Comparison of the Belgian Rheumatoid Arthritis Disability Assessment and Health Assessment Questionnaires as Tools to Predict the Need for Support Measures in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis
- PMID: 26800345
- PMCID: PMC4723361
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0146688
Comparison of the Belgian Rheumatoid Arthritis Disability Assessment and Health Assessment Questionnaires as Tools to Predict the Need for Support Measures in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis
Abstract
Objective: Scores on the Health Assessment Questionnaire (HAQ) predict the need for support measures in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA). In this study we compare the performance of the HAQ in this context with that of the more disease-specific Belgian Rheumatoid Arthritis Disability Assessment (BRADA) questionnaire.
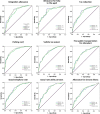
Methods: In this multicenter observational study, patients with RA and disease duration of at least one year who consulted their rheumatologist for a routine follow-up visit filled out the HAQ, and BRADA questionnaires. The performance of HAQ and BRADA to predict the need for support measures available to patients with RA was evaluated using Receiver Operator Characteristic (ROC) curves, with the expert opinion of the rheumatologist as a reference.
Results: The study analyzed data of 301 patients with RA (70.8% females) with mean age 59.8 ± 12.8, disease duration 11.4 ± 9.3 years, and DAS28 values of 2.84 ± 1.18. HAQ scores averaged 0.97 ± 0.73 and BRADA scores were 3.92 ± 3.49 over the last week and 3.89 ± 3.50 over the last 3 months. The area under the ROC curves for the BRADA scores for the support measures investigated ranged from 0.702 to 0.862 and did not differ significantly from those of the HAQ (range 0.725-0.860).
Conclusion: The disease-specific BRADA questionnaire is equivalent to the HAQ in predicting the need for support measures in patients with stable RA.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Assessment of activity limitations with the health assessment questionnaire predicts the need for support measures in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a multicenter observational study.PLoS One. 2014 Sep 4;9(9):e106749. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0106749. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25188388 Free PMC article.
-
Construction and psychometric properties of the Belgian Rheumatoid Arthritis Disability Assessment (BRADA) questionnaire: a new tool for the evaluation of activity limitations in patients with rheumatoid arthritis.Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2013 Jul-Aug;31(4):596-605. Epub 2013 Jul 30. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2013. PMID: 23899969 Clinical Trial.
-
Comparison of the Recent-Onset Arthritis Disability questionnaire with the Health Assessment Questionnaire disability index in patients with rheumatoid arthritis.Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2010 Nov-Dec;28(6):855-65. Epub 2011 Jan 3. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2010. PMID: 21122262
-
The consequences of rheumatoid arthritis: quality of life measures in the individual patient.Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2005 Sep-Oct;23(5 Suppl 39):S43-52. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2005. PMID: 16273784 Review.
-
Measures of functional status and quality of life in rheumatoid arthritis: Health Assessment Questionnaire Disability Index (HAQ), Modified Health Assessment Questionnaire (MHAQ), Multidimensional Health Assessment Questionnaire (MDHAQ), Health Assessment Questionnaire II (HAQ-II), Improved Health Assessment Questionnaire (Improved HAQ), and Rheumatoid Arthritis Quality of Life (RAQoL).Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2011 Nov;63 Suppl 11:S4-13. doi: 10.1002/acr.20620. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2011. PMID: 22588760 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
LncRNA: An All-rounder in Rheumatoid Arthritis.J Transl Int Med. 2019 Mar 29;7(1):3-9. doi: 10.2478/jtim-2019-0002. eCollection 2019 Mar. J Transl Int Med. 2019. PMID: 30997350 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Uhlig T, Loge JH, Kristiansen IS, Kvien TK (2007) Quantification of reduced health-related quality of life in patients with rheumatoid arthritis compared to the general population. J Rheumatol 34: 1241–1247. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

