miR-508-3p concordantly silences NFKB1 and RELA to inactivate canonical NF-κB signaling in gastric carcinogenesis
- PMID: 26801246
- PMCID: PMC4724081
- DOI: 10.1186/s12943-016-0493-7
miR-508-3p concordantly silences NFKB1 and RELA to inactivate canonical NF-κB signaling in gastric carcinogenesis
Abstract
Background: NF-κB signaling pathway plays an important role in gastric carcinogenesis. The basic expression and functional role of NFKB1 and RELA (components of canonical NF-κB pathway) in gastric cancer (GC) have not been well elucidated. In this study, the role of NFKB1 and RELA in gastric tumorigenesis will be investigated and their regulation by microRNAs (miRNAs) will be deeply explored.
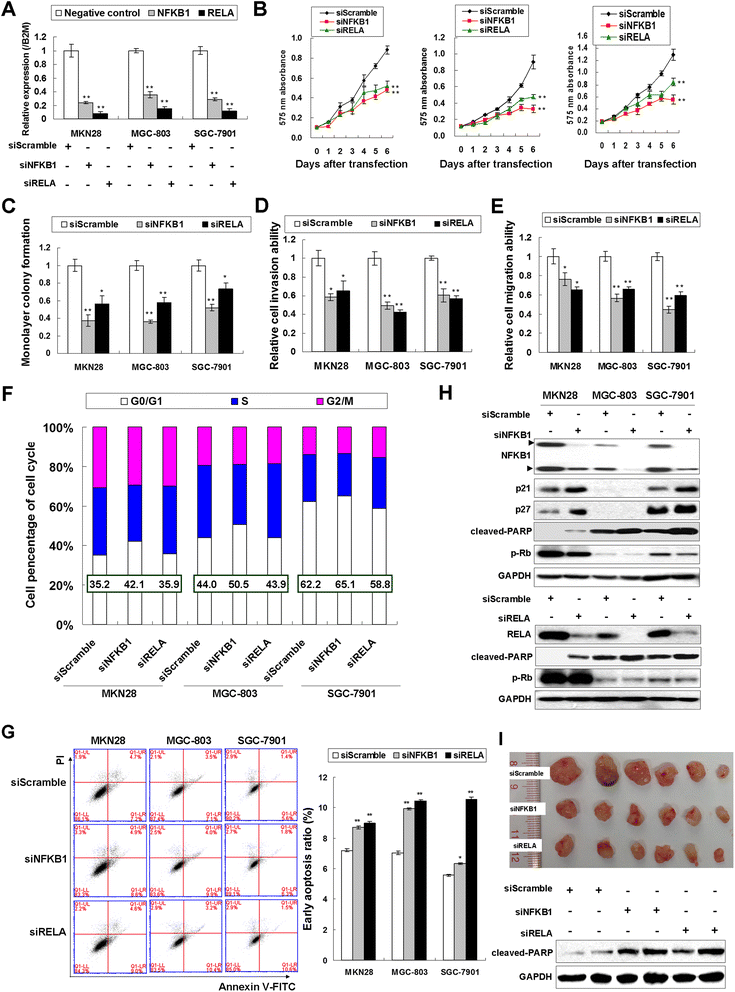
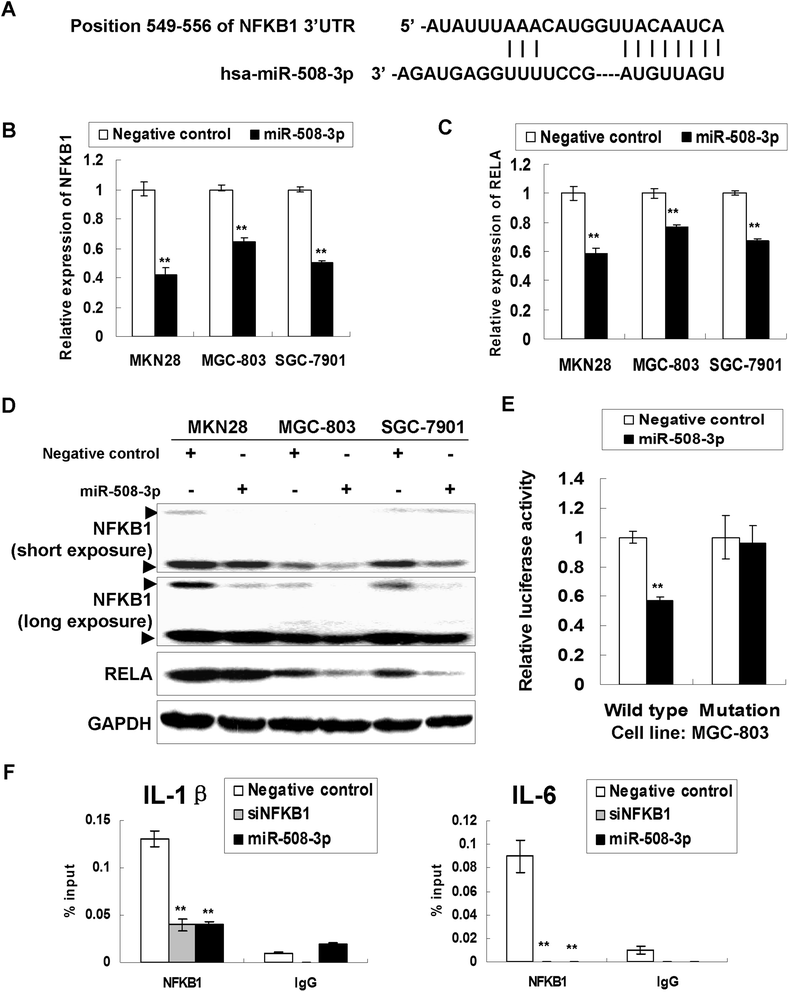
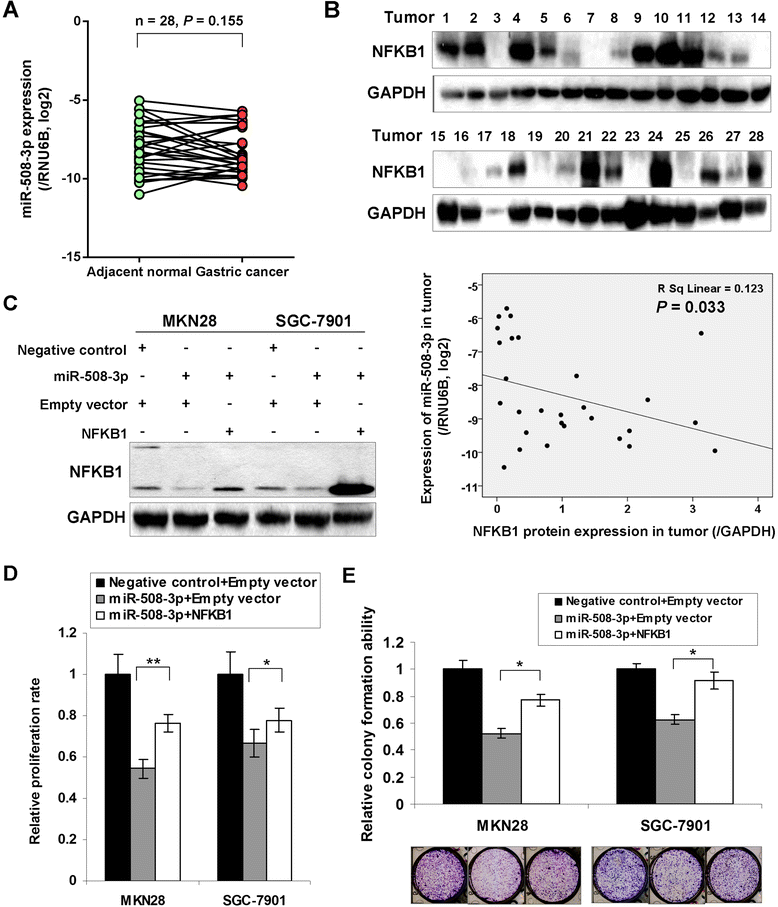
Methods: The mRNA and protein expression of NFKB1 and RELA were investigated by qRT-PCR and Western blot in GC cell lines and primary tumors. The functional roles of NFKB1 and RELA in GC were demonstrated by MTT proliferation assay, monolayer colony formation, cell invasion and migration, cell cycle analysis and in vivo study through siRNA mediated knockdown. Identification of NFKB1 as a direct target of tumor suppressor miRNA miR-508-3p was achieved by expression regulation assays together with dual luciferase activity experiments.
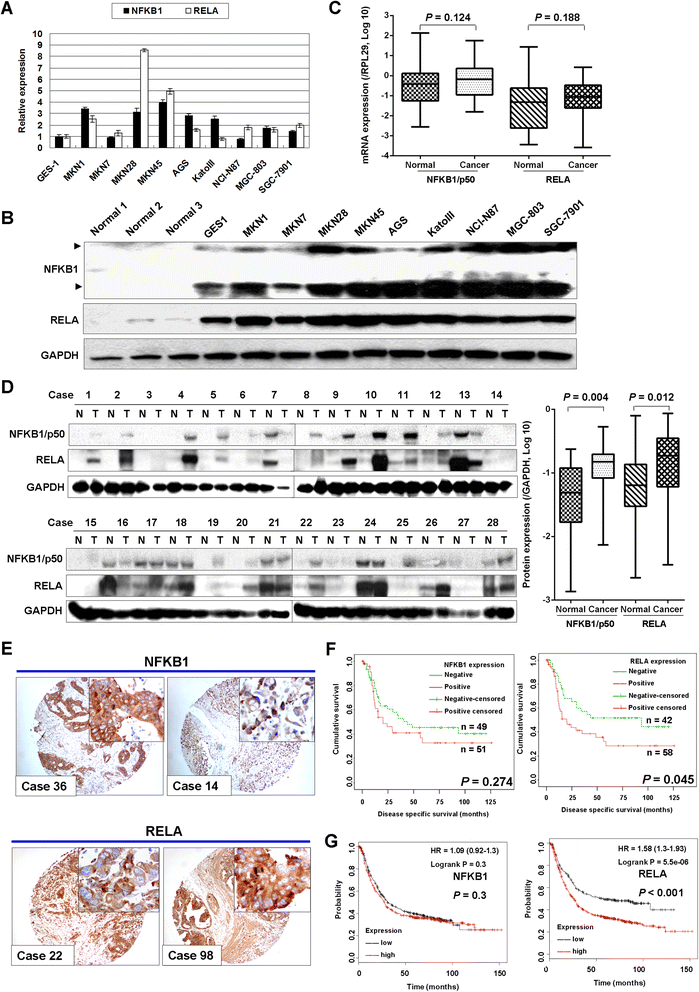
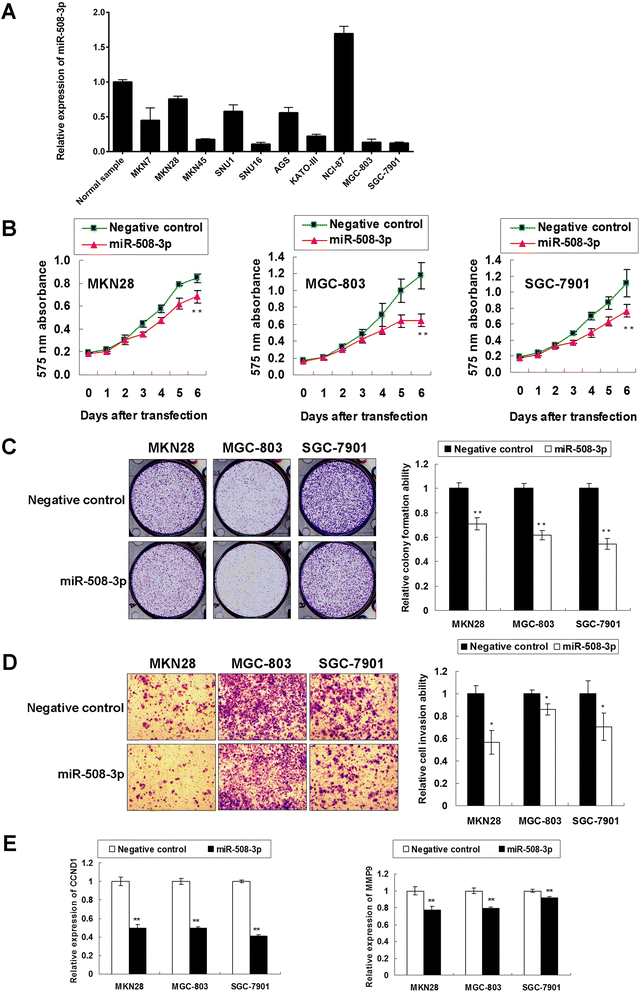
Results: NFKB1 and RELA were up-regulated in GC cell lines and primary tumors compared with normal gastric epithelium cells and their upregulation correlation with poor survival in GC. siRNA mediated knockdown of NFKB1 or RELA exhibited anti-oncogenic effect both in vitro and in vivo. NFKB1 was further revealed to be a direct target of miR-508-3p in gastric tumorigenesis and their expression showed negative correlation in primary GC samples. miR-508-3p was down-regulated in GC cells compared with normal gastric epithelium samples and its ectopic expression in GC cell lines also exerts tumor suppressor function. NFKB1 re-expression was found to partly abolish the tumor-suppressive effect of miR-508-3p in GC.
