Single dose sublingual testosterone and oral sildenafil vs. a dual route/dual release fixed dose combination tablet: a pharmacokinetic comparison
- PMID: 26804967
- PMCID: PMC4876180
- DOI: 10.1111/bcp.12887
Single dose sublingual testosterone and oral sildenafil vs. a dual route/dual release fixed dose combination tablet: a pharmacokinetic comparison
Abstract
Aim: The aim was to compare the pharmacokinetic profiles of two formulations of a combination drug product containing 0.5 mg testosterone and 50 mg sildenafil for female sexual interest/arousal disorder. The prototype (formulation 1) consists of a testosterone solution for sublingual administration and a sildenafil tablet that is administered 2.5 h later. The dual route/dual release fixed dose combination tablet (formulation 2) employs a sublingual and an oral route for systemic uptake. This tablet has an inner core of sildenafil with a polymeric time delay coating and an outer polymeric coating containing testosterone. It was designed to increase dosing practicality and decrease potential temporal non-adherence through circumventing the relatively complex temporal dosing scheme.
Methods: Twelve healthy premenopausal subjects received both formulations randomly on separate days. Blood was sampled frequently to determine the pharmacokinetics of free testosterone, total testosterone, dihydrotestosterone, sildenafil and N-desmethyl-sildenafil.
Results: Formulation 2 had a higher maximum concentration (Cmax ) for testosterone, 8.06 ng ml(-1) (95% confidence interval [CI] 6.84, 9.28) and higher area under the plasma concentration-time curve (AUC), 7.69 ng ml(-1) h (95% CI 6.22, 9.16) than formulation 1, 5.66 ng ml(-1) (95% CI 4.63, 6.69) and 5.12 ng ml(-1) h (95% CI 4.51, 5.73), respectively. Formulation 2 had a lower Cmax for sildenafil, 173 ng ml(-1) (95% CI 126, 220) and a lower AUC, 476 ng ml(-1) h (95% CI 401, 551) than formulation 1, 268 ng ml(-1) (95% CI 188, 348) and 577 ng ml(-1) h (95% CI 462, 692), respectively. Formulation 2 released sildenafil after 2.75 h (95% CI 2.40, 3.10).
Conclusions: The dual route/dual release fixed dose combination tablet fulfilled its design criteria and is considered suitable for further clinical testing.
What is already known about this subject: Female sexual interest/arousal disorder (FSIAD) is a significant problem impacting psychological well-being, but the pharmacotherapeutic options for this problem are lacking. The combined, on-demand, sublingual administration of low dose sublingual testosterone and oral administration of sildenafil is a novel pharmacotherapeutic option under development for FSIAD. In proof-of-concept trials, these compounds were successfully administered via different dosage forms (sublingual and oral) at different time points (separated by 2.5 h) because of their markedly different pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic profiles. For future larger scale studies and the clinical practice, this raises obvious adherence issues.
What this study adds: A newly developed dual route/dual release fixed dose combination tablet containing testosterone and sildenafil mimics the pharmacokinetic profile of these components when they are administered as different dosage forms, 2.5 h apart. This combination tablet is a suitable final pharmaceutical drug product that will be used in future studies.
Keywords: Lybrido; combination-tablet; pharmacokinetics; sildenafil; testosterone.
© 2016 The British Pharmacological Society.
Figures
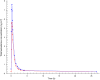
 Formulation 1: separate dosage forms prototype,
Formulation 1: separate dosage forms prototype,  Formulation 2: dual‐route/dual‐release fixed‐dose combination tablet
Formulation 2: dual‐route/dual‐release fixed‐dose combination tablet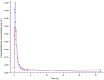
 Formulation 1: separate dosage forms prototype,
Formulation 1: separate dosage forms prototype,  Formulation 2: dual‐route/dual‐release fixed‐dose combination tablet
Formulation 2: dual‐route/dual‐release fixed‐dose combination tablet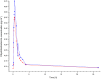
 Formulation 1: separate dosage forms prototype,
Formulation 1: separate dosage forms prototype,  Formulation 2: dual‐route/dual‐release fixed‐dose combination tablet
Formulation 2: dual‐route/dual‐release fixed‐dose combination tablet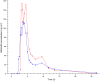
 Formulation 1: separate dosage forms prototype,
Formulation 1: separate dosage forms prototype,  Formulation 2: dual‐route/dua‐release fixed‐dose combination tablet
Formulation 2: dual‐route/dua‐release fixed‐dose combination tablet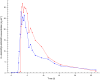
 Formulation 1: separate dosage forms prototype,
Formulation 1: separate dosage forms prototype,  Formulation 2: dual‐route/dual‐release fixed‐dose combination tablet
Formulation 2: dual‐route/dual‐release fixed‐dose combination tabletSimilar articles
-
The Effect of Food on the Pharmacokinetics of Sildenafil after Single Administration of a Sublingual Testosterone and Oral Sildenafil Combination Tablet in Healthy Female Subjects.J Sex Med. 2019 Sep;16(9):1433-1443. doi: 10.1016/j.jsxm.2019.06.015. J Sex Med. 2019. PMID: 31488289 Clinical Trial.
