Obestatin Accelerates the Healing of Acetic Acid-Induced Colitis in Rats
- PMID: 26798415
- PMCID: PMC4698545
- DOI: 10.1155/2016/2834386
Obestatin Accelerates the Healing of Acetic Acid-Induced Colitis in Rats
Abstract
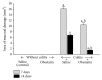
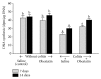
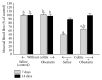
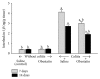
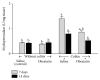
Obestatin, a 23-amino acid peptide derived from the proghrelin, has been shown to exhibit some protective and therapeutic effects in the gut. The aim of present study was to determine the effect of obestatin administration on the course of acetic acid-induced colitis in rats. Materials and Methods. Studies have been performed on male Wistar rats. Colitis was induced by a rectal enema with 3.5% acetic acid solution. Obestatin was administered intraperitoneally twice a day at a dose of 8 nmol/kg, starting 24 h after the induction of colitis. Seven or 14 days after the induction of colitis, the healing rate of the colon was evaluated. Results. Treatment with obestatin after induction of colitis accelerated the healing of colonic wall damage and this effect was associated with a decrease in the colitis-evoked increase in mucosal activity of myeloperoxidase and content of interleukin-1β. Moreover, obestatin administration significantly reversed the colitis-evoked decrease in mucosal blood flow and DNA synthesis. Conclusion. Administration of exogenous obestatin exhibits therapeutic effects in the course of acetic acid-induced colitis and this effect is related, at least in part, to the obestatin-evoked anti-inflammatory effect, an improvement of local blood flow, and an increase in cell proliferation in colonic mucosa.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The influence of pretreatment with ghrelin on the development of acetic-acid-induced colitis in rats.J Physiol Pharmacol. 2015 Dec;66(6):875-85. J Physiol Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 26769837
-
Essential Role of Growth Hormone and IGF-1 in Therapeutic Effect of Ghrelin in the Course of Acetic Acid-Induced Colitis.Int J Mol Sci. 2017 May 24;18(6):1118. doi: 10.3390/ijms18061118. Int J Mol Sci. 2017. PMID: 28538694 Free PMC article.
-
Treatment with Obestatin-A Ghrelin Gene-Encoded Peptide-Reduces the Severity of Experimental Colitis Evoked by Trinitrobenzene Sulfonic Acid.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Jun 1;19(6):1643. doi: 10.3390/ijms19061643. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29865176 Free PMC article.
-
Exogenous Ghrelin Accelerates the Healing of Acetic Acid-Induced Colitis in Rats.Int J Mol Sci. 2016 Sep 1;17(9):1455. doi: 10.3390/ijms17091455. Int J Mol Sci. 2016. PMID: 27598133 Free PMC article.
-
Function of obestatin in the digestive system.Nutrition. 2017 Feb;34:21-28. doi: 10.1016/j.nut.2016.08.009. Epub 2016 Sep 7. Nutrition. 2017. PMID: 28063509 Review.
Cited by
-
The Digestive Health among Participants of the Woodstock Rock Festival in Poland-A Cross-Sectional Survey.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2018 Oct 15;15(10):2256. doi: 10.3390/ijerph15102256. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2018. PMID: 30326654 Free PMC article.
-
Administration of Warfarin Inhibits the Development of Cerulein-Induced Edematous Acute Pancreatitis in Rats.Biomolecules. 2023 Jun 6;13(6):948. doi: 10.3390/biom13060948. Biomolecules. 2023. PMID: 37371528 Free PMC article.
-
Protective effect of bergapten in acetic acid-induced colitis in rats.Heliyon. 2020 Aug 15;6(8):e04710. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e04710. eCollection 2020 Aug. Heliyon. 2020. PMID: 32885074 Free PMC article.
-
Diverse and Complementary Effects of Ghrelin and Obestatin.Biomolecules. 2022 Mar 29;12(4):517. doi: 10.3390/biom12040517. Biomolecules. 2022. PMID: 35454106 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Colonic inflammation induces changes in glucose levels through modulation of incretin system.Pharmacol Rep. 2021 Dec;73(6):1670-1679. doi: 10.1007/s43440-021-00327-y. Epub 2021 Sep 17. Pharmacol Rep. 2021. PMID: 34535873 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ceranowicz P., Warzecha Z., Dembinski A. Peptidyl hormones of endocrine cells origin in the gut—their discovery and physiological relevance. Journal of Physiology and Pharmacology. 2015;66(1):11–27. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

