Static and Dynamic Factors Limit Chromosomal Replication Complexity in Escherichia coli, Avoiding Dangers of Runaway Overreplication
- PMID: 26801182
- PMCID: PMC4788131
- DOI: 10.1534/genetics.115.184697
Static and Dynamic Factors Limit Chromosomal Replication Complexity in Escherichia coli, Avoiding Dangers of Runaway Overreplication
Abstract
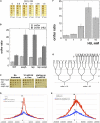
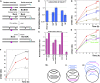
We define chromosomal replication complexity (CRC) as the ratio of the copy number of the most replicated regions to that of unreplicated regions on the same chromosome. Although a typical CRC of eukaryotic or bacterial chromosomes is 2, rapidly growing Escherichia coli cells induce an extra round of replication in their chromosomes (CRC = 4). There are also E. coli mutants with stable CRC∼6. We have investigated the limits and consequences of elevated CRC in E. coli and found three limits: the "natural" CRC limit of ∼8 (cells divide more slowly); the "functional" CRC limit of ∼22 (cells divide extremely slowly); and the "tolerance" CRC limit of ∼64 (cells stop dividing). While the natural limit is likely maintained by the eclipse system spacing replication initiations, the functional limit might reflect the capacity of the chromosome segregation system, rather than dedicated mechanisms, and the tolerance limit may result from titration of limiting replication factors. Whereas recombinational repair is beneficial for cells at the natural and functional CRC limits, we show that it becomes detrimental at the tolerance CRC limit, suggesting recombinational misrepair during the runaway overreplication and giving a rationale for avoidance of the latter.
Keywords: hydroxyurea; overinitiation; recA; rep; seqA.
Copyright © 2016 by the Genetics Society of America.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Chromosomal Replication Complexity: A Novel DNA Metrics and Genome Instability Factor.PLoS Genet. 2016 Oct 6;12(10):e1006229. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1006229. eCollection 2016 Oct. PLoS Genet. 2016. PMID: 27711112 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Thymineless Death in Escherichia coli Is Unaffected by Chromosomal Replication Complexity.J Bacteriol. 2019 Apr 9;201(9):e00797-18. doi: 10.1128/JB.00797-18. Print 2019 May 1. J Bacteriol. 2019. PMID: 30745374 Free PMC article.
-
Replication fork inhibition in seqA mutants of Escherichia coli triggers replication fork breakage.Mol Microbiol. 2014 Jul;93(1):50-64. doi: 10.1111/mmi.12638. Epub 2014 May 23. Mol Microbiol. 2014. PMID: 24806348 Free PMC article.
-
Host controlled plasmid replication: Escherichia coli minichromosomes.Plasmid. 2004 Nov;52(3):151-68. doi: 10.1016/j.plasmid.2004.08.001. Plasmid. 2004. PMID: 15518873 Review.
-
Overinitiation of replication of the Escherichia coli chromosome from an integrated runaway-replication derivative of plasmid R1.J Bacteriol. 1989 Feb;171(2):674-83. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.2.674-683.1989. J Bacteriol. 1989. PMID: 2644232 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Robust linear DNA degradation supports replication-initiation-defective mutants in Escherichia coli.G3 (Bethesda). 2022 Nov 4;12(11):jkac228. doi: 10.1093/g3journal/jkac228. G3 (Bethesda). 2022. PMID: 36165702 Free PMC article.
-
Electron Microscopy Reveals Unexpected Cytoplasm and Envelope Changes during Thymineless Death in Escherichia coli.J Bacteriol. 2021 Aug 9;203(17):e0015021. doi: 10.1128/JB.00150-21. Epub 2021 Aug 9. J Bacteriol. 2021. PMID: 34152201 Free PMC article.
-
Host nucleases generate prespacers for primed adaptation in the E. coli type I-E CRISPR-Cas system.Sci Adv. 2022 Nov 25;8(47):eabn8650. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.abn8650. Epub 2022 Nov 25. Sci Adv. 2022. PMID: 36427302 Free PMC article.
-
Does the eclipse limit bacterial nucleoid complexity and cell width?Synth Syst Biotechnol. 2017 Nov 29;2(4):267-275. doi: 10.1016/j.synbio.2017.11.004. eCollection 2017 Dec. Synth Syst Biotechnol. 2017. PMID: 29552651 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Does the Nucleoid Determine Cell Dimensions in Escherichia coli?Front Microbiol. 2019 Aug 6;10:1717. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.01717. eCollection 2019. Front Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31447799 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ahmad S. I., Kirk S. H., Eisenstark A., 1998. Thymine metabolism and thymineless death in prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 52: 591–625. - PubMed
-
- Bird R. E., Louarn J., Martuscelli J., Caro L., 1972. Origin and sequence of chromosome replication in Escherichia coli. J. Mol. Biol. 70: 549–566. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

