Application of Bioactive Quercetin in Oncotherapy: From Nutrition to Nanomedicine
- PMID: 26797598
- PMCID: PMC6273093
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules21010108
Application of Bioactive Quercetin in Oncotherapy: From Nutrition to Nanomedicine
Abstract
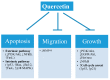
Phytochemicals as dietary constituents are being explored for their cancer preventive properties. Quercetin is a major constituent of various dietary products and recently its anti-cancer potential has been extensively explored, revealing its anti-proliferative effect on different cancer cell lines, both in vitro and in vivo. Quercetin is known to have modulatory effects on cell apoptosis, migration and growth via various signaling pathways. Though, quercetin possesses great medicinal value, its applications as a therapeutic drug are limited. Problems like low oral bioavailability and poor aqueous solubility make quercetin an unreliable candidate for therapeutic purposes. Additionally, the rapid gastrointestinal digestion of quercetin is also a major barrier for its clinical translation. Hence, to overcome these disadvantages quercetin-based nanoformulations are being considered in recent times. Nanoformulations of quercetin have shown promising results in its uptake by the epithelial system as well as enhanced delivery to the target site. Herein we have tried to summarize various methods utilized for nanofabrication of quercetin formulations and for stable and sustained delivery of quercetin. We have also highlighted the various desirable measures for its use as a promising onco-therapeutic agent.
Keywords: anticancer; bioavailability; nanoformulation; oncotherapy; phytochemical; quercetin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Nanoparticle-delivered quercetin for cancer therapy.Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2014;14(6):826-32. doi: 10.2174/1871520614666140521122932. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2014. PMID: 24851877 Review.
-
Quercetin nanoformulations: a promising strategy for tumor therapy.Food Funct. 2021 Aug 2;12(15):6664-6681. doi: 10.1039/d1fo00851j. Food Funct. 2021. PMID: 34152346 Review.
-
Quercetin in Oncology: A Phytochemical with Immense Therapeutic Potential.Curr Drug Targets. 2024;25(11):740-751. doi: 10.2174/0113894501292466240627050638. Curr Drug Targets. 2024. PMID: 38988154 Review.
-
Development and characterization of self-assembling lecithin-based mixed polymeric micelles containing quercetin in cancer treatment and an in vivo pharmacokinetic study.Int J Nanomedicine. 2016 Apr 15;11:1557-66. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S103681. eCollection 2016. Int J Nanomedicine. 2016. PMID: 27143878 Free PMC article.
-
Quercetin Loaded Nanoparticles in Targeting Cancer: Recent Development.Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2019;19(13):1560-1576. doi: 10.2174/1871520619666190705150214. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2019. PMID: 31284873 Review.
Cited by
-
Participation of MicroRNAs in the Treatment of Cancer with Phytochemicals.Molecules. 2020 Oct 14;25(20):4701. doi: 10.3390/molecules25204701. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 33066509 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Reversal of Multidrug Resistance in Cancer by Multi-Functional Flavonoids.Front Oncol. 2019 Jun 12;9:487. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2019.00487. eCollection 2019. Front Oncol. 2019. PMID: 31245292 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fanconi anaemia and cancer: an intricate relationship.Nat Rev Cancer. 2018 Mar;18(3):168-185. doi: 10.1038/nrc.2017.116. Epub 2018 Jan 29. Nat Rev Cancer. 2018. PMID: 29376519 Review.
-
The mechanisms of wine phenolic compounds for preclinical anticancer therapeutics.Food Nutr Res. 2021 Aug 23;65. doi: 10.29219/fnr.v65.6507. eCollection 2021. Food Nutr Res. 2021. PMID: 34512232 Free PMC article.
-
Up-regulation of microRNA let-7c by quercetin inhibits pancreatic cancer progression by activation of Numbl.Oncotarget. 2016 Sep 6;7(36):58367-58380. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.11122. Oncotarget. 2016. Retraction in: Oncotarget. 2025 Jun 25;16:531. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.28751. PMID: 27521217 Free PMC article. Retracted.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical