Randomized, controlled trial comparing laryngeal mask versus endotracheal intubation during neonatal resuscitation---a secondary publication
- PMID: 26811060
- PMCID: PMC4727391
- DOI: 10.1186/s12887-016-0553-6
Randomized, controlled trial comparing laryngeal mask versus endotracheal intubation during neonatal resuscitation---a secondary publication
Abstract
Background: This study aimed to study the feasibility, efficacy and safety of using laryngeal mask (LM) ventilation compared with endotracheal intubation (ETI) during neonatal resuscitation.
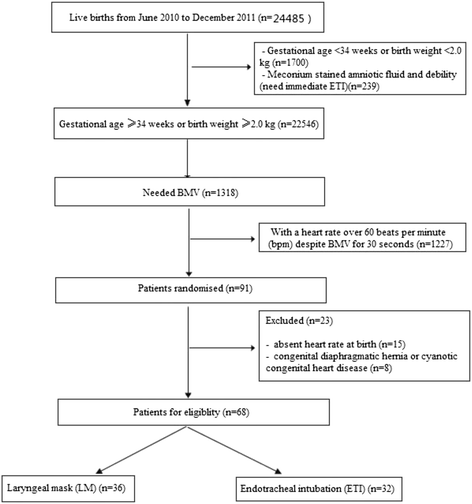
Methods: Neonates with a heart rate below 60 beats per minute despite 30 s of face mask ventilation were assigned quasi-randomly (odd/even birth date) to LM (n = 36) or ETI (n = 32) ventilation. Differences in first attempt insertion success, insertion time, Apgar score, resuscitation outcome, and adverse effects were compared.
Results: There were no significant differences in first attempt at successful insertion (LM, 94.4 % vs. ETI, 90.6 %), insertion time (LM, 7.58 ± 1.16 s vs. ETI, 7.89 ± 1.52 s), Apgar score at 1 and 5 min, response time, ventilation time, successful resuscitation (LM, 86.1 % vs. ETI, 96.9 %), and adverse events (LM, n =3 vs. ETI, n =4) between groups.
Conclusions: Laryngeal mask ventilation is an effective alternative to endotracheal intubation during resuscitation of depressed newborns who do not respond to face-mask ventilation. During an emergency, laryngeal mask ventilation may be a preferred technique for medical staff who are unable to acquire or maintain endotracheal intubation skills.
Trial registration: Current Controlled Trials ChiCTR-IOQ-15006488. Registered on 2 June 2015.
References
-
- Lin W, Zhu X, Yang C, Su J, Lin B, Liu T, et al. Case control study of laryngeal mask airway versus endotracheal intubation in neonatal resuscitation. J Chin Pediatr Emerg Med. 2012;19(3):259–63.
-
- Finucane T, Santora H. Principles of airway management. New York: Springer; 2003. The laryngeal mask airway (LMA) pp. 438–490s.
-
- Niermeyer S, Kattwinkel J, Reempts PV, Nadkarni V, Phillips B, Zideman D, et al. International guidelines for neonatal resuscitation: an excerpt from the guideline 2000 for cardiopulmonary resuscitation and emergency cardiovascular care: international consensus on science. J Pediatr. 2000;106:e29. doi: 10.1542/peds.106.3.e29. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical