Surface vimentin is critical for the cell entry of SARS-CoV
- PMID: 26801988
- PMCID: PMC4724099
- DOI: 10.1186/s12929-016-0234-7
Surface vimentin is critical for the cell entry of SARS-CoV
Abstract
Background: Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus (SARS-CoV) caused a global panic due to its high morbidity and mortality during 2002 and 2003. Soon after the deadly disease outbreak, the angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) was identified as a functional cellular receptor in vitro and in vivo for SARS-CoV spike protein. However, ACE2 solely is not sufficient to allow host cells to become susceptible to SARS-CoV infection, and other host factors may be involved in SARS-CoV spike protein-ACE2 complex.
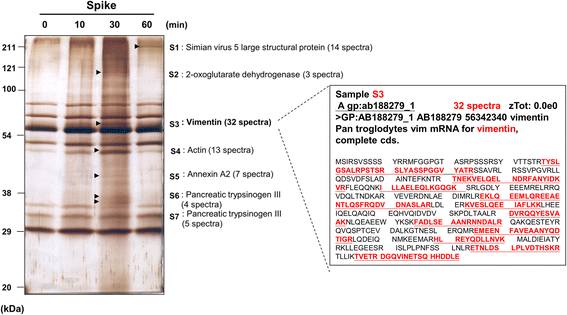
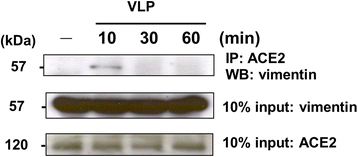
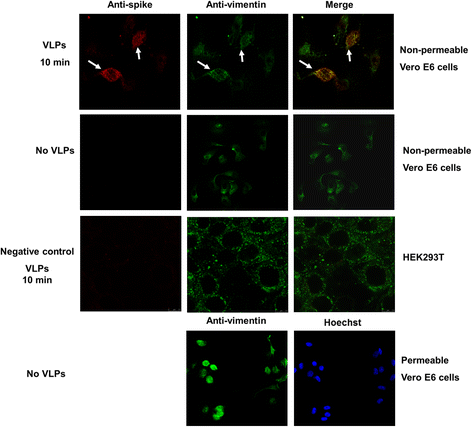
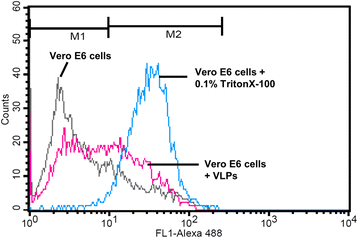
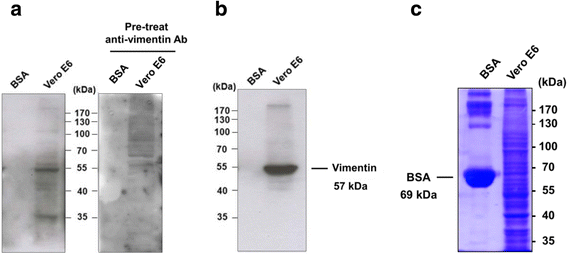
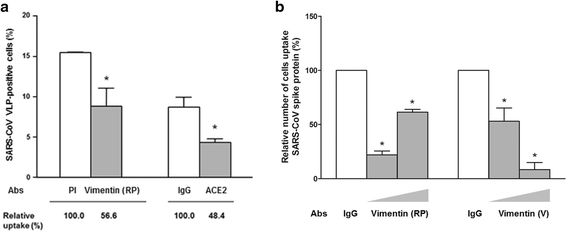
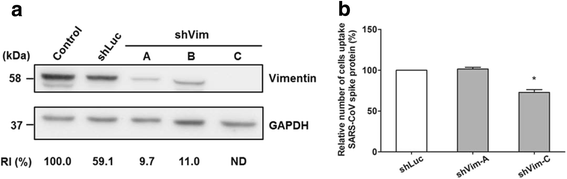
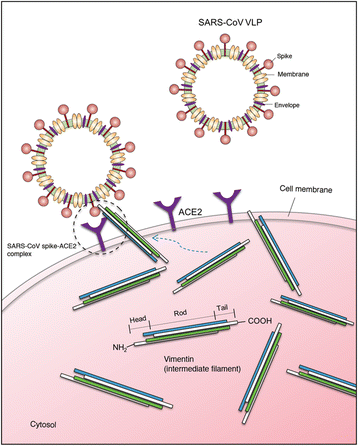
Results: A host intracellular filamentous cytoskeletal protein vimentin was identified by immunoprecipitation and LC-MS/MS analysis following chemical cross-linking on Vero E6 cells that were pre-incubated with the SARS-CoV spike protein. Moreover, flow cytometry data demonstrated an increase of the cell surface vimentin level by 16.5 % after SARS-CoV permissive Vero E6 cells were treated with SARS-CoV virus-like particles (VLPs). A direct interaction between SARS-CoV spike protein and host surface vimentin was further confirmed by far-Western blotting. In addition, antibody neutralization assay and shRNA knockdown experiments indicated a vital role of vimentin in cell binding and uptake of SARS-CoV VLPs and the viral spike protein.