-
Pharmacokinetics of a prototype formulation of sublingual testosterone and a buspirone tablet, versus an advanced combination tablet of testosterone and buspirone in healthy premenopausal women.Drugs R D. 2014 Jun;14(2):125-32. doi: 10.1007/s40268-014-0047-7. Drugs R D. 2014. PMID: 24849043 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Bioequivalence study of a new sildenafil 100 mg orodispersible film compared to the conventional film-coated 100 mg tablet administered to healthy male volunteers.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2017 Apr 11;11:1183-1192. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S124034. eCollection 2017. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2017. PMID: 28442892 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Recent Developments in Psychopharmaceutical Approaches to Treating Female Sexual Interest and Arousal Disorder.Curr Sex Health Rep. 2017;9(4):192-199. doi: 10.1007/s11930-017-0124-3. Epub 2017 Oct 19. Curr Sex Health Rep. 2017. PMID: 29225554 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Edaravone for the Treatment of Motor Neurone Disease: A Critical Review of Approved and Alternative Formulations against a Proposed Quality Target Product Profile.Pharmaceutics. 2024 Jul 26;16(8):993. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16080993. Pharmaceutics. 2024. PMID: 39204338 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Effect of Food on the Pharmacokinetics of Buspirone After Single Administration of a Sublingual Testosterone and Oral Buspirone Combination Tablet in Healthy Female Subjects.Sex Med. 2020 Jun;8(2):186-194. doi: 10.1016/j.esxm.2020.01.005. Epub 2020 Feb 20. Sex Med. 2020. PMID: 32088143 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Bupropion in the Treatment of Women with Sexual Desire Disorder: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Curr Neuropharmacol. 2022;20(10):1941-1955. doi: 10.2174/1570159X20666220222145735. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35193485 Free PMC article.
-
How publication guidelines for clinical pharmacology trials may help to accelerate knowledge transfer.Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2018 Apr;84(4):611-614. doi: 10.1111/bcp.13489. Epub 2018 Feb 9. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 29427380 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Medicinal Use of Testosterone and Related Steroids Revisited.Molecules. 2021 Feb 15;26(4):1032. doi: 10.3390/molecules26041032. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 33672087 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genotype scores predict drug efficacy in subtypes of female sexual interest/arousal disorder: A double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled cross-over trial.Womens Health (Lond). 2018 Jan-Dec;14:1745506518788970. doi: 10.1177/1745506518788970. Womens Health (Lond). 2018. PMID: 30016917 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Laumann EO, Paik A, Rosen RC. Sexual dysfunction in the <styled-content style="fixed-case">United States</styled-content>: prevalence and predictors. JAMA 1999; 281: 537–44. - PubMed
-
- Fugl‐Meyer KS. Sexual disabilities and sexual problems In: Sex in <styled-content style="fixed-case">Sweden</styled-content>, ed Lewin B. Stockholm: The National Institute of Public Health, 2000; 199–215.
-
- Shifren JL, Monz BU, Russo PA, Segreti A, Johannes CB. Sexual problems and distress in <styled-content style="fixed-case">United States</styled-content> women: prevalence and correlates. Obstet Gynecol 2008; 112: 970–8. - PubMed
-
- Davison SL, Bell RJ, LaChina M, Holden SL, Davis SR. The relationship between self‐reported sexual satisfaction and general well‐being in women. J Sex Med 2009; 6: 2690–7. - PubMed
-
- <styled-content style="fixed-case">American</styled-content> Psychiatric Association . Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM‐IV), 4th Edition, Washington DC: <styled-content style="fixed-case">American</styled-content> Psychiatric Association, 2000.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

