Syndecan-4 in intervertebral disc and cartilage: Saint or synner?
- PMID: 26796346
- PMCID: PMC4875798
- DOI: 10.1016/j.matbio.2016.01.005
Syndecan-4 in intervertebral disc and cartilage: Saint or synner?
Abstract
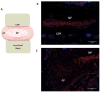
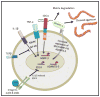
The ECM of the intervertebral disc and articular cartilage contains a highly organised network of collagens and proteoglycans which resist compressive forces applied to these tissues. A pathological hallmark of the intervertebral disc is the imbalance between production of anabolic and catabolic factors by the resident cells. This process is thought to be mediated by pro-inflammatory cytokines, predominantly TNF-α and IL-1β, which upregulate expression of matrix degrading enzymes such as MMPs and ADAMTSs. This imbalance ultimately results in tissue degeneration causing failure of the biomechanical function of the tissues. A similar cascade of events is thought to occur in articular cartilage during development of osteoarthritis. Within these skeletal tissues a small, cell surface heparan sulphate proteoglycan; syndecan-4 (SDC4) has been implicated in maintaining physiological functions. However in the degenerating niche of the intervertebral disc and cartilage, dysregulated activities of this molecule may exacerbate pathological changes. Studies in recent years have elucidated a role for SDC4 in mediating matrix degradation in both intervertebral discs and cartilage by controlling ADAMTS-5 function and MMP3 expression. Discourse presented in this review highlights the potential of SDC4 as a possible therapeutic target in slowing the progression of ECM degradation in both degenerative disc disease and osteoarthritis.
Keywords: Cartilage; Cytokines; Disc degeneration; Extracellular matrix; Intervertebral disc; Syndecan-4.
Copyright © 2015 International Society of Matrix Biology. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
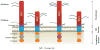
References
-
- Adams MA, Roughley PJ. What is intervertebral disc degeneration, and what causes it? Spine. 2006;31:2151–2161. - PubMed
-
- Hutton WC, Ganey TM, Elmer WA, Kozlowska E, Ugbo JL, Doh ES, Whitesides TE., Jr Does long-term compressive loading on the intervertebral disc cause degeneration? Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2000;25:2993–3004. - PubMed
-
- Mwale F, Roughley P, Antoniou J. Distinction between the extracellular matrix of the nucleus pulposus and hyaline cartilage: a requisite for tissue engineering of intervertebral disc. Eur Cell Mater. 2004;8:58–63. discussion 63–4. - PubMed
-
- Haefeli M, Kalberer F, Saegesser D, Nerlich A, Boos N, Paesold G. The course of macroscopic degeneration in the human lumbar intervertebral disc. Europ Cells Mater. 2005;10:25. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

