Making authentic science accessible-the benefits and challenges of integrating bioinformatics into a high-school science curriculum
- PMID: 26801769
- PMCID: PMC5221422
- DOI: 10.1093/bib/bbv113
Making authentic science accessible-the benefits and challenges of integrating bioinformatics into a high-school science curriculum
Abstract
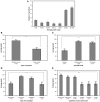
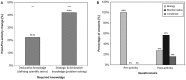
Despite the central place held by bioinformatics in modern life sciences and related areas, it has only recently been integrated to a limited extent into high-school teaching and learning programs. Here we describe the assessment of a learning environment entitled 'Bioinformatics in the Service of Biotechnology'. Students' learning outcomes and attitudes toward the bioinformatics learning environment were measured by analyzing their answers to questions embedded within the activities, questionnaires, interviews and observations. Students' difficulties and knowledge acquisition were characterized based on four categories: the required domain-specific knowledge (declarative, procedural, strategic or situational), the scientific field that each question stems from (biology, bioinformatics or their combination), the associated cognitive-process dimension (remember, understand, apply, analyze, evaluate, create) and the type of question (open-ended or multiple choice). Analysis of students' cognitive outcomes revealed learning gains in bioinformatics and related scientific fields, as well as appropriation of the bioinformatics approach as part of the students' scientific 'toolbox'. For students, questions stemming from the 'old world' biology field and requiring declarative or strategic knowledge were harder to deal with. This stands in contrast to their teachers' prediction. Analysis of students' affective outcomes revealed positive attitudes toward bioinformatics and the learning environment, as well as their perception of the teacher's role. Insights from this analysis yielded implications and recommendations for curriculum design, classroom enactment, teacher education and research. For example, we recommend teaching bioinformatics in an integrative and comprehensive manner, through an inquiry process, and linking it to the wider science curriculum.
Keywords: Bloom’s taxonomy; assessment; bioinformatics education; domain-specific knowledge; secondary school.
© The Author 2016. Published by Oxford University Press.
Figures


References
-
- National Institutes of Health [NIH]. NIH working definition of bioinformatics and computational biology. http://www.bisti.nih.gov (17 July 2000 date last accessed).
-
- National Center for Biotechnology Information [NCBI]. A science primer: bioinformatics. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/About/primer/bioinformatics.html (15 June 2011 date last accessed).
-
- Counsell D. A review of bioinformatics education in the UK. Brief Bioinform 2003;4:7–21. - PubMed
-
- Koch I, Fuellen G. A review of bioinformatics education in Germany. Brief Bioinform 2008;9:232–42. - PubMed
-
- National Research Council [NRC].BIO2010: Transforming Undergraduate Education for Future Research Biologists. Washington, DC: The National Academies Press, 2003. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

