Integrated analysis of microRNA regulatory network in nasopharyngeal carcinoma with deep sequencing
- PMID: 26795575
- PMCID: PMC4722718
- DOI: 10.1186/s13046-016-0292-4
Integrated analysis of microRNA regulatory network in nasopharyngeal carcinoma with deep sequencing
Erratum in
-
Correction to: Integrated analysis of microRNA regulatory network in nasopharyngeal carcinoma with deep sequencing.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2022 Mar 8;41(1):84. doi: 10.1186/s13046-022-02311-7. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2022. PMID: 35260185 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
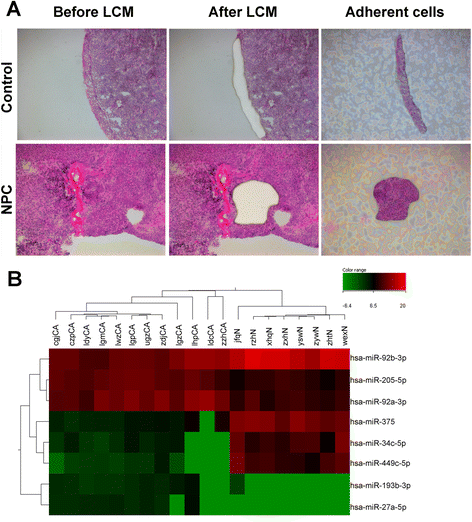
Background: MicroRNAs (miRNAs) have been shown to play a critical role in the development and progression of nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC). Although accumulating studies have been performed on the molecular mechanisms of NPC, the miRNA regulatory networks in cancer progression remain largely unknown. Laser capture microdissection (LCM) and deep sequencing are powerful tools that can help us to detect the integrated view of miRNA-target network.
Methods: Illumina Hiseq2000 deep sequencing was used to screen differentially expressed miRNAs in laser-microdessected biopsies between 12 NPC and 8 chronic nasopharyngitis patients. The result was validated by real-time PCR on 201 NPC and 25 chronic nasopharyngitis patients. The potential candidate target genes of the miRNAs were predicted using published target prediction softwares (RNAhybrid, TargetScan, Miranda, PITA), and the overlay part was analyzed in Gene Ontology (GO) and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) biological process. The miRNA regulatory network analysis was performed using the Ingenuity Pathway Analysis (IPA) software.
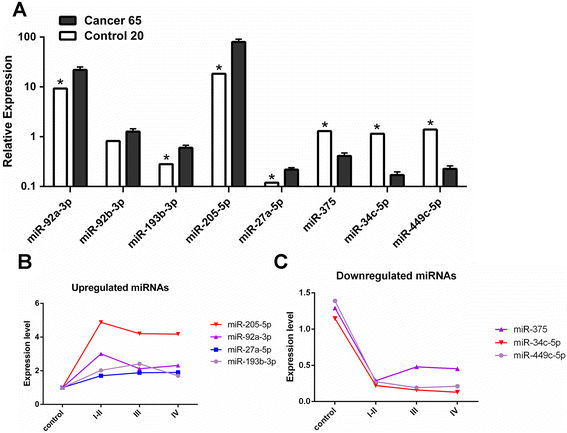
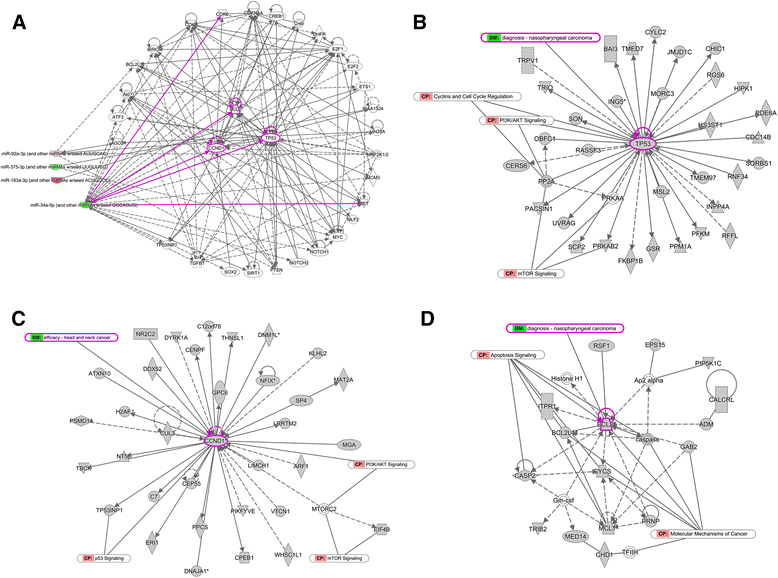
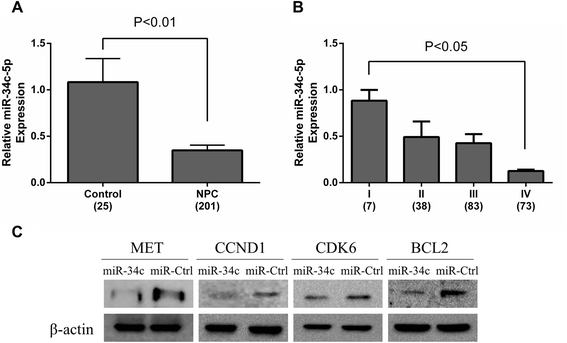
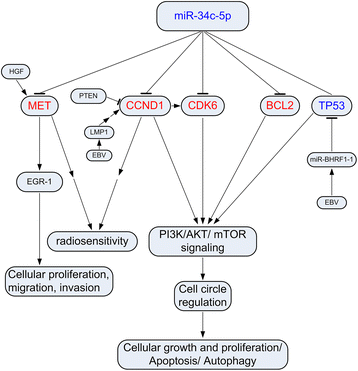
Results: Eight differentially expressed miRNAs were identified between NPC and chronic nasopharyngitis patients by deep sequencing. Further qRT-PCR assays confirmed 3 down-regulated miRNAs (miR-34c-5p, miR-375 and miR-449c-5p), 4 up-regulated miRNAs (miR-205-5p, miR-92a-3p, miR-193b-3p and miR-27a-5p). Additionally, the low level of miR-34c-5p (miR-34c) was significantly correlated with advanced TNM stage. GO and KEGG enrichment analyses showed that 914 target genes were involved in cell cycle, cytokine secretion and tumor immunology, and so on. IPA revealed that cancer was the top disease associated with those dysregulated miRNAs, and the genes regulated by miR-34c were in the center of miRNA-mRNA regulatory network, including TP53, CCND1, CDK6, MET and BCL2, and the PI3K/AKT/ mTOR signaling was regarded as a significant function pathway in this network.
Conclusion: Our study presents the current knowledge of miRNA regulatory network in NPC with combination of bioinformatics analysis and literature research. The hypothesis of miR-34c regulatory pathway may be beneficial in guiding further studies on the molecular mechanism of NPC tumorigenesis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
