Genetic Evidence for Genotoxic Effect of Entecavir, an Anti-Hepatitis B Virus Nucleotide Analog
- PMID: 26800464
- PMCID: PMC4723259
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0147440
Genetic Evidence for Genotoxic Effect of Entecavir, an Anti-Hepatitis B Virus Nucleotide Analog
Abstract
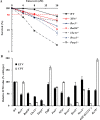
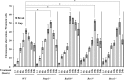
Nucleoside analogues (NAs) have been the most frequently used treatment option for chronic hepatitis B patients. However, they may have genotoxic potentials due to their interference with nucleic acid metabolism. Entecavir, a deoxyguanosine analog, is one of the most widely used oral antiviral NAs against hepatitis B virus. It has reported that entecavir gave positive responses in both genotoxicity and carcinogenicity assays. However the genotoxic mechanism of entecavir remains elusive. To evaluate the genotoxic mechanisms, we analyzed the effect of entecavir on a panel of chicken DT40 B-lymphocyte isogenic mutant cell line deficient in DNA repair and damage tolerance pathways. Our results showed that Parp1-/- mutant cells defective in single-strand break (SSB) repair were the most sensitive to entecavir. Brca1-/-, Ubc13-/- and translesion-DNA-synthesis deficient cells including Rad18-/- and Rev3-/- were hypersensitive to entecavir. XPA-/- mutant deficient in nucleotide excision repair was also slightly sensitive to entecavir. γ-H2AX foci forming assay confirmed the existence of DNA damage by entecavir in Parp1-/-, Rad18-/- and Brca1-/- mutants. Karyotype assay further showed entecavir-induced chromosomal aberrations, especially the chromosome gaps in Parp1-/-, Brca1-/-, Rad18-/- and Rev3-/- cells when compared with wild-type cells. These genetic comprehensive studies clearly identified the genotoxic potentials of entecavir and suggested that SSB and postreplication repair pathways may suppress entecavir-induced genotoxicity.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



Similar articles
-
Multiple repair pathways mediate cellular tolerance to resveratrol-induced DNA damage.Toxicol In Vitro. 2017 Aug;42:130-138. doi: 10.1016/j.tiv.2017.04.017. Epub 2017 Apr 19. Toxicol In Vitro. 2017. PMID: 28431926
-
Tenofovir is a more suitable treatment than entecavir for chronic hepatitis B patients carrying naturally occurring rtM204I mutations.World J Gastroenterol. 2019 Sep 7;25(33):4985-4998. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i33.4985. World J Gastroenterol. 2019. PMID: 31543688 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of genotoxic compounds using isogenic DNA repair deficient DT40 cell lines on a quantitative high throughput screening platform.Mutagenesis. 2016 Jan;31(1):69-81. doi: 10.1093/mutage/gev055. Epub 2015 Aug 4. Mutagenesis. 2016. PMID: 26243743 Free PMC article.
-
An evaluation of entecavir for the treatment of chronic hepatitis B infection in adults.Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2016;10(2):177-86. doi: 10.1586/17474124.2016.1125781. Epub 2016 Jan 8. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2016. PMID: 26610256 Review.
-
[Entecavir--close perspective for using it].Przegl Epidemiol. 2006;60(1):115-8. Przegl Epidemiol. 2006. PMID: 16758749 Review. Polish.
Cited by
-
HeberNasvac: Development and Application in the Context of Chronic Hepatitis B.Euroasian J Hepatogastroenterol. 2024 Jul-Dec;14(2):221-237. doi: 10.5005/jp-journals-10018-1457. Epub 2024 Dec 27. Euroasian J Hepatogastroenterol. 2024. PMID: 39802853 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A mechanism for semaphorin-induced apoptosis: DNA damage of endothelial and myogenic cells in primary cultures from skeletal muscle.Oncotarget. 2018 Apr 27;9(32):22618-22630. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.25200. eCollection 2018 Apr 27. Oncotarget. 2018. PMID: 29854302 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatitis B Virus Treatment and Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Controversies and Approaches to Consensus.Liver Cancer. 2022 Aug 23;11(6):497-510. doi: 10.1159/000525518. eCollection 2022 Dec. Liver Cancer. 2022. PMID: 36589728 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Safety of entecavir antiviral therapyduring an accidental pregnancy in patients with chronic hepatitis B.Biomed Rep. 2023 Aug 31;19(4):72. doi: 10.3892/br.2023.1654. eCollection 2023 Oct. Biomed Rep. 2023. PMID: 37746589 Free PMC article.
-
Tenofovir vs Entecavir Among Patients With HBV-Related HCC After Resection.JAMA Netw Open. 2023 Oct 2;6(10):e2340353. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.40353. JAMA Netw Open. 2023. PMID: 37906195 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Asaad AM, Al-Ayed MS, Aleraky M, Qureshi MA. Hepatitis B virus genotyping in chronic hepatitis B patients in southwestern Saudi Arabia. The Brazilian journal of infectious diseases: an official publication of the Brazilian Society of Infectious Diseases. 2015; 19(5):525–8. 10.1016/j.bjid.2015.03.007 . - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

