
-
Structural and functional specificity of H3K36 methylation.Epigenetics Chromatin. 2022 May 18;15(1):17. doi: 10.1186/s13072-022-00446-7. Epigenetics Chromatin. 2022. PMID: 35581654 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
H3K36 methylation reprograms gene expression to drive early gametocyte development in Plasmodium falciparum.Epigenetics Chromatin. 2021 Apr 1;14(1):19. doi: 10.1186/s13072-021-00393-9. Epigenetics Chromatin. 2021. PMID: 33794978 Free PMC article.
-
The Chaperone FACT and Histone H2B Ubiquitination Maintain S. pombe Genome Architecture through Genic and Subtelomeric Functions.Mol Cell. 2020 Feb 6;77(3):501-513.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2019.11.016. Epub 2019 Dec 11. Mol Cell. 2020. PMID: 31837996 Free PMC article.
-
Chromatin accessibility profiling in Neurospora crassa reveals molecular features associated with accessible and inaccessible chromatin.BMC Genomics. 2021 Jun 19;22(1):459. doi: 10.1186/s12864-021-07774-0. BMC Genomics. 2021. PMID: 34147068 Free PMC article.
-
Surprising phenotypic diversity of cancer-associated mutations of Gly 34 in the histone H3 tail.Elife. 2021 Feb 1;10:e65369. doi: 10.7554/eLife.65369. Elife. 2021. PMID: 33522486 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of centromeric heterochromatin in the cell cycle by phosphorylation of histone H3 tyrosine 41.Curr Genet. 2019 Aug;65(4):829-836. doi: 10.1007/s00294-019-00962-2. Epub 2019 Apr 8. Curr Genet. 2019. PMID: 30963244 Review.
References
-
- Jenuwein T., Allis C.D. Translating the histone code. Science. 2001;293:1074–1080. - PubMed
-
- Peters A.H.F.M., Mermoud J.E., O'Carroll D., Pagani M., Schweizer D., Brockdorff N., Jenuwein T. Histone H3 lysine 9 methylation is an epigenetic imprint of facultative heterochromatin. Nat. Genet. 2002;30:77–80. - PubMed
-
- Venkatesh S., Smolle M., Li H., Gogol M.M., Saint M., Kumar S., Natarajan K., Workman J.L. Set2 methylation of histone H3 lysine 36 suppresses histone exchange on transcribed genes. Nature. 2012;489:452–455. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

