Re-examining the Nature and Function of Self-Reactive T cells
- PMID: 26795134
- PMCID: PMC7611850
- DOI: 10.1016/j.it.2015.12.005
Re-examining the Nature and Function of Self-Reactive T cells
Abstract
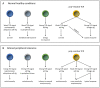
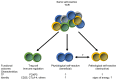
Recent studies have leveraged MHC tetramer and TCR sequencing approaches towards a more precise characterization of the peripheral T cell repertoire, providing important insight into both the contribution of self-reactive T cells to the overall repertoire and their function. The peripheral T cell repertoire of healthy individuals contains a high frequency of diverse, self-reactive T cells. Furthermore, self-reactive T cells can perform essential beneficial physiological functions. We review these recent findings here, and discuss their implications to the current understanding of peripheral tolerance and the role of self-reactive T cells in autoimmune disease. We outline gaps in understanding, and argue that an important step forward is to revise the definition of self-reactive T cells to incorporate new concepts regarding the nature and physiological functions of different populations of T cells capable of recognizing self-antigens.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

