Hedgehog Signaling Strength Is Orchestrated by the mir-310 Cluster of MicroRNAs in Response to Diet
- PMID: 26801178
- PMCID: PMC4788116
- DOI: 10.1534/genetics.115.185371
Hedgehog Signaling Strength Is Orchestrated by the mir-310 Cluster of MicroRNAs in Response to Diet
Abstract
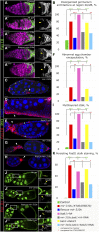
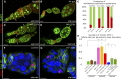
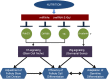
Since the discovery of microRNAs (miRNAs) only two decades ago, they have emerged as an essential component of the gene regulatory machinery. miRNAs have seemingly paradoxical features: a single miRNA is able to simultaneously target hundreds of genes, while its presence is mostly dispensable for animal viability under normal conditions. It is known that miRNAs act as stress response factors; however, it remains challenging to determine their relevant targets and the conditions under which they function. To address this challenge, we propose a new workflow for miRNA function analysis, by which we found that the evolutionarily young miRNA family, the mir-310s (mir-310/mir-311/mir-312/mir-313), are important regulators of Drosophila metabolic status. mir-310s-deficient animals have an abnormal diet-dependent expression profile for numerous diet-sensitive components, accumulate fats, and show various physiological defects. We found that the mir-310s simultaneously repress the production of several regulatory factors (Rab23, DHR96, and Ttk) of the evolutionarily conserved Hedgehog (Hh) pathway to sharpen dietary response. As the mir-310s expression is highly dynamic and nutrition sensitive, this signal relay model helps to explain the molecular mechanism governing quick and robust Hh signaling responses to nutritional changes. Additionally, we discovered a new component of the Hh signaling pathway in Drosophila, Rab23, which cell autonomously regulates Hh ligand trafficking in the germline stem cell niche. How organisms adjust to dietary fluctuations to sustain healthy homeostasis is an intriguing research topic. These data are the first to report that miRNAs can act as executives that transduce nutritional signals to an essential signaling pathway. This suggests miRNAs as plausible therapeutic agents that can be used in combination with low calorie and cholesterol diets to manage quick and precise tissue-specific responses to nutritional changes.
Keywords: Drosophila; Hedgehog signaling; Hh ligand; Rab23; dietary restriction; follicle stem cell; metabolic stress; miRNA; oogenesis; the mir-310s.
Copyright © 2016 by the Genetics Society of America.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Drosophila miR-932 modulates hedgehog signaling by targeting its co-receptor Brother of ihog.Dev Biol. 2013 May 1;377(1):166-76. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2013.02.002. Epub 2013 Feb 21. Dev Biol. 2013. PMID: 23453925
-
The mir-7 and bag of marbles genes regulate Hedgehog pathway signaling in blood cell progenitors in Drosophila larval lymph glands.Genesis. 2018 May;56(5):e23210. doi: 10.1002/dvg.23210. Epub 2018 May 11. Genesis. 2018. PMID: 29663653 Free PMC article.
-
Dissection of the microRNA Network Regulating Hedgehog Signaling in Drosophila.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Apr 28;10:866491. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.866491. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 35573695 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNAs in liver fibrosis: Focusing on the interaction with hedgehog signaling.World J Gastroenterol. 2016 Aug 7;22(29):6652-62. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i29.6652. World J Gastroenterol. 2016. PMID: 27547008 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hedgehog signaling, epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and miRNA (review).Int J Mol Med. 2008 Sep;22(3):271-5. Int J Mol Med. 2008. PMID: 18698484 Review.
Cited by
-
Stereotypical architecture of the stem cell niche is spatiotemporally established by miR-125-dependent coordination of Notch and steroid signaling.Development. 2018 Feb 8;145(3):dev159178. doi: 10.1242/dev.159178. Development. 2018. PMID: 29361571 Free PMC article.
-
A polycistronic locus encodes both a tumor-suppressive microRNA and a long non-coding RNA regulating testis morphology in Drosophila.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 May 16:2024.10.10.617551. doi: 10.1101/2024.10.10.617551. bioRxiv. 2025. PMID: 39416153 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Specific circulating miRNAs are associated with plasma lipids in a healthy American cohort.Physiol Genomics. 2024 Jul 1;56(7):492-505. doi: 10.1152/physiolgenomics.00087.2023. Epub 2024 Apr 1. Physiol Genomics. 2024. PMID: 38557280 Free PMC article.
-
Mapping of genotype-by-environment interaction loci for Metabolic Syndrome-like traits using the multi-parent Drosophila Synthetic Population Resource determines that main genetic effects are distinct from environment dependent plastic loci.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Aug 6:2025.08.04.668530. doi: 10.1101/2025.08.04.668530. bioRxiv. 2025. PMID: 40799541 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
MicroRNAs and the metabolic hallmarks of aging.Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2017 Nov 5;455:131-147. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2016.12.021. Epub 2017 Jan 3. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2017. PMID: 28062199 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Barrio L., Dekanty A., Milan M., 2014. MicroRNA-mediated regulation of Dp53 in the Drosophila fat body contributes to metabolic adaptation to nutrient deprivation. Cell Reports 8: 528–541. - PubMed
-
- Besse F., Busson D., Pret A.-M., 2002. Fused-dependent Hedgehog signal transduction is required for somatic cell differentiation during Drosophila egg chamber formation. Development 129: 4111–4124. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

