The Ankrd13 Family of Ubiquitin-interacting Motif-bearing Proteins Regulates Valosin-containing Protein/p97 Protein-mediated Lysosomal Trafficking of Caveolin 1
- PMID: 26797118
- PMCID: PMC4813590
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M115.710707
The Ankrd13 Family of Ubiquitin-interacting Motif-bearing Proteins Regulates Valosin-containing Protein/p97 Protein-mediated Lysosomal Trafficking of Caveolin 1
Abstract
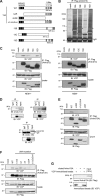
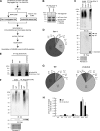
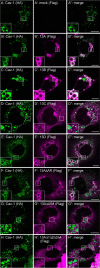
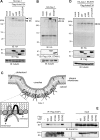
Caveolin 1 (Cav-1) is an oligomeric protein that forms flask-shaped, lipid-rich pits, termed caveolae, on the plasma membrane. Cav-1 is targeted for lysosomal degradation in ubiquitination- and valosin-containing protein (VCP)-dependent manners. VCP, an ATPase associated with diverse cellular activities that remodels or segregates ubiquitinated protein complexes, has been proposed to disassemble Cav-1 oligomers on the endosomal membrane, facilitating the trafficking of Cav-1 to the lysosome. Genetic mutations in VCP compromise the lysosomal trafficking of Cav-1, leading to a disease called inclusion body myopathy with Paget disease of bone and/or frontotemporal dementia (IBMPFD). Here we identified the Ankrd13 family of ubiquitin-interacting motif (UIM)-containing proteins as novel VCP-interacting molecules on the endosome. Ankrd13 proteins formed a ternary complex with VCP and Cav-1 and exhibited high binding affinity for ubiquitinated Cav-1 oligomers in an UIM-dependent manner. Mass spectrometric analyses revealed that Cav-1 undergoes Lys-63-linked polyubiquitination, which serves as a lysosomal trafficking signal, and that the UIMs of Ankrd13 proteins bind preferentially to this ubiquitin chain type. The overexpression of Ankrd13 caused enlarged hollow late endosomes, which was reminiscent of the phenotype of the VCP mutations in IBMPFD. Overexpression of Ankrd13 proteins also stabilized ubiquitinated Cav-1 oligomers on the limiting membrane of enlarged endosomes. The interaction with Ankrd13 was abrogated in IMBPFD-associated VCP mutants. Collectively, our results suggest that Ankrd13 proteins cooperate with VCP to regulate the lysosomal trafficking of ubiquitinated Cav-1.
Keywords: VCP/p97; caveolin; cell surface protein; endocytosis; endosome; membrane trafficking; protein degradation; ubiquitin; ubiquitin-interacting motif; ubiquitylation (ubiquitination).
© 2016 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Ubiquitination of the N-terminal region of caveolin-1 regulates endosomal sorting by the VCP/p97 AAA-ATPase.J Biol Chem. 2013 Mar 8;288(10):7363-72. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.429076. Epub 2013 Jan 19. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23335559 Free PMC article.
-
Endolysosomal sorting of ubiquitylated caveolin-1 is regulated by VCP and UBXD1 and impaired by VCP disease mutations.Nat Cell Biol. 2011 Aug 7;13(9):1116-23. doi: 10.1038/ncb2301. Nat Cell Biol. 2011. PMID: 21822278 Free PMC article.
-
Transgenic expression of inclusion body myopathy associated mutant p97/VCP causes weakness and ubiquitinated protein inclusions in mice.Hum Mol Genet. 2007 Apr 15;16(8):919-28. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddm037. Epub 2007 Feb 28. Hum Mol Genet. 2007. PMID: 17329348
-
Valosin-Containing Protein (VCP)/p97 Oligomerization.Subcell Biochem. 2024;104:485-501. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-58843-3_18. Subcell Biochem. 2024. PMID: 38963497 Review.
-
Inclusion body myopathy, Paget's disease of the bone and fronto-temporal dementia: a disorder of autophagy.Hum Mol Genet. 2010 Apr 15;19(R1):R38-45. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddq157. Epub 2010 Apr 21. Hum Mol Genet. 2010. PMID: 20410287 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
POH1 contributes to hyperactivation of TGF-β signaling and facilitates hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis through deubiquitinating TGF-β receptors and caveolin-1.EBioMedicine. 2019 Mar;41:320-332. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2019.01.058. Epub 2019 Feb 7. EBioMedicine. 2019. PMID: 30745168 Free PMC article.
-
Valosin containing protein (VCP): initiator, modifier, and potential drug target for neurodegenerative diseases.Mol Neurodegener. 2023 Aug 7;18(1):52. doi: 10.1186/s13024-023-00639-y. Mol Neurodegener. 2023. PMID: 37545006 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Caveolins and cavins in the trafficking, maturation, and degradation of caveolae: implications for cell physiology.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2017 Apr 1;312(4):C459-C477. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00355.2016. Epub 2017 Jan 25. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2017. PMID: 28122734 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A targeted multi-proteomics approach generates a blueprint of the ciliary ubiquitinome.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023 Jan 26;11:1113656. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2023.1113656. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023. PMID: 36776558 Free PMC article.
-
Ubiquitination of G3BP1 mediates stress granule disassembly in a context-specific manner.Science. 2021 Jun 25;372(6549):eabf6548. doi: 10.1126/science.abf6548. Epub 2021 Aug 5. Science. 2021. PMID: 34739333 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Parton R. G., and Simons K. (2007) The multiple faces of caveolae. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 8, 185–194 - PubMed
-
- Hayer A., Stoeber M., Bissig C., and Helenius A. (2010) Biogenesis of caveolae: stepwise assembly of large caveolin and cavin complexes. Traffic 11, 361–382 - PubMed
-
- Parton R. G., and del Pozo M. A. (2013) Caveolae as plasma membrane sensors, protectors and organizers. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 14, 98–112 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

