Compendium of Immune Signatures Identifies Conserved and Species-Specific Biology in Response to Inflammation
- PMID: 26795250
- PMCID: PMC5330663
- DOI: 10.1016/j.immuni.2015.12.006
Compendium of Immune Signatures Identifies Conserved and Species-Specific Biology in Response to Inflammation
Abstract
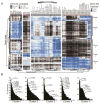
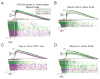
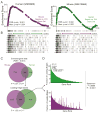
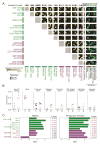
Gene-expression profiling has become a mainstay in immunology, but subtle changes in gene networks related to biological processes are hard to discern when comparing various datasets. For instance, conservation of the transcriptional response to sepsis in mouse models and human disease remains controversial. To improve transcriptional analysis in immunology, we created ImmuneSigDB: a manually annotated compendium of ∼5,000 gene-sets from diverse cell states, experimental manipulations, and genetic perturbations in immunology. Analysis using ImmuneSigDB identified signatures induced in activated myeloid cells and differentiating lymphocytes that were highly conserved between humans and mice. Sepsis triggered conserved patterns of gene expression in humans and mouse models. However, we also identified species-specific biological processes in the sepsis transcriptional response: although both species upregulated phagocytosis-related genes, a mitosis signature was specific to humans. ImmuneSigDB enables granular analysis of transcriptomic data to improve biological understanding of immune processes of the human and mouse immune systems.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


Similar articles
-
RNA-seq based transcriptomic map reveals new insights into mouse salivary gland development and maturation.BMC Genomics. 2016 Nov 16;17(1):923. doi: 10.1186/s12864-016-3228-7. BMC Genomics. 2016. PMID: 27852218 Free PMC article.
-
PathCellNet: Cell-type specific pathogen-response network explorer.J Immunol Methods. 2016 Dec;439:15-22. doi: 10.1016/j.jim.2016.09.005. Epub 2016 Sep 20. J Immunol Methods. 2016. PMID: 27659011
-
Meta-analysis of mouse transcriptomic studies supports a context-dependent astrocyte reaction in acute CNS injury versus neurodegeneration.J Neuroinflammation. 2020 Jul 31;17(1):227. doi: 10.1186/s12974-020-01898-y. J Neuroinflammation. 2020. PMID: 32736565 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptomic Profiling Identifies Neutrophil-Specific Upregulation of Cystatin F as a Marker of Acute Inflammation in Humans.Front Immunol. 2021 Apr 1;12:634119. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.634119. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33868254 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Key hepatic signatures of human and mouse nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: A transcriptome-proteome data meta-analysis.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 Oct 4;13:934847. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.934847. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 36267572 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Cell of origin alters myeloid-mediated immunosuppression in lung adenocarcinoma.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Jun 23:2024.06.19.599651. doi: 10.1101/2024.06.19.599651. bioRxiv. 2024. PMID: 38948812 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Regnase-1 suppresses TCF-1+ precursor exhausted T-cell formation to limit CAR-T-cell responses against ALL.Blood. 2021 Jul 15;138(2):122-135. doi: 10.1182/blood.2020009309. Blood. 2021. PMID: 33690816 Free PMC article.
-
Human variation in population-wide gene expression data predicts gene perturbation phenotype.iScience. 2022 Oct 12;25(11):105328. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2022.105328. eCollection 2022 Nov 18. iScience. 2022. PMID: 36310583 Free PMC article.
-
Clonal germinal center B cells function as a niche for T-cell lymphoma.Blood. 2022 Nov 3;140(18):1937-1950. doi: 10.1182/blood.2022015451. Blood. 2022. PMID: 35921527 Free PMC article.
-
Alternative splicing impacts microRNA regulation within coding regions.NAR Genom Bioinform. 2023 Sep 11;5(3):lqad081. doi: 10.1093/nargab/lqad081. eCollection 2023 Sep. NAR Genom Bioinform. 2023. PMID: 37705830 Free PMC article.

