Insights into epigenetic landscape of recombination-free regions
- PMID: 26801812
- PMCID: PMC4830869
- DOI: 10.1007/s00412-016-0574-9
Insights into epigenetic landscape of recombination-free regions
Abstract
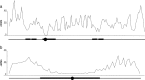
Genome architecture is shaped by gene-rich and repeat-rich regions also known as euchromatin and heterochromatin, respectively. Under normal conditions, the repeat-containing regions undergo little or no meiotic crossover (CO) recombination. COs within repeats are risky for the genome integrity. Indeed, they can promote non-allelic homologous recombination (NAHR) resulting in deleterious genomic rearrangements associated with diseases in humans. The assembly of heterochromatin is driven by the combinatorial action of many factors including histones, their modifications, and DNA methylation. In this review, we discuss current knowledge dealing with the epigenetic signatures of the major repeat regions where COs are suppressed. Then we describe mutants for epiregulators of heterochromatin in different organisms to find out how chromatin structure influences the CO rate and distribution.
Keywords: DNA methylation; Euchromatin; Heterochromatin; Histone acetylation; Histone methylation; Meiosis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Meiotic recombination is suppressed near the histone-defined border of euchromatin and heterochromatin on chromosome 2L of Drosophila melanogaster.Genome. 2016 Apr;59(4):289-94. doi: 10.1139/gen-2015-0171. Genome. 2016. PMID: 27031007
-
Deficiency in DNA methylation increases meiotic crossover rates in euchromatic but not in heterochromatic regions in Arabidopsis.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012 Apr 17;109(16):E981-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1120742109. Epub 2012 Mar 28. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012. PMID: 22460791 Free PMC article.
-
Histone variant H2A.W7 represses meiotic crossover formation in Arabidopsis heterochromatin.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2025 Jun 3;122(22):e2414166122. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2414166122. Epub 2025 May 29. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2025. PMID: 40440068 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic regulation during meiosis and crossover.Physiol Mol Biol Plants. 2023 Dec;29(12):1945-1958. doi: 10.1007/s12298-023-01390-w. Epub 2023 Nov 20. Physiol Mol Biol Plants. 2023. PMID: 38222277 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epigenetic control of meiotic recombination in plants.Sci China Life Sci. 2015 Mar;58(3):223-31. doi: 10.1007/s11427-015-4811-x. Epub 2015 Feb 5. Sci China Life Sci. 2015. PMID: 25651968 Review.
Cited by
-
Histone Code and Higher-Order Chromatin Folding: A Hypothesis.Genom Comput Biol. 2017;3(2):e41. doi: 10.18547/gcb.2017.vol3.iss2.e41. Epub 2017 Jan 30. Genom Comput Biol. 2017. PMID: 31245531 Free PMC article.
-
BREC: an R package/Shiny app for automatically identifying heterochromatin boundaries and estimating local recombination rates along chromosomes.BMC Bioinformatics. 2021 Aug 6;22(Suppl 6):396. doi: 10.1186/s12859-021-04233-1. BMC Bioinformatics. 2021. PMID: 34362304 Free PMC article.
-
A catalogue of recombination coldspots in interspecific tomato hybrids.PLoS Genet. 2024 Jul 1;20(7):e1011336. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1011336. eCollection 2024 Jul. PLoS Genet. 2024. PMID: 38950081 Free PMC article.
-
The Evolution of Sexual Reproduction and the Mating-Type Locus: Links to Pathogenesis of Cryptococcus Human Pathogenic Fungi.Annu Rev Genet. 2019 Dec 3;53:417-444. doi: 10.1146/annurev-genet-120116-024755. Epub 2019 Sep 19. Annu Rev Genet. 2019. PMID: 31537103 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ESA1 regulates meiotic chromosome axis and crossover frequency via acetylating histone H4.Nucleic Acids Res. 2021 Sep 20;49(16):9353-9373. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkab722. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021. PMID: 34417612 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

