Emerging role of hydrogen sulfide-microRNA crosstalk in cardiovascular diseases
- PMID: 26801305
- PMCID: PMC4867357
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpheart.00660.2015
Emerging role of hydrogen sulfide-microRNA crosstalk in cardiovascular diseases
Abstract
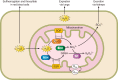
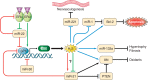
Despite an obnoxious smell and toxicity at a high dose, hydrogen sulfide (H2S) is emerging as a cardioprotective gasotransmitter. H2S mitigates pathological cardiac remodeling by regulating several cellular processes including fibrosis, hypertrophy, apoptosis, and inflammation. These encouraging findings in rodents led to initiation of a clinical trial using a H2S donor in heart failure patients. However, the underlying molecular mechanisms by which H2S mitigates cardiac remodeling are not completely understood. Empirical evidence suggest that H2S may regulate signaling pathways either by directly influencing a gene in the cascade or interacting with nitric oxide (another cardioprotective gasotransmitter) or both. Recent studies revealed that H2S may ameliorate cardiac dysfunction by up- or downregulating specific microRNAs. MicroRNAs are noncoding, conserved, regulatory RNAs that modulate gene expression mostly by translational inhibition and are emerging as a therapeutic target for cardiovascular disease (CVD). Few microRNAs also regulate H2S biosynthesis. The inter-regulation of microRNAs and H2S opens a new avenue for exploring the H2S-microRNA crosstalk in CVD. This review embodies regulatory mechanisms that maintain the physiological level of H2S, exogenous H2S donors used for increasing the tissue levels of H2S, H2S-mediated regulation of CVD, H2S-microRNAs crosstalk in relation to the pathophysiology of heart disease, clinical trials on H2S, and future perspectives for H2S as a therapeutic agent for heart failure.
Keywords: apoptosis; clinical trial; fibrosis; heart failure; inflammation; microRNAs.
Copyright © 2016 the American Physiological Society.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Cross-talk of MicroRNA and hydrogen sulfide: A novel therapeutic approach for bone diseases.Biomed Pharmacother. 2017 Aug;92:1073-1084. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2017.06.007. Epub 2017 Jun 10. Biomed Pharmacother. 2017. PMID: 28618652 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The interplay of hydrogen sulfide and microRNAs in cardiovascular diseases: insights and future perspectives.Mamm Genome. 2024 Sep;35(3):309-323. doi: 10.1007/s00335-024-10043-6. Epub 2024 Jun 4. Mamm Genome. 2024. PMID: 38834923 Review.
-
Hydrogen sulfide rescues high glucose-induced migration dysfunction in HUVECs by upregulating miR-126-3p.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2020 May 1;318(5):C857-C869. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00406.2019. Epub 2020 Mar 18. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2020. PMID: 32186933
-
Role of hydrogen sulfide-microRNA crosstalk in health and disease.Nitric Oxide. 2024 Nov 1;152:19-30. doi: 10.1016/j.niox.2024.09.002. Epub 2024 Sep 12. Nitric Oxide. 2024. PMID: 39260562 Review.
-
Hydrogen Sulfide and Functional Therapy: Novel Mechanisms from Epigenetics.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2024 Jan;40(1-3):110-121. doi: 10.1089/ars.2023.0425. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2024. PMID: 37950704 Review.
Cited by
-
The crucial relationship between miRNA-27 and CSE/H2S, and the mechanism of action of GLP-1 in myocardial hypertrophy.Int J Med Sci. 2024 Mar 31;21(5):965-977. doi: 10.7150/ijms.93720. eCollection 2024. Int J Med Sci. 2024. PMID: 38616996 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-140-5p aggravates doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity by promoting myocardial oxidative stress via targeting Nrf2 and Sirt2.Redox Biol. 2018 May;15:284-296. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2017.12.013. Epub 2017 Dec 29. Redox Biol. 2018. PMID: 29304479 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and Validation of the miR/RAS/RUNX2 Autophagy Regulatory Network in AngII-Induced Hypertensive Nephropathy in MPC5 Cells Treated with Hydrogen Sulfide Donors.Antioxidants (Basel). 2024 Aug 7;13(8):958. doi: 10.3390/antiox13080958. Antioxidants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39199205 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Hydrogen Sulfide in Oncological and Non-Oncological Disorders and Its Regulation by Non-Coding RNAs: A Comprehensive Review.Noncoding RNA. 2024 Jan 18;10(1):7. doi: 10.3390/ncrna10010007. Noncoding RNA. 2024. PMID: 38250807 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hydrogen Sulfide Attenuates Angiotensin II-Induced Cardiac Fibroblast Proliferation and Transverse Aortic Constriction-Induced Myocardial Fibrosis through Oxidative Stress Inhibition via Sirtuin 3.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021 Sep 23;2021:9925771. doi: 10.1155/2021/9925771. eCollection 2021. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021. PMID: 34603602 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ahmad FU, Sattar MA, Rathore HA, Abdullah MH, Tan S, Abdullah NA, Johns EJ. Exogenous hydrogen sulfide (H2S) reduces blood pressure and prevents the progression of diabetic nephropathy in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Ren Fail 34: 203–210, 2012. - PubMed
-
- Aitken SM, Lodha PH, Morneau DJ. The enzymes of the transsulfuration pathways: active-site characterizations. Biochim Biophys Acta 1814: 1511–1517, 2011. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

