Serum Magnesium and the Risk of Death From Coronary Heart Disease and Sudden Cardiac Death
- PMID: 26802105
- PMCID: PMC4859391
- DOI: 10.1161/JAHA.115.002707
Serum Magnesium and the Risk of Death From Coronary Heart Disease and Sudden Cardiac Death
Abstract
Background: Low serum magnesium has been implicated in cardiovascular mortality, but results are conflicting and the pathway is unclear. We studied the association of serum magnesium with coronary heart disease (CHD) mortality and sudden cardiac death (SCD) within the prospective population-based Rotterdam Study, with adjudicated end points and long-term follow-up.
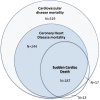
Methods and results: Nine-thousand eight-hundred and twenty participants (mean age 65.1 years, 56.8% female) were included with a median follow-up of 8.7 years. We used multivariable Cox proportional hazard models and found that a 0.1 mmol/L increase in serum magnesium level was associated with a lower risk for CHD mortality (hazard ratio: 0.82, 95% CI 0.70-0.96). Furthermore, we divided serum magnesium in quartiles, with the second and third quartile combined as reference group (0.81-0.88 mmol/L). Low serum magnesium (≤0.80 mmol/L) was associated with an increased risk of CHD mortality (N=431, hazard ratio: 1.36, 95% CI 1.09-1.69) and SCD (N=217, hazard ratio: 1.54, 95% CI 1.12-2.11). Low serum magnesium was associated with accelerated subclinical atherosclerosis (expressed as increased carotid intima-media thickness: +0.013 mm, 95% CI 0.005-0.020) and increased QT-interval, mainly through an effect on heart rate (RR-interval: -7.1 ms, 95% CI -13.5 to -0.8). Additional adjustments for carotid intima-media thickness and heart rate did not change the associations with CHD mortality and SCD.
Conclusions: Low serum magnesium is associated with an increased risk of CHD mortality and SCD. Although low magnesium was associated with both carotid intima-media thickness and heart rate, this did not explain the relationship between serum magnesium and CHD mortality or SCD. Future studies should focus on why magnesium associates with CHD mortality and SCD and whether intervention reduces these risks.
Keywords: cardiovascular diseases; death, sudden; epidemiology; mortality; risk factors.
© 2016 The Authors. Published on behalf of the American Heart Association, Inc., by Wiley Blackwell.
Figures

Comment in
-
[Higher cradiovascular risc with hypomagnesemia].Dtsch Med Wochenschr. 2016 Mar;141(6):379. doi: 10.1055/s-0042-101839. Epub 2016 Mar 16. Dtsch Med Wochenschr. 2016. PMID: 26983102 German. No abstract available.
References
-
- de Baaij JH, Hoenderop JG, Bindels RJ. Magnesium in man: implications for health and disease. Physiol Rev. 2015;95:1–46. - PubMed
-
- Liamis G, Rodenburg EM, Hofman A, Zietse R, Stricker BH, Hoorn EJ. Electrolyte disorders in community subjects: prevalence and risk factors. Am J Med. 2013;126:256–263. - PubMed
-
- Ishimura E, Okuno S, Yamakawa T, Inaba M, Nishizawa Y. Serum magnesium concentration is a significant predictor of mortality in maintenance hemodialysis patients. Magnes Res. 2007;20:237–244. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

