Two members of TaRLK family confer powdery mildew resistance in common wheat
- PMID: 26810982
- PMCID: PMC4727334
- DOI: 10.1186/s12870-016-0713-8
Two members of TaRLK family confer powdery mildew resistance in common wheat
Abstract
Background: Powdery mildew, caused by Blumeria graminearum f.sp. tritici (Bgt), is one of the most severe fungal diseases of wheat. The exploration and utilization of new gene resources is the most effective approach for the powdery mildew control.
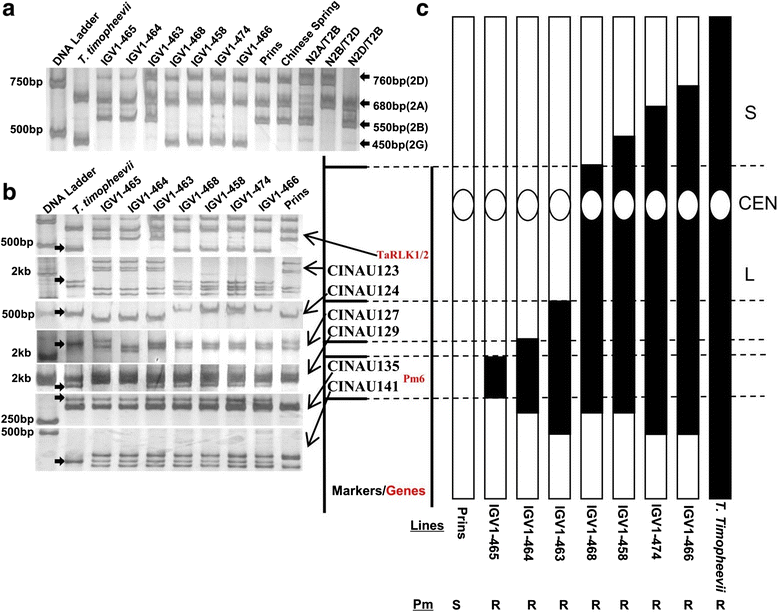
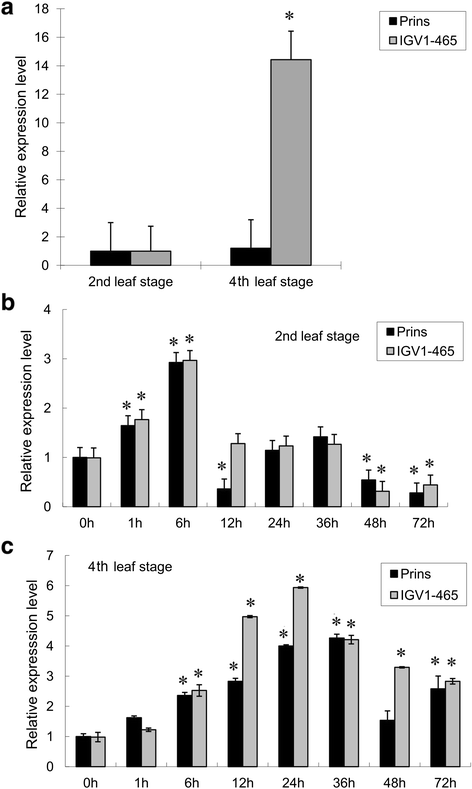
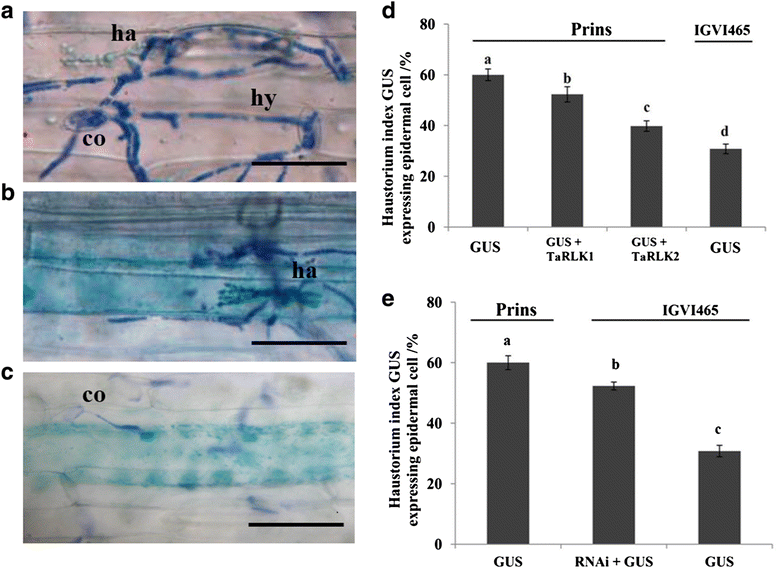
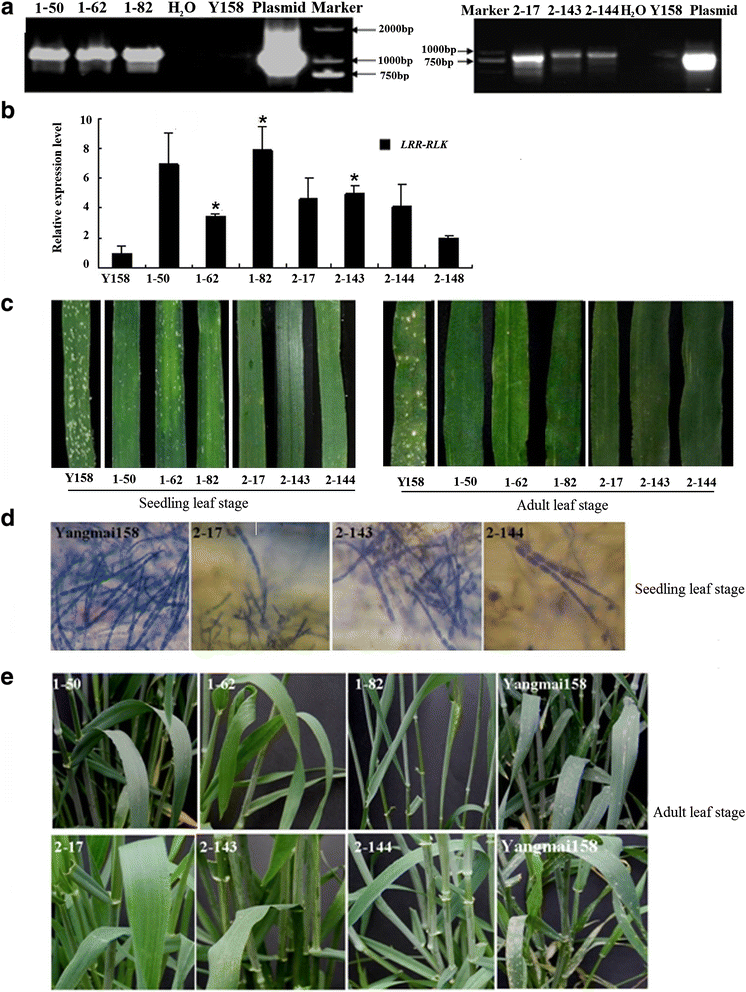
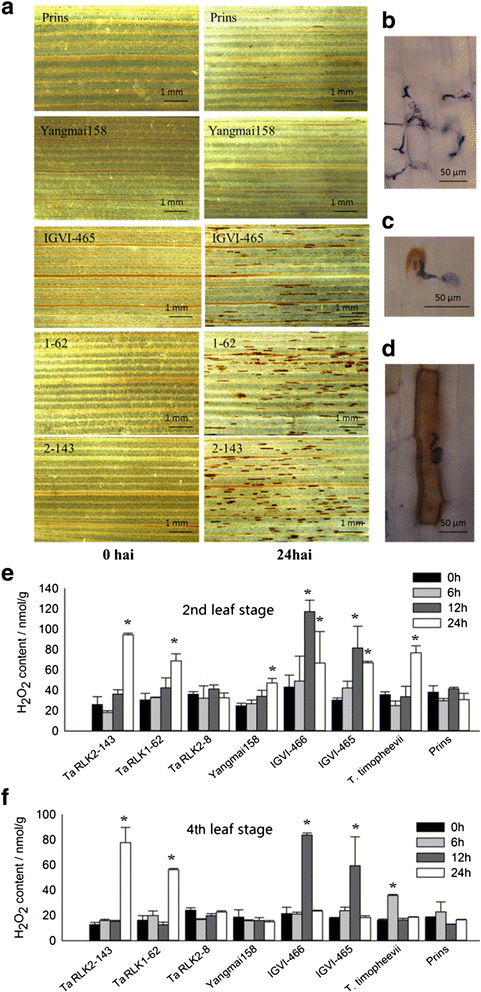
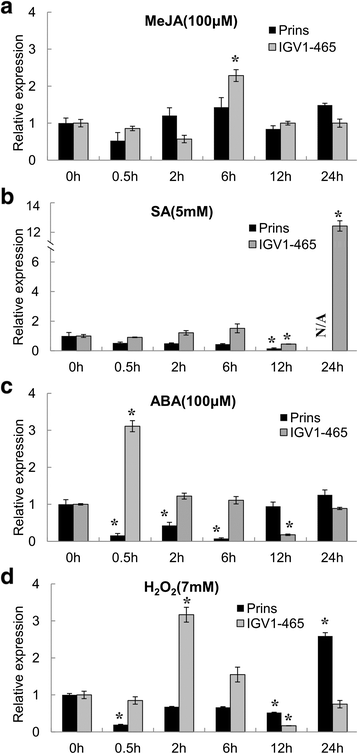
Results: We report the cloning and functional analysis of two wheat LRR-RLKs from T. aestivum c.v. Prins- T. timopheevii introgression line IGV1-465, named TaRLK1 and TaRLK2, which play