Amyloid Plaque-Associated Oxidative Degradation of Uniformly Radiolabeled Arachidonic Acid
- PMID: 26800372
- PMCID: PMC5654537
- DOI: 10.1021/acschemneuro.5b00316
Amyloid Plaque-Associated Oxidative Degradation of Uniformly Radiolabeled Arachidonic Acid
Abstract
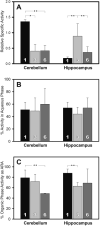
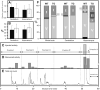
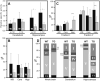
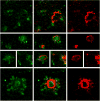
Oxidative stress is a frequently observed feature of Alzheimer's disease, but its pathological significance is not understood. To explore the relationship between oxidative stress and amyloid plaques, uniformly radiolabeled arachidonate was introduced into transgenic mouse models of Alzheimer's disease via intracerebroventricular injection. Uniform labeling with carbon-14 is used here for the first time, and made possible meaningful quantification of arachidonate oxidative degradation products. The injected arachidonate entered a fatty acid pool that was subject to oxidative degradation in both transgenic and wild-type animals. However, the extent of its degradation was markedly greater in the hippocampus of transgenic animals where amyloid plaques were abundant. In human Alzheimer's brain, plaque-associated proteins were post-translationally modified by hydroxynonenal, a well-known oxidative degradation product of arachidonate. These results suggest that several recurring themes in Alzheimer's pathogenesis, amyloid β proteins, transition metal ions, oxidative stress, and apolipoprotein isoforms, may be involved in a common mechanism that has the potential to explain both neuronal loss and fibril formation in this disease.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; Oxidative stress; polyunsaturated fatty acids.
Figures

Similar articles
-
First effects of rising amyloid-β in transgenic mouse brain: synaptic transmission and gene expression.Brain. 2015 Jul;138(Pt 7):1992-2004. doi: 10.1093/brain/awv127. Epub 2015 May 16. Brain. 2015. PMID: 25981962 Free PMC article.
-
Phenylbutyric acid reduces amyloid plaques and rescues cognitive behavior in AD transgenic mice.Aging Cell. 2011 Jun;10(3):418-28. doi: 10.1111/j.1474-9726.2011.00680.x. Epub 2011 Mar 22. Aging Cell. 2011. PMID: 21272191
-
Probing amyloid-β pathology in transgenic Alzheimer's disease (tgArcSwe) mice using MALDI imaging mass spectrometry.J Neurochem. 2016 Aug;138(3):469-78. doi: 10.1111/jnc.13645. Epub 2016 May 26. J Neurochem. 2016. PMID: 27115712
-
Alzheimer's disease and amyloid: culprit or coincidence?Int Rev Neurobiol. 2012;102:277-316. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-386986-9.00011-9. Int Rev Neurobiol. 2012. PMID: 22748834 Review.
-
Phospholipase A2 and arachidonic acid in Alzheimer's disease.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2010 Aug;1801(8):784-90. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2010.05.013. Epub 2010 May 27. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2010. PMID: 20553961 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Biosynthesis of uniformly carbon isotope-labeled docosahexaenoic acid in Crypthecodinium cohnii.AMB Express. 2020 Mar 11;10(1):45. doi: 10.1186/s13568-020-00981-0. AMB Express. 2020. PMID: 32162160 Free PMC article.
-
Cortical thickness is differently associated with ALDH2 rs671 polymorphism according to level of amyloid deposition.Sci Rep. 2021 Sep 30;11(1):19529. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-98834-8. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34593890 Free PMC article.
-
Intraneuronal Amylin Deposition, Peroxidative Membrane Injury and Increased IL-1β Synthesis in Brains of Alzheimer's Disease Patients with Type-2 Diabetes and in Diabetic HIP Rats.J Alzheimers Dis. 2016 May 5;53(1):259-72. doi: 10.3233/JAD-160047. J Alzheimers Dis. 2016. PMID: 27163815 Free PMC article.
-
A new synthetic medium for the optimization of docosahexaenoic acid production in Crypthecodinium cohnii.PLoS One. 2020 Mar 20;15(3):e0229556. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0229556. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32196504 Free PMC article.
-
Editorial: Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Neurodegeneration.Front Neurosci. 2019 Dec 18;13:1372. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2019.01372. eCollection 2019. Front Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 31920522 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Axelsen PH, Komatsu H, Murray IVJ. Oxidative Stress and Cell Membranes in the Pathogenesis of Alzheimer's Disease. Physiology. 2011;26:54–69. - PubMed
-
- Pratico D, Delanty N. Oxidative Injury in Diseases of the Central Nervous System: Focus on Alzheimer's Disease. Am J Med. 2000;109:577–585. - PubMed
-
- Butterfield DA, Lauderback CM. Lipid Peroxidation and Protein Oxidation in Alzheimer's Disease Brain:Potential Causes and Consequences Involving Amyloid Beta-Peptide-Associated Free Radical Oxidative Stress. Free Radical Biol Med. 2002;32:1050–1060. - PubMed
-
- Markesbery WR. The Role of Oxidative Stress in Alzheimer Disease. Arch Neurol. 1999;56:1449–1452. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

