Comparative Study of Essential Oils Extracted from Egyptian Basil Leaves (Ocimum basilicum L.) Using Hydro-Distillation and Solvent-Free Microwave Extraction
- PMID: 26797599
- PMCID: PMC6273689
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules21010113
Comparative Study of Essential Oils Extracted from Egyptian Basil Leaves (Ocimum basilicum L.) Using Hydro-Distillation and Solvent-Free Microwave Extraction
Abstract
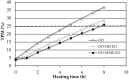
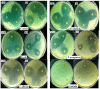
Solvent-free microwave extraction (SFME) and conventional hydro-distillation (HD) were used for the extraction of essential oils (EOs) from Egyptian sweet basil (Ocimum basilicum L.) leaves. The two resulting EOs were compared with regards to their chemical composition, antioxidant, and antimicrobial activities. The EO analyzed by GC and GC-MS, presented 65 compounds constituting 99.3% and 99.0% of the total oils obtained by SFME and HD, respectively. The main components of both oils were linalool (43.5% SFME; 48.4% HD), followed by methyl chavicol (13.3% SFME; 14.3% HD) and 1,8-cineole (6.8% SFME; 7.3% HD). Their antioxidant activity were studied with the 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH(•)) radical scavenging method. The heating conditions effect was evaluated by the determination of the Total Polar Materials (TPM) content. The antimicrobial activity was investigated against five microorganisms: two Gram-positive bacteria, Staphylococcus aureus and Bacillus subtilis, two Gram-negative bacteria, Escherichia coli and Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and one yeast, Candida albicans. Both EOs showed high antimicrobial, but weak antioxidant, activities. The results indicated that the SFME method may be a better alternative for the extraction of EO from O. basilicum since it could be considered as providing a richer source of natural antioxidants, as well as strong antimicrobial agents for food preservation.
Keywords: DDPH assay; GC/MS; antimicrobial activity; antioxidant activity; basil (Ocimum basilicum L.); chemical composition; essential oil; hydro-distillation; microwave.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Teles Andrade B.F.M., Barbosa L.N., da Silva Probst I., Fernandes Júnior A. Antimicrobial activity of essential oils. J. Essent. Oil Res. 2014;26:34–40. doi: 10.1080/10412905.2013.860409. - DOI
-
- Delille L. Les Plantes Médicinales D'Algérie. BERTI; Algiers, Algeria: 2007. pp. 47–48.
-
- Hanif M.A., Al-Maskari M.Y., Al-Maskari A., Al-Shukaili A., Al-Maskari A.Y., Al-Sabahi J.N. Essential oil composition antimicrobial and antioxidant activities of unexplored Omani basil. J. Med. Plants Res. 2011;5:751–757.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