An in silico analysis of dynamic changes in microRNA expression profiles in stepwise development of nasopharyngeal carcinoma.BMC Med Genomics. 2012 Jan 19;5:3. doi: 10.1186/1755-8794-5-3. BMC Med Genomics. 2012. PMID: 22260379 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide analyses of radioresistance-associated miRNA expression profile in nasopharyngeal carcinoma using next generation deep sequencing.PLoS One. 2013 Dec 19;8(12):e84486. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0084486. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24367666 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of miRNA/mRNA-Negative Regulation Pairs in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma.Med Sci Monit. 2016 Jun 28;22:2215-34. doi: 10.12659/msm.896047. Med Sci Monit. 2016. PMID: 27350400 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring nasopharyngeal carcinoma genetics: Bioinformatics insights into pathways and gene associations.Med J Malaysia. 2024 Sep;79(5):615-625. Med J Malaysia. 2024. PMID: 39352166 Review.
-
MicroRNA expression in osteoarthritis: a meta-analysis.Clin Exp Med. 2023 Nov;23(7):3737-3749. doi: 10.1007/s10238-023-01063-8. Epub 2023 Apr 7. Clin Exp Med. 2023. PMID: 37027064
Cited by
-
MiR-34c downregulation leads to SOX4 overexpression and cisplatin resistance in nasopharyngeal carcinoma.BMC Cancer. 2020 Jun 26;20(1):597. doi: 10.1186/s12885-020-07081-z. BMC Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32586280 Free PMC article.
-
Head and Neck Cancers Are Not Alike When Tarred with the Same Brush: An Epigenetic Perspective from the Cancerization Field to Prognosis.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Nov 11;13(22):5630. doi: 10.3390/cancers13225630. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34830785 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MiR-203a-3p suppresses cell proliferation and metastasis through inhibiting LASP1 in nasopharyngeal carcinoma.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2017 Oct 5;36(1):138. doi: 10.1186/s13046-017-0604-3. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2017. PMID: 28982387 Free PMC article.
-
miRNAs from Plasma Extracellular Vesicles Are Signatory Noninvasive Prognostic Biomarkers against Atherosclerosis in LDLr-/-Mice.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022 Aug 17;2022:6887192. doi: 10.1155/2022/6887192. eCollection 2022. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022. PMID: 36035214 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-19b-3p regulates nasopharyngeal carcinoma radiosensitivity by targeting TNFAIP3/NF-κB axis.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2016 Dec 5;35(1):188. doi: 10.1186/s13046-016-0465-1. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2016. PMID: 27919278 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Henderson BE. Nasopharyngeal carcinoma: present status of knowledge. Cancer Res. 1974;34(5):1187–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

