Relationship Between Respiratory Muscle Strength and Conventional Sarcopenic Indices in Young Adults: A Preliminary Study
- PMID: 26798601
- PMCID: PMC4720763
- DOI: 10.5535/arm.2015.39.6.880
Relationship Between Respiratory Muscle Strength and Conventional Sarcopenic Indices in Young Adults: A Preliminary Study
Abstract
Objective: To investigate the relationships between respiratory muscle strength and conventional sarcopenic indices such as skeletal muscle mass and limb muscle strength.
Methods: Eighty-nine young adult volunteers who had no history of medical or musculoskeletal disease were enrolled. Skeletal muscle mass was measured by bioelectrical impedance analysis and expressed as a skeletal muscle mass index (SMI). Upper and lower limb muscle strength were evaluated by hand grip strength (HGS) and isometric knee extensor muscle strength, respectively. Peak expiratory flow (PEF), maximal inspiratory pressure (MIP), and maximal expiratory pressure (MEP) were evaluated using a spirometer to demonstrate respiratory muscle strength. The relationships between respiratory muscle strength and sarcopenic indices were investigated using Pearson correlation coefficients and multiple linear regression analysis adjusted by age, height, and body mass index.
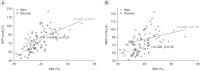
Results: MIP showed positive correlations with SMI (r=0.457 in men, r=0.646 in women; both p<0.01). MIP also correlated with knee extensor strength (p<0.01 in both sexes) and HGS (p<0.05 in men, p<0.01 in women). However, PEF and MEP had no significant correlations with these sarcopenic variables. In multivariate regression analysis, MIP was the only independent factor related to SMI (p<0.01).
Conclusion: Among the respiratory muscle strength variables, MIP was the only value associated with skeletal muscle mass.
Keywords: Muscle strength; Respiratory muscles; Sarcopenia; Skeletal muscle; Spirometry.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Association of Diaphragm Thickness and Respiratory Muscle Strength With Indices of Sarcopenia.Ann Rehabil Med. 2023 Aug;47(4):307-314. doi: 10.5535/arm.23081. Epub 2023 Aug 28. Ann Rehabil Med. 2023. PMID: 37644714 Free PMC article.
-
Relation Between Respiratory Muscle Strength and Skeletal Muscle Mass and Hand Grip Strength in the Healthy Elderly.Ann Rehabil Med. 2017 Aug;41(4):686-692. doi: 10.5535/arm.2017.41.4.686. Epub 2017 Aug 31. Ann Rehabil Med. 2017. PMID: 28971054 Free PMC article.
-
Relation between hand grip strength, respiratory muscle strength and spirometric measures in male nursing home residents.Aging Male. 2014 Sep;17(3):136-40. doi: 10.3109/13685538.2014.936001. Epub 2014 Jul 4. Aging Male. 2014. PMID: 24993454
-
Correlation between grip strength and pulmonary function and respiratory muscle strength in stroke patients over 50 years of age.J Exerc Rehabil. 2018 Dec 27;14(6):1017-1023. doi: 10.12965/jer.1836444.222. eCollection 2018 Dec. J Exerc Rehabil. 2018. PMID: 30656164 Free PMC article.
-
Maximal Static Respiratory and Sniff Pressures in Healthy Children. A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2019 Apr;16(4):478-487. doi: 10.1513/AnnalsATS.201808-506OC. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2019. PMID: 30562038
Cited by
-
Prediction of lung function using handgrip strength in healthy young adults.Physiol Rep. 2019 Jan;7(1):e13960. doi: 10.14814/phy2.13960. Physiol Rep. 2019. PMID: 30632320 Free PMC article.
-
Novel lateral whole-body dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry of lumbar paraspinal muscle mass: results from the SarcoSpine study.J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2021 Aug;12(4):913-920. doi: 10.1002/jcsm.12721. Epub 2021 May 28. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2021. PMID: 34047494 Free PMC article.
-
Respiratory sarcopenia: A position paper by four professional organizations.Geriatr Gerontol Int. 2023 Jan;23(1):5-15. doi: 10.1111/ggi.14519. Epub 2022 Dec 7. Geriatr Gerontol Int. 2023. PMID: 36479799 Free PMC article.
-
Association of Diaphragm Thickness and Respiratory Muscle Strength With Indices of Sarcopenia.Ann Rehabil Med. 2023 Aug;47(4):307-314. doi: 10.5535/arm.23081. Epub 2023 Aug 28. Ann Rehabil Med. 2023. PMID: 37644714 Free PMC article.
-
Relationships between Spinal Sarcopenia and Spinal Sagittal Balance in Older Women.Ann Geriatr Med Res. 2019 Sep;23(3):141-148. doi: 10.4235/agmr.19.0030. Epub 2019 Sep 25. Ann Geriatr Med Res. 2019. PMID: 32743302 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