positive roles in regulating powdery mildew resistance in wheat. The two LRR-RLKs contain an ORF of 3,045 nucleotides, encoding a peptide of 1014 amino acids, with seven amino acids difference. Their predicted proteins possess a signal peptide, several LRRs, a trans-membrane domain, and a Ser/Thr protein kinase domain. In response to Bgt infection, the TaRLK1/2 expression is up-regulated in a developmental-stage-dependent manner. Single-cell transient over-expression and gene-silencing assays indicate that both genes positively regulate the resistance to mixed Bgt inoculums. Transgenic lines over-expressing TaRLK1 or TaRLK2 in a moderate powdery mildew susceptible wheat variety Yangmai 158 led to significantly enhanced powdery mildew resistance. Exogenous applied salicylic acid (SA) or hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) induced the expression of both genes, and H2O2 had a higher accumulation at the Bgt penetration sites in RLK over-expression transgenic plants, suggesting a possible involvement of SA and altered ROS homeostasis in the defense response to Bgt infection. The two LRR-RLKs are located in the long arm of wheat chromosome 2B, in which the powdery mildew resistance gene Pm6 is located, but in different regions.
Conclusions: Two members of TaRLK family were cloned from IGV1-465. TaRLK1 and TaRLK2 contribute to powdery mildew resistance of wheat, providing new resistance gene resources for wheat breeding.
Figures

References
-
- Hervé C, Serres J, Dabos P, Canut H, Barre A, Rougé P, et al. Characterization of the Arabidopsis lecRK-a genes: members of a superfamily encoding putative receptors with an extracellular domain homologous to legume lectins. Plant Mol Biol. 1999;39(4):671–682. doi: 10.1023/A:1006136701595. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

