Use of complementary and alternative medicine in patients with health complaints attributed to former dental amalgam fillings
- PMID: 26801898
- PMCID: PMC4722717
- DOI: 10.1186/s12906-016-0996-1
Use of complementary and alternative medicine in patients with health complaints attributed to former dental amalgam fillings
Abstract
Background: The dental filling material amalgam is generally well tolerated. However, a small proportion of dental patients experience health complaints which they attribute to amalgam. The symptom pattern is often similar to patients with medically unexplained physical symptoms (MUPS) and the health complaints may persist after amalgam removal. Among patients with MUPS, the use of complementary and alternative medicine (CAM) seems to be high. The aim of this survey was to describe the prevalence and range of CAM use among people with health complaints attributed to dental amalgam fillings in which the health problems persist after the removal of all amalgam fillings. Specific attention was paid to (1) self-reported effects of CAM, (2) differences in CAM use dependent on self-reported health, and (3) gender differences in self-reported CAM use.
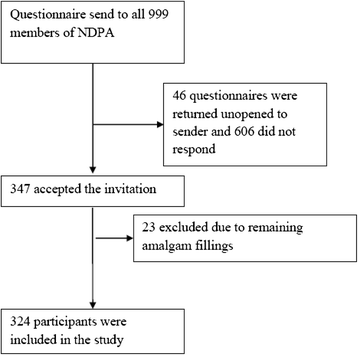
Methods: A survey was distributed to all members of The Norwegian dental patient association (NDPA) (n = 999), the response rate was 36.4%. The anonymous questionnaire asked for socio-demographic data, health complaints related to former amalgam fillings, subjectively perceived health status, symptoms, and experience with therapeutic interventions, mostly from the spectrum of CAM. Only participants who had all their fillings removed, which was the vast majority, were analysed.
Results: A total of 88.9% of included respondents had used at least one CAM modality, with a higher proportion of men (95.7%) compared to women (86.2%, p = 0.015). The most frequently used therapies were dietary supplements, vitamins and minerals recommended by a therapist (used by 66.7%) followed by self-prescribed dietary supplements, vitamins and minerals (59.0%), homeopathy (54.0%), acupuncture (48.8%) and special diets (47.5%). Use of CAM was similar for participants reporting normal to good health compared to participants reporting poor health. For all but two CAM modalities, the self-reported treatment effect was better in the group reporting normal to good health compared to the group reporting poor health.
Conclusions: CAM was widely used by participants in our study, a finding similar to findings from studies of MUPS patients. To date, health problems associated with the use of dental amalgam is not an accepted diagnosis in the healthcare system. Consequently, people suffering from such complaints experience a lack of adequate treatment and support within conventional health care, which might have contributed to the high number of CAM users in this study.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A 7-year prospective quasi-experimental study of the effects of removing dental amalgam in 76 self-referred patients compared with 146 controls.J Psychosom Res. 2004 Jul;57(1):103-11. doi: 10.1016/S0022-3999(03)00542-7. J Psychosom Res. 2004. PMID: 15256302 Clinical Trial.
-
Can removal of amalgam restorations reduce health complaints in patients with medically unexplained physical symptoms?Evid Based Dent. 2021 Jan;22(3):118-119. doi: 10.1038/s41432-021-0190-2. Evid Based Dent. 2021. PMID: 34561668
-
Health complaints before and at one and five years after removal of dental amalgam restorations - data from a prospective cohort study in Norway.Acta Odontol Scand. 2024 May 3;83:219-229. doi: 10.2340/aos.v83.40260. Acta Odontol Scand. 2024. PMID: 38699922 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Replacing Amalgam Fillings on the Suspicion of Adverse Health Effects from Amalgam [Internet].Oslo, Norway: Knowledge Centre for the Health Services at The Norwegian Institute of Public Health (NIPH); 2006 Aug. Report from Norwegian Knowledge Centre for the Health Services (NOKC) No. 10-2006. Oslo, Norway: Knowledge Centre for the Health Services at The Norwegian Institute of Public Health (NIPH); 2006 Aug. Report from Norwegian Knowledge Centre for the Health Services (NOKC) No. 10-2006. PMID: 29320025 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
[Dental care using silver amalgam].Verh K Acad Geneeskd Belg. 1996;58(5):587-634. Verh K Acad Geneeskd Belg. 1996. PMID: 9027133 Review. Dutch.
Cited by
-
Validity and responsiveness of EQ-5D-5L and SF-6D in patients with health complaints attributed to their amalgam fillings: a prospective cohort study of patients undergoing amalgam removal.Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2021 Apr 17;19(1):125. doi: 10.1186/s12955-021-01762-4. Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2021. PMID: 33865400 Free PMC article.
-
Use of traditional and complementary medicine among Norwegian cancer patients in the seventh survey of the Tromsø study.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2019 Nov 29;19(1):341. doi: 10.1186/s12906-019-2762-7. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2019. PMID: 31783842 Free PMC article.
-
Health Complaints Attributed to Dental Amalgam: A Retrospective Survey Exploring Perceived Health Changes Related to Amalgam Removal.Open Dent J. 2016 Dec 30;10:739-751. doi: 10.2174/1874210601610010739. eCollection 2016. Open Dent J. 2016. PMID: 28217190 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence, and health- and sociodemographic associations for visits to traditional and complementary medical providers in the seventh survey of the Tromsø study.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2019 Nov 11;19(1):305. doi: 10.1186/s12906-019-2707-1. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2019. PMID: 31711478 Free PMC article.
-
"Struggle to obtain redress": Women's experiences of living with symptoms attributed to dental restorative materials and/or electromagnetic fields.Int J Qual Stud Health Well-being. 2016 Dec 9;11:32820. doi: 10.3402/qhw.v11.32820. eCollection 2016. Int J Qual Stud Health Well-being. 2016. PMID: 27938629 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Helsedirektoratet. Nasjonale faglige retningslinjer for utredning og behandling ved mistanke om bivirkninger fra odontologiske biomaterialer [National guidance for assessment and treatment for suspected side effects from dental biomaterials]: Helsedirektoratet, Avdeling omsorg og tannhelse; 2008.
-
- Östlin L. Amalgamutbyte - en väg mot bättre hälsa? [Amalgam Replacement - a path towards better health?]. Stockholms Län: 1991.
-
- Lygre GB, Helland V, Gjerdet NR, Bjørkman L. Pasienter med helseplager relatert til tannfyllinger. Tidsskr Nor Laegeforen. 2007;11(127):1524–1528. - PubMed
-
- Norheim AJ, Ramstad S. Opplevde sammenhenger mellom amalgam og helse i den norske befolkning [Perceived associations between amalgam and health in the Norwegian population]. Nasjonalt Forskningssenter innen komplementær og alternativ medisin - NAFKAM, Universitetet i Tromsø: 2006 829267201X.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical