Osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow stromal cells is hindered by the presence of intervertebral disc cells
- PMID: 26809343
- PMCID: PMC4727301
- DOI: 10.1186/s13075-015-0900-2
Osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow stromal cells is hindered by the presence of intervertebral disc cells
Abstract
Background: Clinical observations indicate that the presence of nucleus pulposus (NP) tissue during spinal fusion hinders the rate of disc ossification. While the underlying mechanism remains unknown, this observation could be due to incomplete removal of NP cells (NPCs) that secrete factors preventing disc calcification, such as bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) antagonists including noggin and members of the DAN (differential screening selected gene aberrative in neuroblastoma) family.
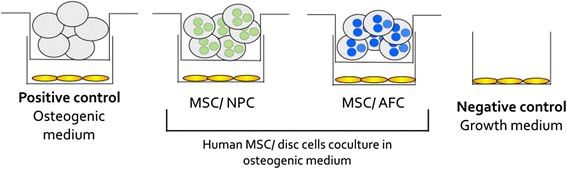
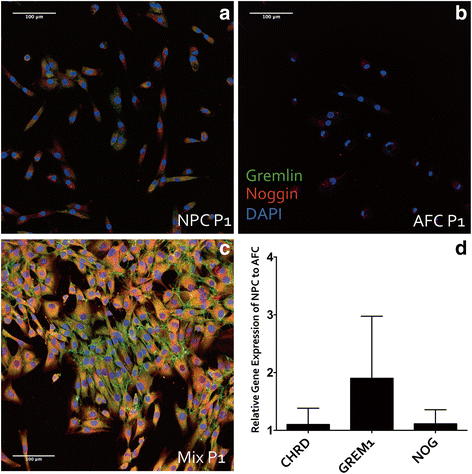
Methods: Monolayer human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) were cocultured withNPCs and annulus fibrosus cells (AFCs) embedded in alginate for 21 days. At the end of coculture, MSCs were stained for mineral deposition by alizarin red, and relative expression of bone-related genes [Runt-related transcription factor 2, (RUNX2), Osteopontin (OPN), and Alkaline phosphatase (ALP)] and ALP activity were analyzed. Relative expression of three BMP antagonists, chordin (CHRD), gremlin (GREM1), and noggin (NOG), was determined in primary human NPCs and AFCs. These cells were also stained for Gremlin and Noggin by immunocytochemistry.
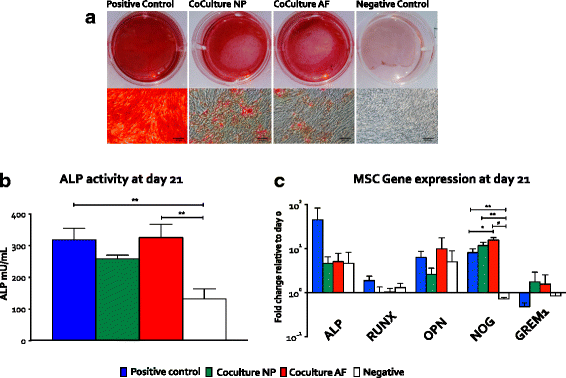
Results: Alizarin red staining showed that MSC osteogenesis in monolayer cultures was inhibited by coculture with NPCs or AFCs. ALP activity and RT-PCR analyses confirmed these results and demonstrated inhibition of osteogenesis of MSC in the presence of disc cells. NOG was significantly up-regulated in MSCs after coculture. Relative gene expression of intervertebral disc (IVD) cells showed higher expression of GREM1 in NPCs than in AFCs.
Conclusions: We show that primary IVD cells inhibit osteogenesis of MSCs. BMP inhibitors NOG, GREM1 and CHRD were expressed in IVD cells. GREM1 appears to be differentially expressed in NPCs and AFCs. Our results have implications for the design and development of treatments for non-union in spinal fusion.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Application of Cytokines of the Bone Morphogenetic Protein (BMP) Family in Spinal Fusion - Effects on the Bone, Intervertebral Disc and Mesenchymal Stromal Cells.Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019;14(8):618-643. doi: 10.2174/1574888X14666190628103528. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019. PMID: 31455201 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The BMP2 variant L51P restores the osteogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stromal cells in the presence of intervertebral disc cells.Eur Cell Mater. 2017 Feb 23;33:197-210. doi: 10.22203/eCM.v033a15. Eur Cell Mater. 2017. PMID: 28266688
-
Noggin suppression decreases BMP-2-induced osteogenesis of human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells in vitro.J Cell Biochem. 2012 Dec;113(12):3672-80. doi: 10.1002/jcb.24240. J Cell Biochem. 2012. PMID: 22740073
-
Autogenous Mesenchymal Stem Cells from the Vertebral Body Enhance Intervertebral Disc Regeneration via Paracrine Interaction: An in Vitro Pilot Study.Cell Transplant. 2016 Oct;25(10):1819-1832. doi: 10.3727/096368916X691420. Cell Transplant. 2016. PMID: 27075568
-
The effects of microenvironment in mesenchymal stem cell-based regeneration of intervertebral disc.Spine J. 2013 Mar;13(3):352-62. doi: 10.1016/j.spinee.2012.12.005. Epub 2013 Jan 20. Spine J. 2013. PMID: 23340343 Review.
Cited by
-
Conditioned Medium of Intervertebral Disc Cells Inhibits Osteo-Genesis on Autologous Bone-Marrow-Derived Mesenchymal Stromal Cells and Osteoblasts.Biomedicines. 2024 Feb 6;12(2):376. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12020376. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 38397978 Free PMC article.
-
Application of Cytokines of the Bone Morphogenetic Protein (BMP) Family in Spinal Fusion - Effects on the Bone, Intervertebral Disc and Mesenchymal Stromal Cells.Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019;14(8):618-643. doi: 10.2174/1574888X14666190628103528. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019. PMID: 31455201 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Grem1 accelerates nucleus pulposus cell apoptosis and intervertebral disc degeneration by inhibiting TGF-β-mediated Smad2/3 phosphorylation.Exp Mol Med. 2022 Apr;54(4):518-530. doi: 10.1038/s12276-022-00753-9. Epub 2022 Apr 19. Exp Mol Med. 2022. PMID: 35440754 Free PMC article.
-
GREM1, LRPPRC and SLC39A4 as potential biomarkers of intervertebral disc degeneration: a bioinformatics analysis based on multiple microarray and single-cell sequencing data.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2023 Sep 12;24(1):729. doi: 10.1186/s12891-023-06854-4. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2023. PMID: 37700277 Free PMC article.
-
Is Osteogenic Differentiation of Human Nucleus Pulposus Cells a Possibility for Biological Spinal Fusion?Cartilage. 2020 Apr;11(2):181-191. doi: 10.1177/1947603518754628. Epub 2018 Jan 23. Cartilage. 2020. PMID: 29361851 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

