Identification of valid reference genes for microRNA expression studies in a hepatitis B virus replicating liver cell line
- PMID: 26801621
- PMCID: PMC4724106
- DOI: 10.1186/s13104-016-1848-2
Identification of valid reference genes for microRNA expression studies in a hepatitis B virus replicating liver cell line
Abstract
Background: MicroRNAs are regulatory molecules and suggested as non-invasive biomarkers for molecular diagnostics and prognostics. Altered expression levels of specific microRNAs are associated with hepatitis B virus infection and hepatocellular carcinoma. We previously identified differentially expressed microRNAs with liver-specific target genes in plasma from children with chronic hepatitis B. To further understand the biological role of these microRNAs in the pathogenesis of chronic hepatitis B, we have used the human liver cell line HepG2, with and without HBV replication, after transfection of hepatitis B virus expression vectors. RT-qPCR is the preferred method for microRNA studies, and a careful normalisation strategy, verifying the optimal set of reference genes, is decisive for correctly evaluating microRNA expression levels. The aim of this study was to provide valid reference genes for the human HCC-derived cell line HepG2.
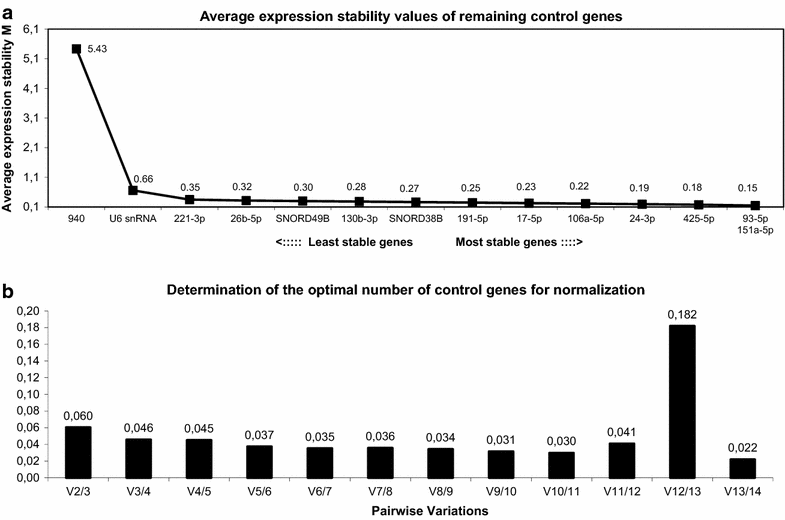
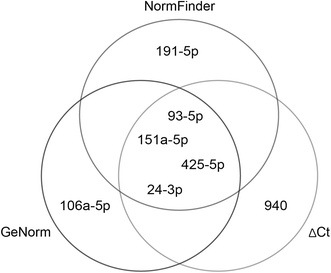
Results: A panel of 739 microRNAs was screened to identify the most stably expressed microRNAs, followed by a PubMed search identifying microRNAs previously used as reference genes. Sixteen candidate reference genes were validated by RT-qPCR. Reference gene stabilities were calculated first by standard deviations of ΔCt values and then by geNorm and NormFinder analyses, taking into account the amplification efficiency of each microRNA primer set. The optimal set of reference genes was verified by a target analysis using RT-qPCR on miR-215-5p.
Conclusion: We identified miR-24-3p, miR-151a-5p, and miR-425-5p as the most valid combination of reference genes for microRNA RT-qPCR studies in our hepatitis B virus replicating HepG2 cell model.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Global microRNA expression profiling in the liver biopsies of hepatitis B virus-infected patients suggests specific microRNA signatures for viral persistence and hepatocellular injury.Hepatology. 2018 May;67(5):1695-1709. doi: 10.1002/hep.29690. Epub 2018 Apr 1. Hepatology. 2018. PMID: 29194684
-
Hepatitis B virus upregulates host microRNAs that target apoptosis-regulatory genes in an in vitro cell model.Exp Cell Res. 2018 Oct 1;371(1):92-103. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2018.07.044. Epub 2018 Jul 27. Exp Cell Res. 2018. PMID: 30059664
-
Selection of reference genes for RT-qPCR analysis in tumor tissues from male hepatocellular carcinoma patients with hepatitis B infection and cirrhosis.Cancer Biomark. 2013;13(5):345-9. doi: 10.3233/CBM-130365. Cancer Biomark. 2013. PMID: 24440974
-
Hepatitis B virus and microRNAs: Complex interactions affecting hepatitis B virus replication and hepatitis B virus-associated diseases.World J Gastroenterol. 2015 Jun 28;21(24):7375-99. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i24.7375. World J Gastroenterol. 2015. PMID: 26139985 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of microRNAs in hepatitis B virus replication and pathogenesis.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2011 Nov-Dec;1809(11-12):678-85. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2011.04.008. Epub 2011 May 4. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2011. PMID: 21565290 Review.
Cited by
-
Selection of reference genes for quantitative analysis of microRNA expression in three different types of cancer.PLoS One. 2022 Feb 17;17(2):e0254304. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0254304. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 35176014 Free PMC article.
-
miRNA Expression Profiling in Subcutaneous Adipose Tissue of Monozygotic Twins Discordant for HIV Infection: Validation of Differentially Expressed miRNA and Bioinformatic Analysis.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Mar 23;23(7):3486. doi: 10.3390/ijms23073486. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35408847 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of reference microRNAs in skeletal muscle of a canine model of Duchenne muscular dystrophy.Wellcome Open Res. 2024 Nov 20;9:362. doi: 10.12688/wellcomeopenres.22481.2. eCollection 2024. Wellcome Open Res. 2024. PMID: 39649621 Free PMC article.
-
Reference Genes for qPCR-Based miRNA Expression Profiling in 14 Human Tissues.Med Princ Pract. 2022;31(4):322-332. doi: 10.1159/000524283. Epub 2022 Mar 30. Med Princ Pract. 2022. PMID: 35354155 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Selection of Reliable Reference Genes for Gene Expression Studies on Rhododendron molle G. Don.Front Plant Sci. 2016 Oct 18;7:1547. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2016.01547. eCollection 2016. Front Plant Sci. 2016. PMID: 27803707 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

