Chemical composition, antioxidant and anticholinesterase potentials of essential oil of Rumex hastatus D. Don collected from the North West of Pakistan
- PMID: 26810212
- PMCID: PMC4727414
- DOI: 10.1186/s12906-016-0998-z
Chemical composition, antioxidant and anticholinesterase potentials of essential oil of Rumex hastatus D. Don collected from the North West of Pakistan
Abstract
Background: Ethnomedicinally Rumex hastatus D. Don has been used since long for various ailments especially in neurological disorders. The reported data and the importance of Rumex genus demonstrate the vital medicinal value of R. hastatus.
Methods: In the current investigational study, isolation of essential oil and its antioxidant and anticholinesterase assays were performed. The essential oil of R. hastatus was analyzed by GC-MS for the first time. The essential oil was evaluated for anticholinesterase and antioxidant assays. The anticholinesterase assay was conducted at various concentrations (62.5 to 1000 μg/ml) against acetylcholinesterase (AChE) and butyrylcholinesterase (BChE). Similarly, the antioxidant potential was determined using DPPH and ABTS free radicals.
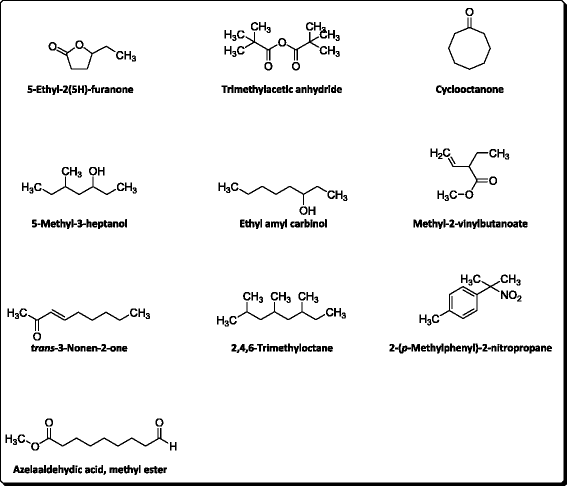
Results: The GC-MS analysis of essential oil showed 123 components. The result recorded for the anticholinesterase assays demonstrated a marked potential against AChE and BChE with IC50 values of 32.54 and 97.38 μg/ml respectively which were comparable with the positive control i.e., galanthamine (AChE, IC50 = 4.73 μg/ml and BChE, IC50 = 11.09 μg/ml). The antioxidant assays against DPPH and ABTS free radicals also exhibited significant scavenging potential with IC50 values of 3.71 and 6.29 μg/ml respectively, while for ascorbic acid the IC50 value was <0.1 μg/ml against both free radicals.
Conclusions: Based on the current investigational studies, it may be concluded that R. hastatus is an effective source of essential oil's components having anticholinesterase and antioxidant potentials, which after subjecting to drug development may lead to novel drug candidates against neurodegenerative disorders.
Figures



References
-
- Van Wyk B-E, Wink M. Medicinal plants of the world: an illustrated scientific guide to important medicinal plants and their uses: Timber Press; Portland, USA 2004.
-
- Samant S, Palni L, Kumar S, Kukreja A, Dwivedi S, Singh A. Diversity, distribution and indigenous uses of essential oil-yielding medicinal plants of the Indian Himalayan region. J Med Arom Plant Sci. 2000;22(1B):671–684.
-
- Ruberto G, Baratta MT. Antioxidant activity of selected essential oil components in two lipid model systems. Food Chem. 2000;69(2):167–174. doi: 10.1016/S0308-8146(99)00247-2. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

