Oral Typhoid Vaccination With Live-Attenuated Salmonella Typhi Strain Ty21a Generates Ty21a-Responsive and Heterologous Influenza Virus-Responsive CD4+ and CD8+ T Cells at the Human Intestinal Mucosa
- PMID: 26810369
- PMCID: PMC4857474
- DOI: 10.1093/infdis/jiw030
Oral Typhoid Vaccination With Live-Attenuated Salmonella Typhi Strain Ty21a Generates Ty21a-Responsive and Heterologous Influenza Virus-Responsive CD4+ and CD8+ T Cells at the Human Intestinal Mucosa
Abstract
Background: Oral vaccination with live-attenuated Salmonella Typhi strain Ty21a is modestly efficacious, but the mechanisms of protection are currently unknown. While humoral and cellular immune responses are well described in peripheral blood, the cellular response at the intestinal mucosa has never been directly assessed.
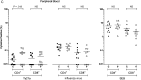
Methods: We vaccinated healthy adults with Ty21a and assessed humoral and cellular immunity in vaccinated volunteers and controls after 18 days. Immunoglobulin levels were assessed in peripheral blood by an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Cellular responses were assessed in peripheral blood and at the duodenal and colonic mucosa by flow cytometry.
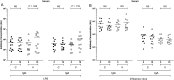
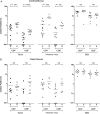
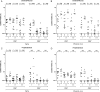
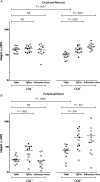
Results: We demonstrate the generation of Ty21a-responsive and heterologous influenza virus-responsive CD4(+) and CD8(+) T cells at the duodenal mucosa. All duodenal responses were consistently correlated, and no responses were observed at the colonic mucosa. Peripheral anti-lipopolysaccharide immunoglobulin G and immunoglobulin A responses were significantly correlated with duodenal responses. The assessment of integrin β7 expression intensity among peripheral and duodenal T-cell subsets revealed varied capacities for mucosal homing and residence.
Conclusions: The breadth of duodenal cellular responses was not reflected peripherally. The direct evaluation of mucosal immune defense may yield functional correlates of protection and could provide insight into mechanisms that may be manipulated to enhance vaccine immunogenicity.
Keywords: Salmonella; T cells; Ty21a; cellular immunity; cytokines; heterologous immunity; humoral immunity; immunoglobulins; typhoid.
© The Author 2016. Published by Oxford University Press for the Infectious Diseases Society of America.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Longevity of duodenal and peripheral T-cell and humoral responses to live-attenuated Salmonella Typhi strain Ty21a.Vaccine. 2018 Jul 25;36(31):4725-4733. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2018.05.114. Epub 2018 Jun 27. Vaccine. 2018. PMID: 29958737 Free PMC article.
-
Association between S. Typhi-specific memory CD4+ and CD8+ T responses in the terminal ileum mucosa and in peripheral blood elicited by the live oral typhoid vaccine Ty21a in humans.Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2019;15(6):1409-1420. doi: 10.1080/21645515.2018.1564570. Epub 2019 Apr 2. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2019. PMID: 30836838 Free PMC article.
-
Diversity of Salmonella Typhi-responsive CD4 and CD8 T cells before and after Ty21a typhoid vaccination in children and adults.Int Immunol. 2019 Apr 26;31(5):315-333. doi: 10.1093/intimm/dxz011. Int Immunol. 2019. PMID: 30951606 Free PMC article.
-
Cell-mediated immunity and antibody responses elicited by attenuated Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhi strains used as live oral vaccines in humans.Clin Infect Dis. 2007 Jul 15;45 Suppl 1:S15-9. doi: 10.1086/518140. Clin Infect Dis. 2007. PMID: 17582562 Review.
-
Experience with registered mucosal vaccines.Vaccine. 2003 Jan 30;21(7-8):678-83. doi: 10.1016/s0264-410x(02)00579-0. Vaccine. 2003. PMID: 12531339 Review.
Cited by
-
Respiratory virus-induced heterologous immunity: Part of the problem or part of the solution?Allergo J Int. 2018;27(3):79-96. doi: 10.1007/s40629-018-0056-0. Epub 2018 Mar 26. Allergo J Int. 2018. PMID: 32226720 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nonspecific effects of oral vaccination with live-attenuated Salmonella Typhi strain Ty21a.Sci Adv. 2019 Feb 27;5(2):eaau6849. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.aau6849. eCollection 2019 Feb. Sci Adv. 2019. PMID: 30820452 Free PMC article.
-
Homologous and heterologous re-challenge with Salmonella Typhi and Salmonella Paratyphi A in a randomised controlled human infection model.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2020 Oct 20;14(10):e0008783. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0008783. eCollection 2020 Oct. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2020. PMID: 33079959 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Systemic and Terminal Ileum Mucosal Immunity Elicited by Oral Immunization With the Ty21a Typhoid Vaccine in Humans.Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2017 Aug 16;4(3):419-437. doi: 10.1016/j.jcmgh.2017.08.002. eCollection 2017 Nov. Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2017. PMID: 29022005 Free PMC article.
-
Intestinal Helminth Infection Impairs Oral and Parenteral Vaccine Efficacy.J Immunol. 2023 Aug 1;211(3):389-402. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.2300084. J Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37272847 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Parry CM, Hien TT, Dougan G, White NJ, Farrar JJ. Typhoid fever. N Engl J Med 2002; 347:1770–82. - PubMed
-
- Germanier R, Fuer E. Isolation and characterization of Gal E mutant Ty 21a of Salmonella typhi: a candidate strain for a live, oral typhoid vaccine. J Infect Dis 1975; 131:553–8. - PubMed
-
- Wahdan MH, Serie C, Cerisier Y, Sallam S, Germanier R. A controlled field trial of live Salmonella typhi strain Ty 21a oral vaccine against typhoid: three-year results. J Infect Dis 1982; 145:292–5. - PubMed
-
- Levine MM, Ferreccio C, Black RE, Germanier R. Large-scale field trial of Ty21a live oral typhoid vaccine in enteric-coated capsule formulation. Lancet 1987; 1:1049–52. - PubMed
-
- Levine MM, Ferreccio C, Black RE, Lagos R, San Martin O, Blackwelder WC. Ty21a live oral typhoid vaccine and prevention of paratyphoid fever caused by Salmonella enterica Serovar Paratyphi B. Clin Infect Dis 2007; 45(suppl 1):S24–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

