Discoidin Domain Receptor-1 Regulates Calcific Extracellular Vesicle Release in Vascular Smooth Muscle Cell Fibrocalcific Response via Transforming Growth Factor-β Signaling
- PMID: 26800565
- PMCID: PMC4767541
- DOI: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.115.307009
Discoidin Domain Receptor-1 Regulates Calcific Extracellular Vesicle Release in Vascular Smooth Muscle Cell Fibrocalcific Response via Transforming Growth Factor-β Signaling
Abstract
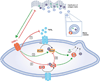
Objective: Collagen accumulation and calcification are major determinants of atherosclerotic plaque stability. Extracellular vesicle (EV)-derived microcalcifications in the collagen-poor fibrous cap may promote plaque rupture. In this study, we hypothesize that the collagen receptor discoidin domain receptor-1 (DDR-1) regulates collagen deposition and release of calcifying EVs by vascular smooth muscle cells (SMCs) through the transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β) pathway.
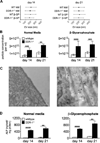
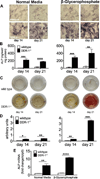
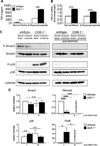
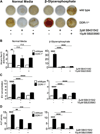
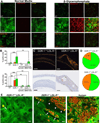
Approach and results: SMCs from the carotid arteries of DDR-1(-/-) mice and wild-type littermates (n=5-10 per group) were cultured in normal or calcifying media. At days 14 and 21, SMCs were harvested and EVs isolated for analysis. Compared with wild-type, DDR-1(-/-) SMCs exhibited a 4-fold increase in EV release (P<0.001) with concomitantly elevated alkaline phosphatase activity (P<0.0001) as a hallmark of EV calcifying potential. The DDR-1(-/-) phenotype was characterized by increased mineralization (Alizarin Red S and Osteosense, P<0.001 and P=0.002, respectively) and amorphous collagen deposition (P<0.001). We further identified a novel link between DDR-1 and the TGF-β pathway previously implicated in both fibrotic and calcific responses. An increase in TGF-β1 release by DDR-1(-/-) SMCs in calcifying media (P<0.001) stimulated p38 phosphorylation (P=0.02) and suppressed activation of Smad3. Inhibition of either TGF-β receptor-I or phospho-p38 reversed the fibrocalcific DDR-1(-/-) phenotype, corroborating a causal relationship between DDR-1 and TGF-β in EV-mediated vascular calcification.
Conclusions: DDR-1 interacts with the TGF-β pathway to restrict calcifying EV-mediated mineralization and fibrosis by SMCs. We therefore establish a novel mechanism of cell-matrix homeostasis in atherosclerotic plaque formation.
Keywords: extracellular matrix; extracellular vesicles; fibrosis; smooth muscle; transforming growth factors.
© 2016 American Heart Association, Inc.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Increased cell and matrix accumulation during atherogenesis in mice with vessel wall-specific deletion of discoidin domain receptor 1.Circ Res. 2010 Jun 11;106(11):1775-83. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.109.213637. Epub 2010 May 6. Circ Res. 2010. PMID: 20448217
-
Estrogen Receptor Control of Atherosclerotic Calcification and Smooth Muscle Cell Osteogenic Differentiation.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2017 Jun;37(6):1127-1137. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.117.309054. Epub 2017 May 4. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2017. PMID: 28473445
-
Indoxyl Sulfate-Induced Extracellular Vesicles Released from Endothelial Cells Stimulate Vascular Smooth Muscle Cell Proliferation by Inducing Transforming Growth Factor-Beta Production.J Vasc Res. 2019;56(3):129-138. doi: 10.1159/000496796. Epub 2019 May 14. J Vasc Res. 2019. PMID: 31085925
-
Role of smooth muscle cells in vascular calcification: implications in atherosclerosis and arterial stiffness.Cardiovasc Res. 2018 Mar 15;114(4):590-600. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvy010. Cardiovasc Res. 2018. PMID: 29514202 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Calcifying Matrix Vesicles and Atherosclerosis.Biomed Res Int. 2017;2017:7463590. doi: 10.1155/2017/7463590. Epub 2017 Nov 7. Biomed Res Int. 2017. PMID: 29238720 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Discoidin domain receptor 2 activation of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase as an important pathway for osteonectin-regulating osteoblast mineralization.J Orthop Surg Res. 2021 Dec 7;16(1):711. doi: 10.1186/s13018-021-02860-1. J Orthop Surg Res. 2021. PMID: 34876214 Free PMC article.
-
Regulatory role of mammalian target of rapamycin signaling in exosome secretion and osteogenic changes in smooth muscle cells lacking acid ceramidase gene.FASEB J. 2021 Jul;35(7):e21732. doi: 10.1096/fj.202100385R. FASEB J. 2021. PMID: 34143450 Free PMC article.
-
Pulmonary hypertension: Linking inflammation and pulmonary arterial stiffening.Front Immunol. 2022 Oct 5;13:959209. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.959209. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36275740 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Innate and adaptive immunity in cardiovascular calcification.Atherosclerosis. 2020 Aug;306:59-67. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2020.02.016. Epub 2020 Feb 28. Atherosclerosis. 2020. PMID: 32222287 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transforming growth factor β1 suppresses proinflammatory gene program independent of its regulation on vascular smooth muscle differentiation and autophagy.Cell Signal. 2018 Oct;50:160-170. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2018.07.002. Epub 2018 Jul 11. Cell Signal. 2018. PMID: 30006123 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Maldonado N, Kelly-Arnold A, Vengrenyuk Y, Laudier D, Fallon JT, Virmani R, Cardoso L, Weinbaum S. A mechanistic analysis of the role of microcalcifications in atherosclerotic plaque stability: Potential implications for plaque rupture. American journal of physiology. Heart and circulatory physiology. 2012;303:H619–H628. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Vengrenyuk Y, Carlier S, Xanthos S, Cardoso L, Ganatos P, Virmani R, Einav S, Gilchrist L, Weinbaum S. A hypothesis for vulnerable plaque rupture due to stress-induced debonding around cellular microcalcifications in thin fibrous caps. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 2006;103:14678–14683. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kapustin AN, Chatrou ML, Drozdov I, Zheng Y, Davidson SM, Soong D, Furmanik M, Sanchis P, De Rosales RT, Alvarez-Hernandez D, Shroff R, Yin X, Muller K, Skepper JN, Mayr M, Reutelingsperger CP, Chester A, Bertazzo S, Schurgers LJ, Shanahan CM. Vascular smooth muscle cell calcification is mediated by regulated exosome secretion. Circ Res. 2015;116:1312–1323. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

