From Autism to Eating Disorders and More: The Role of Oxytocin in Neuropsychiatric Disorders
- PMID: 26793046
- PMCID: PMC4709851
- DOI: 10.3389/fnins.2015.00497
From Autism to Eating Disorders and More: The Role of Oxytocin in Neuropsychiatric Disorders
Abstract
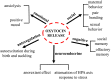
Oxytocin (oxy) is a pituitary neuropeptide hormone synthesized from the paraventricular and supraoptic nuclei within the hypothalamus. Like other neuropeptides, oxy can modulate a wide range of neurotransmitter and neuromodulator activities. Additionally, through the neurohypophysis, oxy is secreted into the systemic circulation to act as a hormone, thereby influencing several body functions. Oxy plays a pivotal role in parturition, milk let-down and maternal behavior and has been demonstrated to be important in the formation of pair bonding between mother and infants as well as in mating pairs. Furthermore, oxy has been proven to play a key role in the regulation of several behaviors associated with neuropsychiatric disorders, including social interactions, social memory response to social stimuli, decision-making in the context of social interactions, feeding behavior, emotional reactivity, etc. An increasing body of evidence suggests that deregulations of the oxytocinergic system might be involved in the pathophysiology of certain neuropsychiatric disorders such as autism, eating disorders, schizophrenia, mood, and anxiety disorders. The potential use of oxy in these mental health disorders is attracting growing interest since numerous beneficial properties are ascribed to this neuropeptide. The present manuscript will review the existing findings on the role played by oxy in a variety of distinct physiological and behavioral functions (Figure 1) and on its role and impact in different psychiatric disorders. The aim of this review is to highlight the need of further investigations on this target that might contribute to the development of novel more efficacious therapies. Figure 1Oxytocin regulatory control of different and complex processes.
Keywords: anxiety; autism; eating disorders; mood disorders; oxytocinergic system.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The role of oxytocin in neuropsychiatric disorders.Curr Med Chem. 2008;15(7):698-704. doi: 10.2174/092986708783885291. Curr Med Chem. 2008. PMID: 18336283 Review.
-
Oxytocin: Narrative Expert Review of Current Perspectives on the Relationship with Other Neurotransmitters and the Impact on the Main Psychiatric Disorders.Medicina (Kaunas). 2022 Jul 11;58(7):923. doi: 10.3390/medicina58070923. Medicina (Kaunas). 2022. PMID: 35888641 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Oxytocin: recent developments.Biomol Concepts. 2010 Dec 1;1(5-6):367-80. doi: 10.1515/bmc.2010.036. Biomol Concepts. 2010. PMID: 25962010
-
The role of oxytocin in psychiatric disorders: a review of biological and therapeutic research findings.Harv Rev Psychiatry. 2013 Sep-Oct;21(5):219-47. doi: 10.1097/HRP.0b013e3182a75b7d. Harv Rev Psychiatry. 2013. PMID: 24651556 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of Oxytocin in Different Neuropsychiatric, Neurodegenerative, and Neurodevelopmental Disorders.Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 2023;186:95-134. doi: 10.1007/112_2022_72. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36416982 Review.
Cited by
-
Aberrant Early in Life Stimulation of the Stress-Response System Affects Emotional Contagion and Oxytocin Regulation in Adult Male Mice.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 May 10;22(9):5039. doi: 10.3390/ijms22095039. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34068684 Free PMC article.
-
Endocrine Disorder in Patients With Craniopharyngioma.Front Neurol. 2021 Dec 2;12:737743. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2021.737743. eCollection 2021. Front Neurol. 2021. PMID: 34925209 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Control of lipolysis by a population of oxytocinergic sympathetic neurons.Nature. 2024 Jan;625(7993):175-180. doi: 10.1038/s41586-023-06830-x. Epub 2023 Dec 13. Nature. 2024. PMID: 38093006 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic, epigenetic, and environmental factors controlling oxytocin receptor gene expression.Clin Epigenetics. 2021 Jan 30;13(1):23. doi: 10.1186/s13148-021-01017-5. Clin Epigenetics. 2021. PMID: 33516250 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of the thermosensory system by oxytocin.Front Mol Neurosci. 2023 Jan 9;15:1075305. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2022.1075305. eCollection 2022. Front Mol Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 36698777 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical