Controlling molecular transport in minimal emulsions
- PMID: 26797564
- PMCID: PMC4735829
- DOI: 10.1038/ncomms10392
Controlling molecular transport in minimal emulsions
Abstract
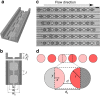
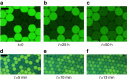
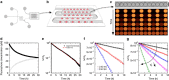
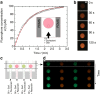
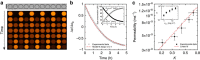
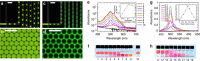
Emulsions are metastable dispersions in which molecular transport is a major mechanism driving the system towards its state of minimal energy. Determining the underlying mechanisms of molecular transport between droplets is challenging due to the complexity of a typical emulsion system. Here we introduce the concept of 'minimal emulsions', which are controlled emulsions produced using microfluidic tools, simplifying an emulsion down to its minimal set of relevant parameters. We use these minimal emulsions to unravel the fundamentals of transport of small organic molecules in water-in-fluorinated-oil emulsions, a system of great interest for biotechnological applications. Our results are of practical relevance to guarantee a sustainable compartmentalization of compounds in droplet microreactors and to design new strategies for the dynamic control of droplet compositions.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Degradation of kinetically-stable o/w emulsions.Adv Colloid Interface Sci. 2004 Mar 19;107(2-3):125-55. doi: 10.1016/S0001-8686(03)00115-5. Adv Colloid Interface Sci. 2004. PMID: 15026289
-
Recent progress in the synthesis of all-aqueous two-phase droplets using microfluidic approaches.Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2022 Nov;219:112795. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2022.112795. Epub 2022 Aug 27. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2022. PMID: 36049253 Review.
-
Microfluidic production of size-tunable hexadecane-in-water emulsions: Effect of droplet size on destabilization of two-dimensional emulsions due to partial coalescence.J Colloid Interface Sci. 2019 Jan 1;533:59-70. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2018.08.045. Epub 2018 Aug 17. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2019. PMID: 30145441
-
Application of Flow Cytometry As Novel Technology in Studying the Effect of Droplet Size on Lipid Oxidation in Oil-in-Water Emulsions.J Agric Food Chem. 2020 Jan 15;68(2):567-573. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.9b04956. Epub 2020 Jan 3. J Agric Food Chem. 2020. PMID: 31860290
-
[Droplets and emulsions: very high-throughput screening in biology].Med Sci (Paris). 2009 Jun-Jul;25(6-7):627-32. doi: 10.1051/medsci/2009256-7627. Med Sci (Paris). 2009. PMID: 19602361 Review. French.
Cited by
-
Surface-Mediated Molecular Transport of a Lipophilic Fluorescent Probe in Polydisperse Oil-in-Water Emulsions.Langmuir. 2023 Mar 28;39(12):4207-4215. doi: 10.1021/acs.langmuir.2c02597. Epub 2023 Mar 15. Langmuir. 2023. PMID: 36919825 Free PMC article.
-
Droplet Microfluidics for High-Throughput Analysis of Antibiotic Susceptibility in Bacterial Cells and Populations.Acc Chem Res. 2022 Mar 1;55(5):605-615. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.1c00729. Epub 2022 Feb 4. Acc Chem Res. 2022. PMID: 35119826 Free PMC article.
-
Monodisperse drops templated by 3D-structured microparticles.Sci Adv. 2020 Nov 4;6(45):eabb9023. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.abb9023. Print 2020 Nov. Sci Adv. 2020. PMID: 33148643 Free PMC article.
-
Indirect enrichment of desirable, but less fit phenotypes, from a synthetic microbial community using microdroplet confinement.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Jan 11:2023.01.11.523444. doi: 10.1101/2023.01.11.523444. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: ACS Synth Biol. 2023 Apr 21;12(4):1239-1251. doi: 10.1021/acssynbio.3c00008. PMID: 36711600 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
A microfluidic Braille valve platform for on-demand production, combinatorial screening and sorting of chemically distinct droplets.Nat Protoc. 2022 Dec;17(12):2920-2965. doi: 10.1038/s41596-022-00740-4. Epub 2022 Oct 19. Nat Protoc. 2022. PMID: 36261631 Review.
References
-
- Bibette J., Leal-Calderon F. & Poulin P. Emulsions: basic principles. Rep. Prog. Phys. 62, 696–1033 (1999) .
-
- McClements D. Nanoemulsions versus microemulsions: terminology, differences, and similarities. Soft Matter 8, 1719–1729 (2012) .
-
- Rosen M. J. Surfactants and Interfacial Phenomena, i-xiii John Wiley & Sons, Inc. (2004) .
-
- Tawfik D. S. & Griffiths A. D. Man-made cell-like compartments for molecular evolution. Nat. Biotechnol. 16, 652–656 (1998) . - PubMed
-
- Taly V., Kelly B. T. & Griffiths A. D. Droplets as microreactors for high-throughput biology. ChemBioChem 8, 263–272 (2007) . - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

