Oligonol Ameliorates CCl₄-Induced Liver Injury in Rats via the NF-Kappa B and MAPK Signaling Pathways
- PMID: 26798422
- PMCID: PMC4699077
- DOI: 10.1155/2016/3935841
Oligonol Ameliorates CCl₄-Induced Liver Injury in Rats via the NF-Kappa B and MAPK Signaling Pathways
Abstract
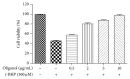
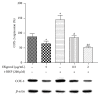
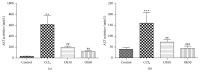
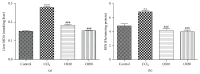
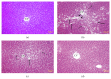
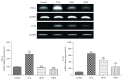
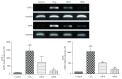
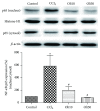
Oxidative stress is thought to be a key risk factor in the development of hepatic diseases. Blocking or retarding the reactions of oxidation and the inflammatory process by antioxidants could be a promising therapeutic intervention for prevention or treatment of liver injuries. Oligonol is a low molecular weight polyphenol containing catechin-type monomers and oligomers derived from lychee fruit. In this study, we investigated the anti-inflammatory effect of oligonol on carbon tetrachloride- (CCl4-) induced acute hepatic injury in rats. Oral administration of oligonol (10 or 50 mg/kg) reduced CCl4-induced abnormalities in liver histology and serum AST and serum ALT levels. Oligonol treatment attenuated the CCl4-induced production of inflammatory mediators, including TNF-α, IL-1β, cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2), and inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) mRNA levels. Western blot analysis showed that oligonol suppressed proinflammatory nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB) p65 activation, phosphorylation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK), c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase (JNK), and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs) as well as Akt. Oligonol exhibited strong antioxidative activity in vitro and in vivo, and hepatoprotective activity against t-butyl hydroperoxide-induced HepG2 cells. Taken together, oligonol showed antioxidative and anti-inflammatory effects in CCl4-intoxicated rats by inhibiting oxidative stress and NF-κB activation via blockade of the activation of upstream kinases including MAPKs and Akt.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Hepatoprotective effects of zingerone on carbon tetrachloride- and dimethylnitrosamine-induced liver injuries in rats.Arch Pharm Res. 2016 Feb;39(2):279-291. doi: 10.1007/s12272-015-0696-2. Epub 2015 Dec 14. Arch Pharm Res. 2016. PMID: 26667466
-
Oligonol, a low-molecular-weight polyphenol derived from lychee peel, attenuates diabetes-induced pancreatic damage by inhibiting inflammatory responses via oxidative stress-dependent mitogen-activated protein kinase/nuclear factor-kappa B signaling.Phytother Res. 2018 Dec;32(12):2541-2550. doi: 10.1002/ptr.6194. Epub 2018 Oct 2. Phytother Res. 2018. PMID: 30280446
-
Oligonol inhibits dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis and colonic adenoma formation in mice.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2013 Jul 10;19(2):102-14. doi: 10.1089/ars.2012.4626. Epub 2013 May 15. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2013. PMID: 23394584 Free PMC article.
-
Low molecular proanthocyanidin dietary biofactor Oligonol: Its modulation of oxidative stress, bioefficacy, neuroprotection, food application and chemoprevention potentials.Biofactors. 2006;27(1-4):245-65. doi: 10.1002/biof.5520270121. Biofactors. 2006. PMID: 17012779 Review.
-
Organophosphorus Compounds and MAPK Signaling Pathways.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jun 15;21(12):4258. doi: 10.3390/ijms21124258. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32549389 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Role of Dietary Polyphenols in the Activity and Expression of Nitric Oxide Synthases: A Review.Antioxidants (Basel). 2023 Jan 7;12(1):147. doi: 10.3390/antiox12010147. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36671009 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of procyanidins on lipid metabolism and inflammation in rats exposed to alcohol and iron.Heliyon. 2020 Sep 7;6(9):e04847. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e04847. eCollection 2020 Sep. Heliyon. 2020. PMID: 32964156 Free PMC article.
-
Kaempferol Suppresses Carbon Tetrachloride-Induced Liver Damage in Rats via the MAPKs/NF-κB and AMPK/Nrf2 Signaling Pathways.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Apr 7;24(8):6900. doi: 10.3390/ijms24086900. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37108064 Free PMC article.
-
Matrix Remodeling Associated 7 Deficiency Alleviates Carbon Tetrachloride-Induced Acute Liver Injury in Mice.Front Immunol. 2018 Apr 18;9:773. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.00773. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29720975 Free PMC article.
-
Litchi chinensis as a Functional Food and a Source of Antitumor Compounds: An Overview and a Description of Biochemical Pathways.Nutrients. 2017 Sep 8;9(9):992. doi: 10.3390/nu9090992. Nutrients. 2017. PMID: 28885570 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Muriel P. Peroxidation of lipids and liver damage: in Baskin. In: Baskin S. I., Salem H., editors. Antioxidants, Oxidants, and Free Radicals. Washington, DC, USA. Taylor and Francis: 1997. pp. 237–257.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

