Modulation of Aromatase by Phytoestrogens
- PMID: 26798508
- PMCID: PMC4699002
- DOI: 10.1155/2015/594656
Modulation of Aromatase by Phytoestrogens
Abstract
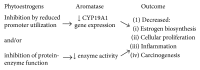
The aromatase enzyme catalyzes the conversion of androgens to estrogens in many human tissues. Estrogens are known to stimulate cellular proliferation associated with certain cancers and protect against adverse symptoms during the peri- and postmenopausal intervals. Phytoestrogens are a group of plant derived naturally occurring compounds that have chemical structures similar to estrogen. Since phytoestrogens are known to be constituents of animal/human food sources, these compounds have received increased research attention. Phytoestrogens may contribute to decreased cancer risk by the inhibition of aromatase enzyme activity and CYP19 gene expression in human tissues. This review covers (a) the aromatase enzyme (historical descriptions on function, activity, and gene characteristics), (b) phytoestrogens in their classifications and applications to human health, and (c) a chronological coverage of aromatase activity modulated by phytoestrogens from the early 1980s to 2015. In general, phytoestrogens act as aromatase inhibitors by (a) decreasing aromatase gene expression, (b) inhibiting the aromatase enzyme itself, or (c) in some cases acting at both levels of regulation. The findings presented herein are consistent with estrogen's impact on health and phytoestrogen's potential as anticancer treatments, but well-controlled, large-scale studies are warranted to determine the effectiveness of phytoestrogens on breast cancer and age-related diseases.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Interference of endocrine disrupting chemicals with aromatase CYP19 expression or activity, and consequences for reproduction of teleost fish.Gen Comp Endocrinol. 2008 Jan 1;155(1):31-62. doi: 10.1016/j.ygcen.2007.03.005. Epub 2007 Mar 21. Gen Comp Endocrinol. 2008. PMID: 17459383 Review.
-
Phytoestrogens decrease brain calcium-binding proteins but do not alter hypothalamic androgen metabolizing enzymes in adult male rats.Brain Res. 2000 Mar 17;859(1):123-31. doi: 10.1016/s0006-8993(00)01968-5. Brain Res. 2000. PMID: 10720621
-
Aromatase and breast cancer.Front Biosci. 1998 Aug 6;3:d922-33. doi: 10.2741/a333. Front Biosci. 1998. PMID: 9696881 Review.
-
Effects of phytoestrogens on aromatase, 3beta and 17beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase activities and human breast cancer cells.Life Sci. 2000 Feb 25;66(14):1281-91. doi: 10.1016/s0024-3205(00)00435-5. Life Sci. 2000. PMID: 10755463
-
Inhibition of human aromatase by mammalian lignans and isoflavonoid phytoestrogens.J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 1993 Feb;44(2):147-53. doi: 10.1016/0960-0760(93)90022-o. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 1993. PMID: 8382517
Cited by
-
Polyphenols in Farm Animals: Source of Reproductive Gain or Waste?Antioxidants (Basel). 2020 Oct 21;9(10):1023. doi: 10.3390/antiox9101023. Antioxidants (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33096704 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Modulation of estrogen synthesis and metabolism by phytoestrogens in vitro and the implications for women's health.Toxicol Res (Camb). 2017 Sep 8;6(6):772-794. doi: 10.1039/c7tx00184c. eCollection 2017 Nov 1. Toxicol Res (Camb). 2017. PMID: 30090542 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multiple Skeletal Anomalies of Sprague Dawley Rats following Prenatal Exposure to Anastatica hierochuntica, as Delineated by a Modified Double-Staining Method.Children (Basel). 2022 May 23;9(5):763. doi: 10.3390/children9050763. Children (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35626940 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative Analysis of the Effects of 17-Beta Estradiol on Proliferation, and Apoptosis in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Hep G2 and LCL-PI 11 Cell Lines.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2018 Sep 26;19(9):2637-2641. doi: 10.22034/APJCP.2018.19.9.2637. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2018. PMID: 30256559 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of Action of Phytoestrogens and Their Role in Familial Adenomatous Polyposis.Pharmaceutics. 2024 May 10;16(5):640. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16050640. Pharmaceutics. 2024. PMID: 38794302 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

