Sustained Nitric Oxide-Releasing Nanoparticles Induce Cell Death in Candida albicans Yeast and Hyphal Cells, Preventing Biofilm Formation In Vitro and in a Rodent Central Venous Catheter Model
- PMID: 26810653
- PMCID: PMC4808184
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.02659-15
Sustained Nitric Oxide-Releasing Nanoparticles Induce Cell Death in Candida albicans Yeast and Hyphal Cells, Preventing Biofilm Formation In Vitro and in a Rodent Central Venous Catheter Model
Abstract
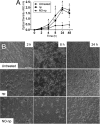
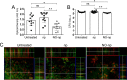
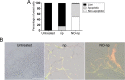
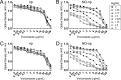
Candida albicansis a leading nosocomial pathogen. Today, candidal biofilms are a significant cause of catheter infections, and such infections are becoming increasingly responsible for the failure of medical-implanted devices.C. albicansforms biofilms in which fungal cells are encased in an autoproduced extracellular polysaccharide matrix. Consequently, the enclosed fungi are protected from antimicrobial agents and host cells, providing a unique niche conducive to robust microbial growth and a harbor for recurring infections. Here we demonstrate that a recently developed platform comprised of nanoparticles that release therapeutic levels of nitric oxide (NO-np) inhibits candidal biofilm formation, destroys the extracellular polysaccharide matrices of mature fungal biofilms, and hinders biofilm development on surface biomaterials such as the lumen of catheters. We found NO-np to decrease both the metabolic activity of biofilms and the cell viability ofC. albicansin vitroandin vivo Furthermore, flow cytometric analysis found NO-np to induce apoptosis in biofilm yeast cellsin vitro Moreover, NO-np behave synergistically when used in combination with established antifungal drug therapies. Here we propose NO-np as a novel treatment modality, especially in combination with standard antifungals, for the prevention and/or remediation of fungal biofilms on central venous catheters and other medical devices.
Copyright © 2016, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Sustained Nitric Oxide-Releasing Nanoparticles Interfere with Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Adhesion and Biofilm Formation in a Rat Central Venous Catheter Model.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2016 Dec 27;61(1):e02020-16. doi: 10.1128/AAC.02020-16. Print 2017 Jan. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2016. PMID: 27821454 Free PMC article.
-
Demonstration of antibiofilm and antifungal efficacy of chitosan against candidal biofilms, using an in vivo central venous catheter model.J Infect Dis. 2010 May 1;201(9):1436-40. doi: 10.1086/651558. J Infect Dis. 2010. PMID: 20331379
-
Antifungal activity of amphotericin B and voriconazole against the biofilms and biofilm-dispersed cells of Candida albicans employing a newly developed in vitro pharmacokinetic model.Ann Clin Microbiol Antimicrob. 2015 Apr 3;14:21. doi: 10.1186/s12941-015-0083-3. Ann Clin Microbiol Antimicrob. 2015. PMID: 25885806 Free PMC article.
-
Antifungal susceptibility of Candida albicans in biofilms.Mycoses. 2012 May;55(3):199-204. doi: 10.1111/j.1439-0507.2011.02076.x. Epub 2011 Jul 28. Mycoses. 2012. PMID: 21793943 Review.
-
Pathogenesis of Candida albicans biofilm.Pathog Dis. 2016 Jun;74(4):ftw018. doi: 10.1093/femspd/ftw018. Pathog Dis. 2016. PMID: 26960943 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Micro- and nanoparticles as platforms for the treatment of fungal infections: present and future perspectives.Future Microbiol. 2023 Nov;18(15):1007-1011. doi: 10.2217/fmb-2023-0079. Epub 2023 Sep 18. Future Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37721209 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Combating Concomitant Bacterial and Fungal Infections via Codelivery of Nitric Oxide and Fluconazole.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2025 Apr 23;17(16):23613-23626. doi: 10.1021/acsami.5c00174. Epub 2025 Apr 14. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2025. PMID: 40228797 Free PMC article.
-
3-Hydroxy coumarin demonstrates anti-biofilm and anti-hyphal efficacy against Candida albicans via inhibition of cell-adhesion, morphogenesis, and virulent genes regulation.Sci Rep. 2023 Jul 19;13(1):11687. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-37851-1. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37468600 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Developments in Nitric Oxide Donors and Delivery for Antimicrobial and Anti-Biofilm Applications.Molecules. 2022 Jan 20;27(3):674. doi: 10.3390/molecules27030674. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35163933 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Intestinal Infection of Candida albicans: Preventing the Formation of Biofilm by C. albicans and Protecting the Intestinal Epithelial Barrier.Front Microbiol. 2022 Feb 2;12:783010. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.783010. eCollection 2021. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35185813 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kuhn DM, Ghannoum MA. 2004. Candida biofilms: antifungal resistance and emerging therapeutic options. Curr Opin Investig Drugs 5:186–197. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

