Pro-Inflammatory Markers in Relation to Cardiovascular Disease in HIV Infection. A Systematic Review
- PMID: 26808540
- PMCID: PMC4726827
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0147484
Pro-Inflammatory Markers in Relation to Cardiovascular Disease in HIV Infection. A Systematic Review
Abstract
Background: In the past years many inflammatory markers have been studied in association with clinically manifest cardiovascular disease (CVD) and carotid intima-media thickness (CIMT) in HIV-infected patients, to obtain insights in the increased cardiovascular risk observed in HIV infection. This systematic review provides an oversight of the current knowledge.
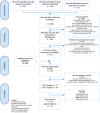
Methods: A search was performed in PubMed, Embase and Cochrane in July 2014, identifying all articles from 1996 onwards addressing the relation between inflammatory markers and CVD or CIMT in HIV-positive adults. Two authors, using predefined criteria, independently conducted the selection of articles, critical appraisal and extraction of the data. Analysis was focused on the immune markers that were most frequently assessed. The review protocol was registered in the PROSPERO database at 11 July 2014 (registration number CRD42014010516). This review was performed according to the PRISMA guideline.
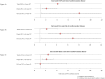
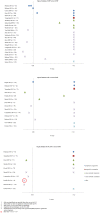
Findings: Forty articles were selected; eight addressing cardiovascular disease (CVD) and thirty-two addressing CIMT. C-reactive protein (CRP), interleukin-6 (IL-6) and d-dimer were assessed most frequently in relation to the occurrence of CVD; in four out of eight studies. All three markers were positively related to CVD in three out of four studies. Studies addressing CIMT were too heterogeneous with respect to patient populations, inflammatory markers, CIMT measurement protocols and statistical methods to allow for a formal meta-analysis to obtain summary statistics. CRP, IL-6 and soluble vascular cell adhesion molecule (sVCAM-1) were the most studied markers in relation to CIMT. None of the inflammatory markers showed an association with CIMT.
Interpretation: This review showed a relation between some inflammatory markers and CVD, however, no consistent relation is observed for CIMT. Statistical approaches that yields effect estimates and standardized CIMT protocols should be chosen. Further research should focus on prospective studies and a selected set of inflammatory markers.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Lewden C, May T, Rosenthal E, Burty C, Bonnet F, Costagliola D, et al. Changes in causes of death among adults infected by HIV between 2000 and 2005: The "Mortalite 2000 and 2005" surveys (ANRS EN19 and Mortavic). J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr 2008. August 15;48(5):590–598. 10.1097/QAI.0b013e31817efb54 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Palella FJ Jr, Baker RK, Moorman AC, Chmiel JS, Wood KC, Brooks JT, et al. Mortality in the highly active antiretroviral therapy era: changing causes of death and disease in the HIV outpatient study. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr 2006. September;43(1):27–34. - PubMed
-
- Data Collection on Adverse Events of Anti-HIV drugs (D:A:D) Study Group, Smith C, Sabin CA, Lundgren JD, Thiebaut R, Weber R, et al. Factors associated with specific causes of death amongst HIV-positive individuals in the D:A:D Study. AIDS 2010. June 19;24(10):1537–1548. 10.1097/QAD.0b013e32833a0918 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

