Simeprevir plus sofosbuvir (12 and 8 weeks) in hepatitis C virus genotype 1-infected patients without cirrhosis: OPTIMIST-1, a phase 3, randomized study
- PMID: 26799692
- PMCID: PMC5412860
- DOI: 10.1002/hep.28467
Simeprevir plus sofosbuvir (12 and 8 weeks) in hepatitis C virus genotype 1-infected patients without cirrhosis: OPTIMIST-1, a phase 3, randomized study
Abstract
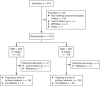
Effective antiviral therapy is essential for achieving sustained virological response (SVR) in hepatitis C virus (HCV)-infected patients. The phase 2 COSMOS study reported high SVR rates in treatment-naive and prior null-responder HCV genotype (GT) 1-infected patients receiving simeprevir+sofosbuvir±ribavirin for 12 or 24 weeks. OPTIMIST-1 (NCT02114177) was a multicenter, randomized, open-label study assessing the efficacy and safety of 12 and 8 weeks of simeprevir+sofosbuvir in HCV GT1-infected treatment-naive and treatment-experienced patients without cirrhosis. Patients were randomly assigned (1:1; stratified by HCV GT/subtype and presence or absence of NS3 Q80K polymorphism [GT1b, GT1a with Q80K, GT1a without Q80K]), prior HCV treatment history, and IL28B GT [CC, non-CC]) to simeprevir 150 mg once daily+sofosbuvir 400 mg once daily for 12 or 8 weeks. The primary efficacy endpoint was SVR rate 12 weeks after end of treatment (SVR12). Superiority in SVR12 was assessed for simeprevir+sofosbuvir at 12 and 8 weeks versus a composite historical control SVR rate. Enrolled were 310 patients, who were randomized and received treatment (n = 155 in each arm). SVR12 with simeprevir+sofosbuvir for 12 weeks (97% [150/155; 95% confidence interval 94%-100%]) was superior to the historical control (87%). SVR12 with simeprevir+sofosbuvir for 8 weeks (83% [128/155; 95% confidence interval 76-89%]) was not superior to the historical control (83%). The most frequent adverse events were nausea, headache, and fatigue (12-week arm: 15% [23/155], 14% [22/155], and 12% [19/155]; 8-week arm: 9% [14/155], 17% [26/155], and 15% [23/155], respectively). No patients discontinued treatment due to an adverse event. One (1%, 12-week arm) and three (2%, 8-week arm) patients experienced a serious adverse event (all unrelated to study treatment).
Conclusion: Simeprevir+sofosbuvir for 12 weeks is highly effective in the treatment of HCV GT1-infected patients without cirrhosis, including those with Q80K. (Hepatology 2016;64:370-380).
© 2016 by the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases.
Figures

Comment in
-
Baseline HCV-RNA levels in genotype 1 chronic hepatitis C patients: The role of different cut-off points.Hepatology. 2016 Oct;64(4):1385-6. doi: 10.1002/hep.28544. Epub 2016 Apr 26. Hepatology. 2016. PMID: 26970320 No abstract available.
-
Hepatitis C Treatment in 2016: Reasons to Be an OPTIMIST.Hepatology. 2016 Aug;64(2):330-2. doi: 10.1002/hep.28559. Epub 2016 Apr 18. Hepatology. 2016. PMID: 26992027 No abstract available.
References
-
- Asselah T, Marcellin P. Second‐wave IFN‐based triple therapy for HCV genotype 1 infection: simeprevir, faldaprevir and sofosbuvir. Liver Int 2014;34(Suppl. 1):60‐68. - PubMed
-
- American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases . HCV guidance: recommendations for testing, managing, and treating hepatitis C. www.hcvguidelines.org/full‐report‐view. Accessed May 5, 2015.
-
- European Association for the Study of the Liver . EASL recommendations on treatment of hepatitis C 2015. http://www.easl.eu/research/our‐contributions/clinical‐practice‐guidelin.... Accessed May 5, 2015. - PubMed
-
- Lawitz E, Mangia A, Wyles D, Rodriguez‐Torres M, Hassanein T, Gordon SC, et al. Sofosbuvir for previously untreated chronic hepatitis C infection. N Engl J Med 2013;368:1878‐1887. - PubMed
-
- Lawitz E, Poordad FF, Pang PS, Hyland RH, Ding X, Mo H, et al. Sofosbuvir and ledipasvir fixed‐dose combination with and without ribavirin in treatment‐naive and previously treated patients with genotype 1 hepatitis C virus infection (LONESTAR): an open‐label, randomised, phase 2 trial. Lancet 2014;383:515‐523. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

