Efficacy and Safety of Topical Timolol Eye Drops in the Treatment of Myopic Regression after Laser In Situ Keratomileusis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 26798507
- PMCID: PMC4698735
- DOI: 10.1155/2015/985071
Efficacy and Safety of Topical Timolol Eye Drops in the Treatment of Myopic Regression after Laser In Situ Keratomileusis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
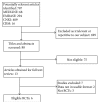
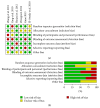
Aims. The aim of this study was to assess the efficacy and safety of timolol in the treatment of myopic regression after laser in situ keratomileusis (LASIK). Methods. We searched MEDLINE, CENTRAL, EMBASE, China National Knowledge Infrastructure (CNKI), and Chinese Biological Medicine (CBM) from the inception to July 2015 for relevant randomized controlled trials that examined timolol therapy for myopic regression. The methodological quality of the studies included was assessed using the Revman 5.3 software. Results. We included six clinical trials involving 483 eyes in this review, including 246 eyes in treated group and 237 eyes in controlled group. We observed statistically significant improvements on the postoperative SE in the 3 months. However, the change of CCT was not statistically different between the control group and the experimental group. There were fewer cases of IOP, UDVA, and CDVA in treated group having significant difference from the controlled group. Conclusions. Topical timolol could be an effective treatment for reduction of myopic regression especially the spherical errors after myopic LASIK. Further RCTs with larger sample sizes for these trials are warranted to determine the efficacy and limitation for myopic regression after LASIK.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Evaluation of the role of timolol 0.1% gel in myopic regression after laser in situ keratomileusis.Saudi J Ophthalmol. 2010 Jul;24(3):81-6. doi: 10.1016/j.sjopt.2010.03.001. Epub 2010 Mar 30. Saudi J Ophthalmol. 2010. PMID: 23960881 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of timolol on refractive outcomes in eyes with myopic regression after laser in situ keratomileusis: a prospective randomized clinical trial.Am J Ophthalmol. 2012 Nov;154(5):790-798.e1. doi: 10.1016/j.ajo.2012.05.013. Epub 2012 Aug 28. Am J Ophthalmol. 2012. PMID: 22935601 Clinical Trial.
-
[Preliminary study on preventive effects of timolol on myopic regression after laser in situ keratomileusis].Zhonghua Yan Ke Za Zhi. 2011 Jul;47(7):596-600. Zhonghua Yan Ke Za Zhi. 2011. PMID: 22041483 Clinical Trial. Chinese.
-
Three-year results of small incision lenticule extraction and wavefront-guided femtosecond laser-assisted laser in situ keratomileusis for correction of high myopia and myopic astigmatism.Int J Ophthalmol. 2018 Mar 18;11(3):470-477. doi: 10.18240/ijo.2018.03.18. eCollection 2018. Int J Ophthalmol. 2018. PMID: 29600182 Free PMC article.
-
Outcomes of presbyopia-correcting intraocular lenses after laser in situ keratomileusis.Int Ophthalmol. 2019 May;39(5):1199-1204. doi: 10.1007/s10792-018-0908-0. Epub 2018 Mar 28. Int Ophthalmol. 2019. PMID: 29594789 Review.
Cited by
-
Reduction of corneal epithelial thickness during medical treatment for myopic regression following FS-LASIK.BMC Ophthalmol. 2020 Jul 18;20(1):296. doi: 10.1186/s12886-020-01570-2. BMC Ophthalmol. 2020. PMID: 32682402 Free PMC article.
-
Reversal of severe myopia by 24 years of hypotony with subsequent stable refraction after 2 years of normal intraocular pressure.Am J Ophthalmol Case Rep. 2023 Dec 26;33:101989. doi: 10.1016/j.ajoc.2023.101989. eCollection 2024 Mar. Am J Ophthalmol Case Rep. 2023. PMID: 38292884 Free PMC article.
-
Brimonidine tartrate 0.15% drops to reduce low post-LASIK residual myopia: A retrospective study.PLoS One. 2025 Jul 30;20(7):e0329364. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0329364. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40737267 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of timolol maleate (0.5%) in the management of myopic regression post laser-assisted in-situ keratomileusis: Clinical and topographical outcomes.Indian J Ophthalmol. 2020 Dec;68(12):2990-2994. doi: 10.4103/ijo.IJO_1503_20. Indian J Ophthalmol. 2020. PMID: 33229683 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zhao J.-R., Zhang J.-Y., Li X.-F., Yu J. Laser in situ keratomileusis for residual myopia after photorefractive keratectomy. Chinese Ophthalmic Research. 2010;28(9):897–899.
-
- Chen Y. I., Chien K. L., Wang I. J., et al. An interval-censoredmodel for predicting myopic regression after laser in situkeratomileusis. Investigative Ophthalmology & Visual Science. 2007;48(8):3516–3523. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

