Prediabetes and Alzheimer's Disease
- PMID: 26798163
- PMCID: PMC4700701
- DOI: 10.4103/0250-474x.169026
Prediabetes and Alzheimer's Disease
Abstract
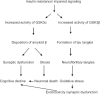
Aging patients with diabetes are at higher risk of developing Alzheimer's disease. Emerging evidences demonstrate the role of brain insulin resistance, which is a key mediator in prediabetes and diabetes mellitus that may lead to Alzheimer's disease. Insulin and insulin-like growth factors regulate many biological processes such as axonal growth, protein synthesis, cell growth, gene expression, proliferation, differentiation, and development. Among these, the energy metabolism and synaptic plasticity are the major transduction processes regulated by insulin, which are the core objectives for learning and memory. It was also proposed that hyper insulinemia induced insulin resistance results in injury to the central nervous system by the activation of glycogen synthase kinase 3β which is the key ailment in the cognitive decline. Hence, the endogenous brain specific insulin impairments and signaling account for the majority of Alzheimer's abnormalities.
Keywords: Aging; Alzheimer's disease; glycogen synthase kinase 3β; insulin resistance; prediabetes.
Figures

References
-
- Yesavage JA, O’Hara R, Kraemer H, Noda A, Taylor JL, Ferris S, et al. Modeling the prevalence and incidence of Alzheimer's disease and mild cognitive impairment. J Psychiatr Res. 2002;36:281–6. - PubMed
-
- Luchsinger JA. Type 2 diabetes, related conditions, in relation and dementia: An opportunity for prevention? J Alzheimers Dis. 2010;20:723–36. - PubMed
-
- Accardi G, Caruso C, Colonna-Romano G, Camarda C, Monastero R, Candore G. Can Alzheimer disease be a form of type 3 diabetes? Rejuvenation Res. 2012;15:217–21. - PubMed
-
- Biessels GJ, Staekenborg S, Brunner E, Brayne C, Scheltens P. Risk of dementia in diabetes mellitus: A systematic review. Lancet Neurol. 2006;5:64–74. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
