Diagnostic accuracy of shear wave elastography for prediction of breast malignancy in patients with pathological nipple discharge
- PMID: 26801462
- PMCID: PMC4735172
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2015-008848
Diagnostic accuracy of shear wave elastography for prediction of breast malignancy in patients with pathological nipple discharge
Abstract
Objectives: Pathological nipple discharge (PND) may indicate malignant breast lesions. As the role of shear wave elastography (SWE) in predicting these malignant lesions has not yet been evaluated, we aim to evaluate the diagnostic value of SWE for this condition.
Design: Prospective diagnostic accuracy study comparing a combination of qualitative and quantitative measurements of SWE (index test) to a ductoscopy and microdochectomy for histological diagnosis (reference test).
Setting: Fuzhou General Hospital of Nanjing military command.
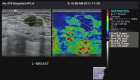
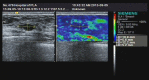
Participants: A total of 379 patients with PND were finally included from January, 2011 to March 2014, after we screened 1084 possible candidates. All participants were evaluated through SWE, with qualitative parameters generated by Virtual Touch tissue imaging (VTI) and quantitative parameters generated by Virtual Touch tissue quantification (VTQ). All the patients were consented to receive a ductoscopy and microdochectomy for histological diagnosis, and the results were set as a reference test.
Outcome measures: Sensitivity and specificity of the combined VTI and VTQ of the SWE for detection of malignancy in patients with PND.
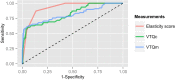
Results: The 379 participants presented with 404 lesions. The results of pathological examination showed that 326 (80.7%) of the 404 lesions were benign and the other 78 (19.3%) were malignant. An area under the curve of elasticity score, VTQm and VTQc, were 0.872, 0.825 and 0.857, respectively, with the corresponding cut-off point as 2.50, 2.860 m/s and 3.015 m/s, respectively. After a combination of these measurements, the sensitivity, specificity, and positive and negative predictive value (PPV and NPV), were 89.7%, 72.1%, 43.5% and 96.7%, respectively. The sensitivity analysis showed 82% of the sensitivity and 96.8% of the specificity, in which patients with no pathological findings in ductoscopy were excluded.
Conclusions: Ultrasonographic elastography is sensitive for patients with PND and could be used as a triage test before ductoscopy examination. Studies for further improvement of diagnostic sensitivity are warranted.
Keywords: ONCOLOGY.
Published by the BMJ Publishing Group Limited. For permission to use (where not already granted under a licence) please go to http://www.bmj.com/company/products-services/rights-and-licensing/
Figures
Similar articles
-
Value of Virtual Touch Tissue Imaging Quantification for Evaluation of Ultrasound Breast Imaging-Reporting and Data System Category 4 Lesions.Ultrasound Med Biol. 2016 Sep;42(9):2050-7. doi: 10.1016/j.ultrasmedbio.2016.04.002. Epub 2016 May 9. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2016. PMID: 27174418
-
Comparison of 3D and 2D shear-wave elastography for differentiating benign and malignant breast masses: focus on the diagnostic performance.Clin Radiol. 2017 Oct;72(10):878-886. doi: 10.1016/j.crad.2017.04.009. Epub 2017 May 16. Clin Radiol. 2017. PMID: 28526455
-
Diagnostic performances of shear-wave elastography and B-mode ultrasound to differentiate benign and malignant breast lesions: the emphasis on the cutoff value of qualitative and quantitative parameters.Clin Imaging. 2018 Jul-Aug;50:302-307. doi: 10.1016/j.clinimag.2018.05.007. Epub 2018 May 4. Clin Imaging. 2018. PMID: 29751202
-
Value of shear wave elastography in discriminating malignant and benign breast lesions: A meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2017 Oct;96(42):e7412. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000007412. Medicine (Baltimore). 2017. PMID: 29049174 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Diagnostic effect of shear wave elastography imaging for differentiation of malignant liver lesions: a meta-analysis.BMC Gastroenterol. 2019 Apr 25;19(1):60. doi: 10.1186/s12876-019-0976-2. BMC Gastroenterol. 2019. PMID: 31023234 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Ultrasonographic evaluation of women with pathologic nipple discharge.Ultrasonography. 2017 Oct;36(4):310-320. doi: 10.14366/usg.17013. Epub 2017 Apr 9. Ultrasonography. 2017. PMID: 28494526 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Diagnostic value of endoscopic appearance during ductoscopy in patients with pathological nipple discharge.BMC Cancer. 2017 May 2;17(1):300. doi: 10.1186/s12885-017-3288-3. BMC Cancer. 2017. PMID: 28464874 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative Diagnostic Accuracy of Contrast-Enhanced Ultrasound and Shear Wave Elastography in Differentiating Benign and Malignant Lesions: A Network Meta-Analysis.Front Oncol. 2019 Mar 5;9:102. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2019.00102. eCollection 2019. Front Oncol. 2019. PMID: 30891425 Free PMC article.
-
Nipple discharge: The state of the art.BJR Open. 2018 Nov 7;1(1):20180016. doi: 10.1259/bjro.20180016. eCollection 2019. BJR Open. 2018. PMID: 33178912 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Low-dose CT combined mammography in diagnosis of overflow breast disease: A protocol of systematic review.Medicine (Baltimore). 2020 Jul 2;99(27):e21063. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000021063. Medicine (Baltimore). 2020. PMID: 32629735 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