Conclusions: A direct interaction between vimentin and SARS-CoV spike protein during viral entry was observed. Vimentin is a putative anti-viral drug target for preventing/reducing the susceptibility to SARS-CoV infection.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Isolation and characterization of a bat SARS-like coronavirus that uses the ACE2 receptor.Nature. 2013 Nov 28;503(7477):535-8. doi: 10.1038/nature12711. Epub 2013 Oct 30. Nature. 2013. PMID: 24172901 Free PMC article.
-
Importance of cholesterol-rich membrane microdomains in the interaction of the S protein of SARS-coronavirus with the cellular receptor angiotensin-converting enzyme 2.Virology. 2008 Nov 25;381(2):215-21. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2008.08.026. Epub 2008 Sep 23. Virology. 2008. PMID: 18814896 Free PMC article.
-
Evolutionary Arms Race between Virus and Host Drives Genetic Diversity in Bat Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome-Related Coronavirus Spike Genes.J Virol. 2020 Sep 29;94(20):e00902-20. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00902-20. Print 2020 Sep 29. J Virol. 2020. PMID: 32699095 Free PMC article.
-
Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2: The old door for new severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 infection.Rev Med Virol. 2020 Sep;30(5):e2122. doi: 10.1002/rmv.2122. Epub 2020 Jun 30. Rev Med Virol. 2020. PMID: 32602627 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Receptor recognition and cross-species infections of SARS coronavirus.Antiviral Res. 2013 Oct;100(1):246-54. doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2013.08.014. Epub 2013 Aug 29. Antiviral Res. 2013. PMID: 23994189 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Vimentin as a target for the treatment of COVID-19.BMJ Open Respir Res. 2020 Sep;7(1):e000623. doi: 10.1136/bmjresp-2020-000623. BMJ Open Respir Res. 2020. PMID: 32913008 Free PMC article.
-
Enterovirus-A71 exploits peripherin and Rac1 to invade the central nervous system.EMBO Rep. 2021 Jun 4;22(6):e51777. doi: 10.15252/embr.202051777. Epub 2021 Apr 19. EMBO Rep. 2021. PMID: 33871166 Free PMC article.
-
Deciphering SARS-CoV-2 Virologic and Immunologic Features.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Aug 18;21(16):5932. doi: 10.3390/ijms21165932. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32824753 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evidence of SARS-CoV-2 infection in postmortem lung, kidney, and liver samples, revealing cellular targets involved in COVID-19 pathogenesis.Arch Virol. 2023 Feb 26;168(3):96. doi: 10.1007/s00705-023-05711-y. Arch Virol. 2023. PMID: 36842152 Free PMC article.
-
A Vimentin-Targeting Oral Compound with Host-Directed Antiviral and Anti-Inflammatory Actions Addresses Multiple Features of COVID-19 and Related Diseases.mBio. 2021 Oct 26;12(5):e0254221. doi: 10.1128/mBio.02542-21. Epub 2021 Oct 12. mBio. 2021. PMID: 34634931 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

