Fibroblast growth factor receptor-1 protein expression is associated with prognosis in estrogen receptor-positive/human epidermal growth factor receptor-2-negative primary breast cancer
- PMID: 26801869
- PMCID: PMC4832856
- DOI: 10.1111/cas.12897
Fibroblast growth factor receptor-1 protein expression is associated with prognosis in estrogen receptor-positive/human epidermal growth factor receptor-2-negative primary breast cancer
Abstract
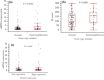
Recently, research into the development of new targeted therapies has focused on specific genetic alterations to create advanced, more personalized treatment. One of the target genes, fibroblast growth factor receptor-1 (FGFR1), has been reported to be amplified in estrogen receptor (ER)-positive subtype breast cancer, and is considered one possible mechanism of endocrine resistance through cross-talk between ER and growth factor receptor signaling. We performed a comprehensive analysis of FGFR1 at the levels of gene copy number, transcript and protein expression, and examined the relationships between FGFR1 status and clinicopathological parameters, including prognosis in 307 ER-positive/HER2-negative primary breast cancer patients treated with standard care at our institute. Most notably, a high level of FGFR1 protein expression was observed in 85 patients (27.7%), and was positively associated with invasive tumor size (P = 0.039). Furthermore, univariate analysis revealed that high FGFR1 protein expression was significantly correlated with poor relapse-free survival rate (P = 0.0019, HR: 2.63, 95% confidence interval: 1.17-5.98), and showed a tendency towards an increase in recurrent events if the observation period extended beyond the 5 years of the standard endocrine treatment term. FGFR1 gain/amplification was found in 43 (14.0%) patients, which was only associated with higher nuclear grade (P = 0.010). No correlation was found between FGFR1 mRNA expression levels and any clinicopathological factors. Overall, the level of FGFR1 protein expression may be a biomarker of ER-positive/HER2-negative primary breast cancer with possible resistance to standard treatment, and may be a useful tool to identify more specific patients who would benefit from FGFR-1 targeted therapy.
Keywords: Biomarker; ER-positive/HER2-negative; breast cancer; fibroblast growth factor receptor-1; protein expression.
© 2016 The Authors. Cancer Science published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd on behalf of Japanese Cancer Association.
Figures


References
-
- Slamon DJ, Clark GM, Wong SG, Levin WJ, Ullrich A, McGuire WL. Human breast cancer: correlation of relapse and survival with amplification of the HER‐2/neu oncogene. Science 1987; 235: 177–82. - PubMed
-
- Slamon DJ, Leyland‐Jones B, Shak S et al Use of chemotherapy plus a monoclonal antibody against HER2 for metastatic breast cancer that overexpresses HER2. N Engl J Med 2001; 344: 783–92. - PubMed
-
- Romond EH, Perez EA, Bryant J et al Trastuzumab plus adjuvant chemotherapy for operable HER2‐positive breast cancer. N Engl J Med 2005; 353: 1673–84. - PubMed
-
- Valachis A, Mauri D, Polyzos NP, Chlouverakis G, Mavroudis D, Georgoulias V. Trastuzumab combined to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in patients with HER2‐positive breast cancer: a systematic review and meta‐analysis. Breast 2011; 20: 485–90. - PubMed
-
- Ross JS, Slodkowska EA, Symmans WF, Pusztai L, Ravdin PM, Hortobagyi GN. The HER‐2 receptor and breast cancer: ten years of targeted anti‐HER‐2 therapy and personalized medicine. Oncologist 2009; 14: 320–68. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