Conclusion: All these findings supports that canonical NF-κB signaling pathway is activated in GC at least by the inactivation of miR-508-3p and this might have therapeutic potential in GC treatment.
Figures
Similar articles
-
TEAD1/4 exerts oncogenic role and is negatively regulated by miR-4269 in gastric tumorigenesis.Oncogene. 2017 Nov 23;36(47):6518-6530. doi: 10.1038/onc.2017.257. Epub 2017 Jul 31. Oncogene. 2017. PMID: 28759040 Free PMC article.
-
miR-27b-3p suppresses cell proliferation through targeting receptor tyrosine kinase like orphan receptor 1 in gastric cancer.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2015 Nov 14;34:139. doi: 10.1186/s13046-015-0253-3. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2015. PMID: 26576539 Free PMC article.
-
MiR-199a/b-3p inhibits gastric cancer cell proliferation via down-regulating PAK4/MEK/ERK signaling pathway.BMC Cancer. 2018 Jan 5;18(1):34. doi: 10.1186/s12885-017-3949-2. BMC Cancer. 2018. PMID: 29304764 Free PMC article.
-
Insights into roles of the miR-1, -133 and -206 family in gastric cancer (Review).Oncol Rep. 2016 Sep;36(3):1191-8. doi: 10.3892/or.2016.4908. Epub 2016 Jun 27. Oncol Rep. 2016. PMID: 27349337 Review.
-
Dysregulation of miRNAs as a signature for diagnosis and prognosis of gastric cancer and their involvement in the mechanism underlying gastric carcinogenesis and progression.IUBMB Life. 2020 May;72(5):884-898. doi: 10.1002/iub.2259. Epub 2020 Feb 20. IUBMB Life. 2020. PMID: 32078236 Review.
Cited by
-
Bioinformatic analysis and validation of microRNA-508-3p as a protective predictor by targeting NR4A3/MEK axis in pulmonary arterial hypertension.J Cell Mol Med. 2021 Jun;25(11):5202-5219. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.16523. Epub 2021 May 4. J Cell Mol Med. 2021. PMID: 33942991 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical significance of expression level of ZNF471 in gastric cancer.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2023 Aug 15;16(8):199-208. eCollection 2023. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2023. PMID: 37693683 Free PMC article.
-
SRGAP1, a crucial target of miR-340 and miR-124, functions as a potential oncogene in gastric tumorigenesis.Oncogene. 2018 Mar;37(9):1159-1174. doi: 10.1038/s41388-017-0029-7. Epub 2017 Dec 13. Oncogene. 2018. PMID: 29234151 Free PMC article.
-
FGF18-FGFR2 signaling triggers the activation of c-Jun-YAP1 axis to promote carcinogenesis in a subgroup of gastric cancer patients and indicates translational potential.Oncogene. 2020 Oct;39(43):6647-6663. doi: 10.1038/s41388-020-01458-x. Epub 2020 Sep 15. Oncogene. 2020. PMID: 32934314 Free PMC article.
-
NFKB1 and Cancer: Friend or Foe?Cells. 2018 Sep 7;7(9):133. doi: 10.3390/cells7090133. Cells. 2018. PMID: 30205516 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Lauren P. The Two Histological Main Types of Gastric Carcinoma: Diffuse and So-Called Intestinal-Type Carcinoma. An Attempt at a Histo-Clinical Classification. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1965;64:31–49. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

