Clinical Phenotypes in Heart Failure With Preserved Ejection Fraction
- PMID: 26811159
- PMCID: PMC4859363
- DOI: 10.1161/JAHA.115.002477
Clinical Phenotypes in Heart Failure With Preserved Ejection Fraction
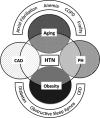
Keywords: Aging; heart failure; hypertension; obesity; preserved ejection fraction.
Figures
References
-
- Cohn JN, Johnson G. Heart failure with normal ejection fraction, the V‐HeFT study. Circulation. 1990;81(suppl III):III‐48–III‐53. - PubMed
-
- Vasan RS, Benjamin EJ, Levy D. Prevalence, clinical features and prognosis of diastolic heart failure: an epidemiologic perspective. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1995;26:1656–1674. - PubMed
-
- Zile MR, Brustaert DL. New concepts in diastolic dysfunction and diastolic heart failure. Part I diagnosis, prognosis and measurements of diastolic function. Circulation. 2002;105:1387–1393. - PubMed
-
- Zile MR, Brustaert DL. New concepts in diastolic dysfunction and diastolic heart failure: part II. Causal mechanisms and treatment. Circulation. 2002;105:1503–1508. - PubMed
-
- Kitzman DL, Little WC, Brubaker PH, Anderson RT, Hundley WG, Marbuger CT, Brosnihan B, Morgan TM, Stewart KP. Pathophysiological characterization of isolated diastolic heart failure in comparison to systolic heart failure. JAMA. 2002;288:2144–2150. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

